A method for increasing oxygen in rh refining process
A refining process and oxygenating agent technology, applied in the metallurgical field, can solve problems such as unstable oxygen absorption rate, and achieve the effects of reducing industrial costs, eliminating influence and improving absorption rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
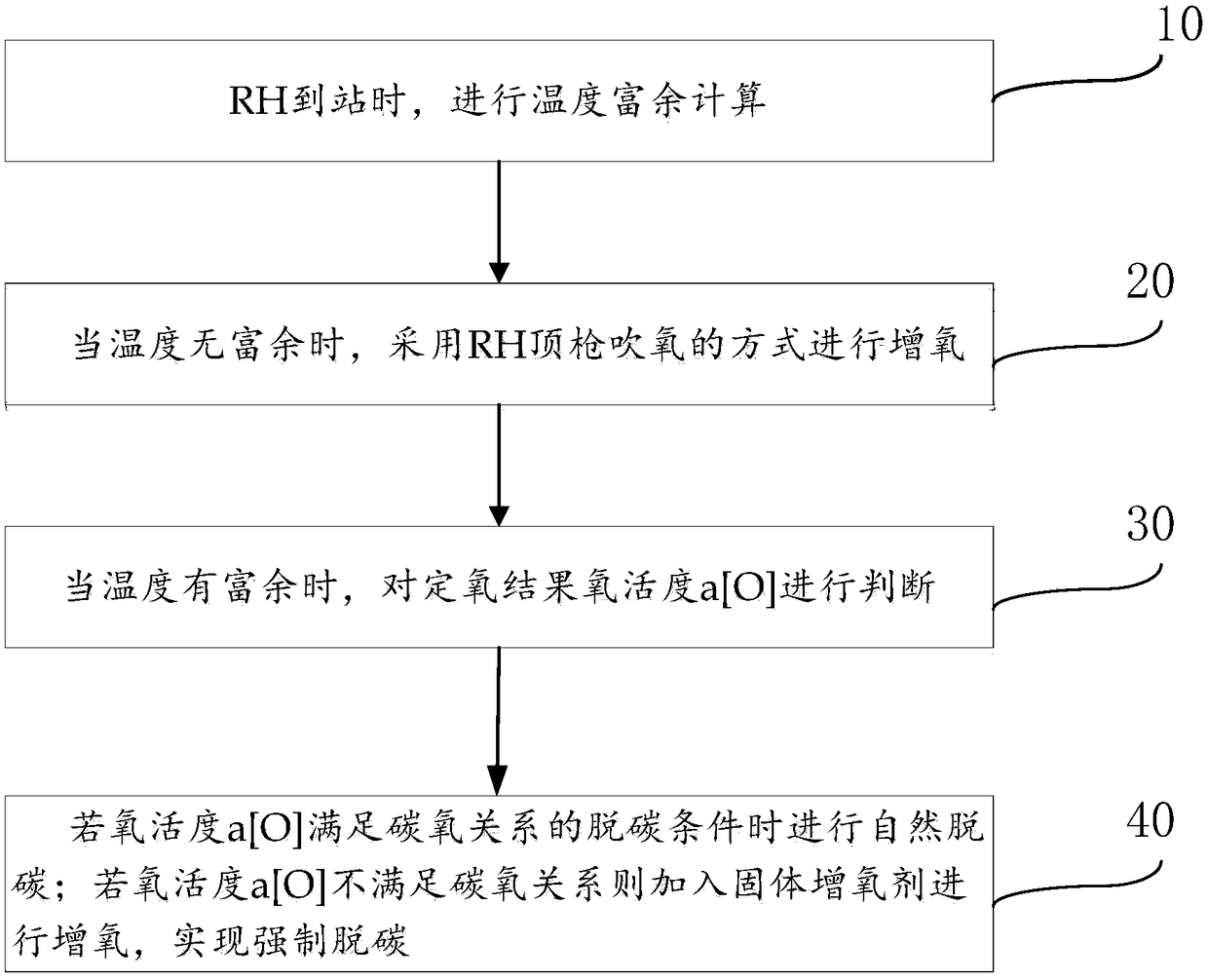
[0038] This embodiment provides a method for increasing oxygen in the RH refining process:
[0039] ΔT1 is the temperature drop related to time, taking a value of 8°C; ΔT2 is the temperature drop caused by adding alloys, taking a value of 7°C; ΔT3 is the temperature rise caused by deoxidation, taking a value of 10°C; ΔT4 is the temperature drop caused by other factors, The value is 2°C. When the RH arrives at the station, use the temperature surplus calculation formula ΔT=ΔT1+ΔT2-ΔT3+ΔT4 to calculate the difference between the arrival temperature and the end temperature ΔT is equal to 7°C. Since ΔT>5°C, it means that there is a surplus in temperature. Further, judge the oxygen activity a[O] of the oxygen determination result, the oxygen activity a[O] takes a value of 250, the RH arrival carbon content-target carbon content △C takes a value of 10, and the oxygen activity a[O] >△C×4 / 3+220, add an oxygenating agent to increase oxygen and perform forced decarburization. Every 10...
Embodiment 2
[0041] This embodiment provides a method for increasing oxygen in the RH refining process:
[0042] ΔT1 is the temperature drop related to time, taking a value of 2°C; ΔT2 is the temperature drop caused by adding alloys, taking a value of 5°C; ΔT3 is the temperature rise caused by deoxidation, taking a value of 8°C; ΔT4 is the temperature drop caused by other factors, The value is 2°C. When the RH arrives at the station, use the temperature surplus calculation formula ΔT=ΔT1+ΔT2-ΔT3+ΔT4 to calculate the difference between the arrival temperature and the end temperature ΔT is equal to 1°C, since ΔT<5°C, it means that there is no surplus in temperature, and the RH top gun is used Oxygenation is carried out by blowing oxygen.
Embodiment 3
[0044] This embodiment provides a method for increasing oxygen in the RH refining process:
[0045] ΔT1 is the temperature drop related to time, taking a value of 5°C; ΔT2 is the temperature drop caused by adding alloys, taking a value of 6°C; ΔT3 is the temperature rise caused by deoxidation, taking a value of 6°C; ΔT4 is the temperature drop caused by other factors, The value is 4°C. When the RH arrives at the station, use the temperature surplus calculation formula ΔT=ΔT1+ΔT2-ΔT3+ΔT4 to calculate the difference between the arrival temperature and the end temperature ΔT is equal to 9°C. Since ΔT>5°C, it means that there is a surplus in temperature. Further, judge the oxygen activity a[O] of the oxygen determination result, the value of oxygen activity a[O] is 200, the value of RH arrival carbon content-target carbon content △C is 20, and the oxygen activity △C×4 / 3+220 is 246.7, a[O]<△C×4 / 3+220, then natural decarburization is adopted.
[0046] One or more technical soluti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com