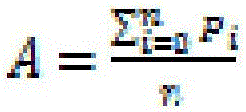Block chain common recognition mechanism
A blockchain and consensus technology, applied in the blockchain field, can solve problems such as being unable to resist computing power attacks, and achieve the effect of improving uniformity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
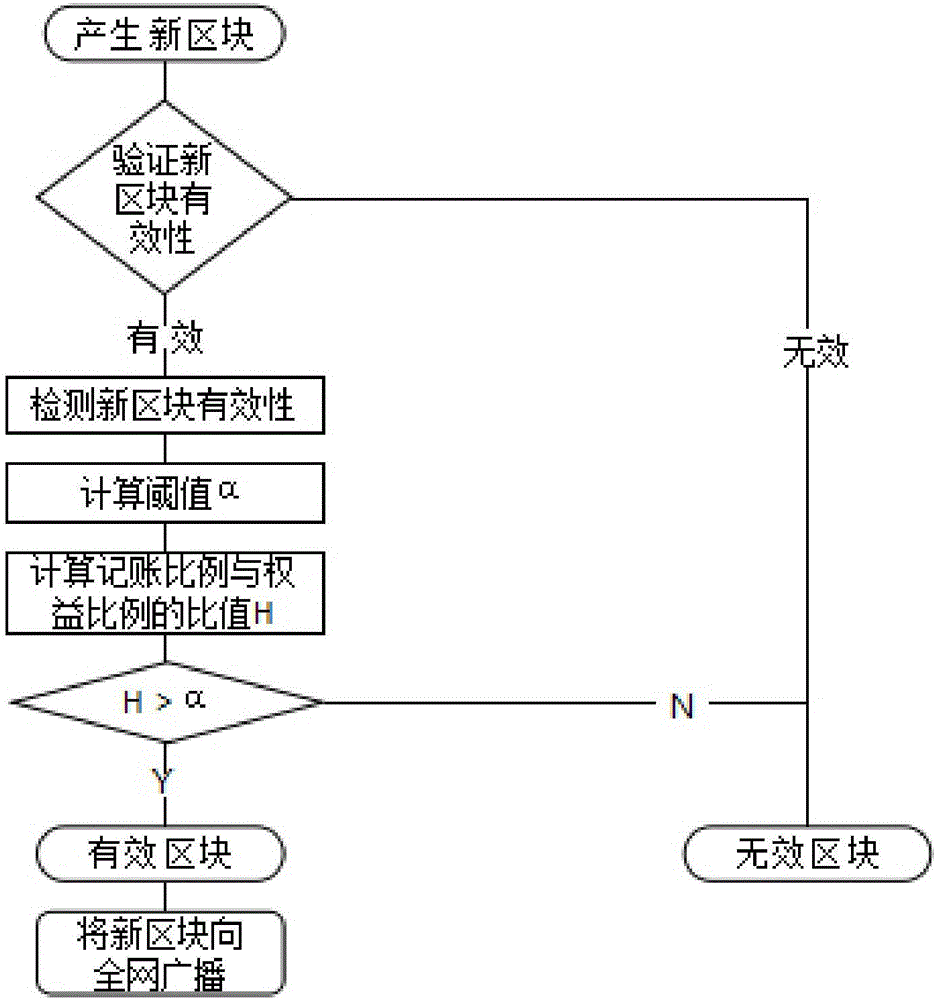
[0023] A block chain consensus mechanism proposed by the present invention, such as figure 1 As shown, the details are as follows:
[0024] Step 1. When a new block is generated, verify the validity of the block.
[0025] The validity of the verification block refers to the block verification method usually adopted by the existing proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. For example, verify whether the block hash is valid, verify whether each transaction in the block is valid, verify whether the previous block pointed to by the block is valid, verify whether the previous block is on a valid and active blockchain, and verify the block Whether the hash is less than the target difficulty divided by the consumed coin age, use the public key of the coin age consumption address to verify whether the signature is correct, etc. If the verification of the above parameters is passed, it is determined that the new block is valid, and the validity of the new block is checked after the new bl...
Embodiment 2
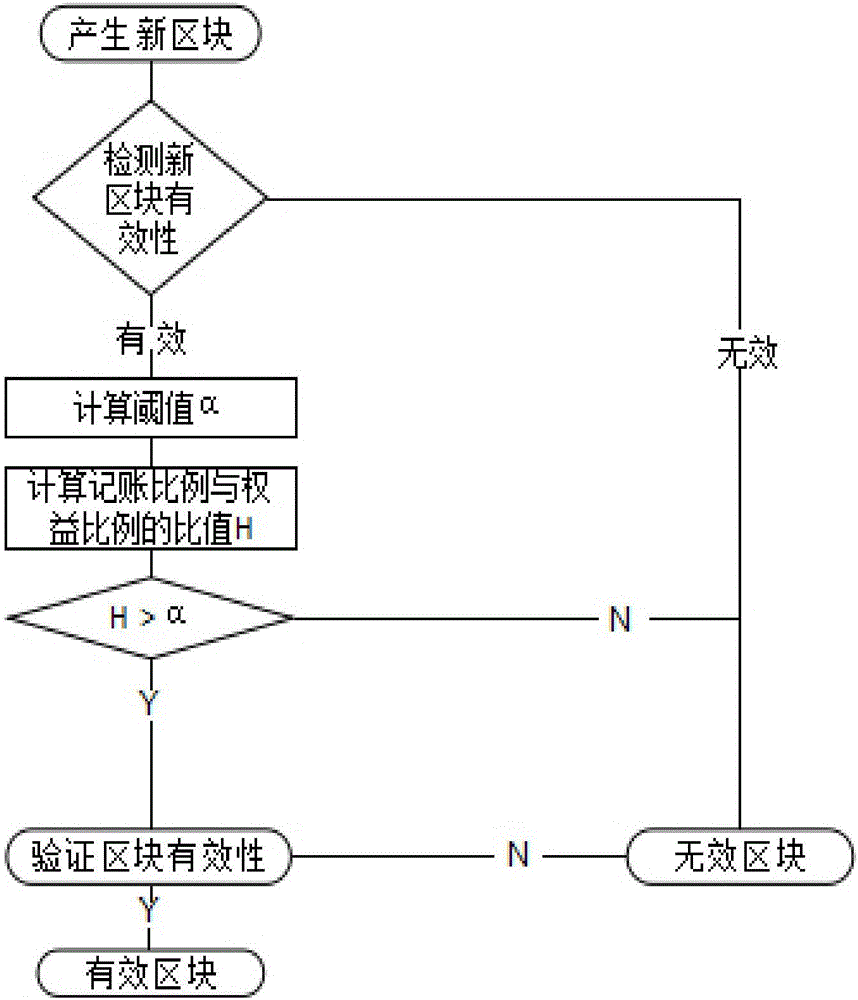
[0039] A block chain consensus mechanism proposed by the present invention, such as figure 2 As shown, the details are as follows:
[0040] Step 1. When a new block is generated, check the validity of the new block.
[0041] Detecting the average equity ratio and accounting ratio of the address generating the new block, if the accounting ratio is higher than the average equity ratio, the new block is considered invalid.
[0042] When the ratio of the billing ratio to the average equity ratio is greater than a threshold α, the new block is considered invalid.
[0043] The calculation method of the average equity ratio A is as follows:
[0044]
[0045] Among them, n is the number of blocks generated in the past period of time by selecting the address that generates the new block; P i is the equity ratio of the address on the i-th block in the selected past blocks. For example, in the past 10 blocks generated by the address that generates the new district fast, the equit...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com