Starting element for bus current differential protection
A technology for differential protection and start-up components, applied in electrical components, emergency protection circuit devices, etc., can solve problems such as inability to judge CT disconnection and inability to accurately identify CT saturation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0100] (1) In-area failure
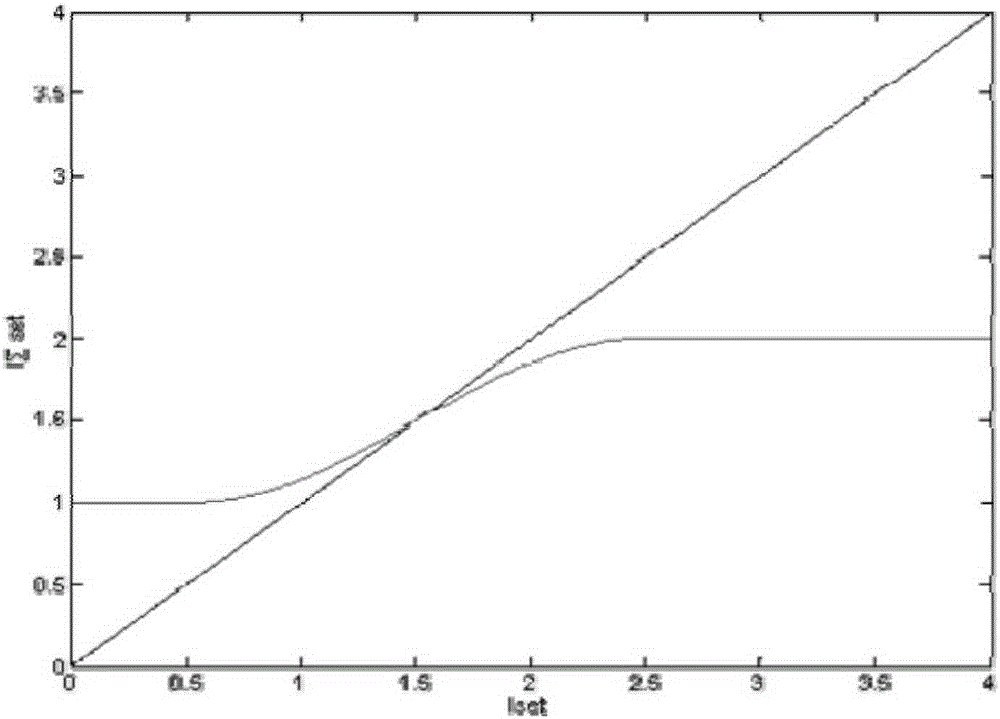
[0101] When a phase B ground fault occurs in the area, the starting action curve of the bus differential current is as follows: Image 6 As shown, the solid line is the fixed value curve, and the dotted solid line is the differential criterion action curve.
[0102] The starting action curve of bus braking current is as follows: Figure 7 As shown, the solid line is the fixed value curve, and the dotted solid line is the braking criterion action curve.
[0103] Other current starting action curves of the busbar are as follows: Figure 8 As shown, the solid line is the fixed value curve, and the dotted solid line is the multi-CT current criterion action curve.
[0104] From the simulation results, it can be seen that for faults in the zone, the braking current start-up criterion, the differential current start-up criterion and the multi-CT current start-up criterion act reliably, and the bus differential start-up element operates.
Embodiment 2
[0106] (2) Out-of-area failure
[0107] When a phase B ground fault outside the zone occurs, the busbar differential start action curve is as follows: Figure 9 As shown, the solid line is the fixed value curve, and the dotted solid line is the differential criterion action curve.
[0108] The bus brake start action curve is as follows: Figure 10 As shown, the solid line is the fixed value curve, and the dotted solid line is the differential criterion action curve.
[0109] Other current starting action curves of the busbar are as follows: Figure 11 As shown, the solid line is the fixed value curve, and the dotted solid line is the differential criterion action curve.
[0110] From the simulation results, it can be seen that when an out-of-area fault occurs, the braking current start-up criterion and other current start-up criteria will act reliably, the differential current start-up element will not act, and the bus differential start-up element will act.
Embodiment 3
[0112] (3) CT disconnection
[0113] In the event of B-phase CT disconnection, the busbar differential start action curve is as follows: Figure 12 As shown, the solid line is the fixed value curve, and the dotted solid line is the differential criterion action curve.
[0114] The bus brake start action curve is as follows: Figure 13 As shown, the solid line is the fixed value curve, and the dotted solid line is the differential criterion action curve.
[0115] Other current starting action curves of the busbar are as follows: Figure 14 As shown, the solid line is the fixed value curve, and the dotted solid line is the differential criterion action curve.
[0116] It can be seen from the simulation results that when the CT disconnection occurs, the differential current start criterion and the brake current start criterion act, but the multi-CT current start criterion does not act, and the bus differential start element does not act.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com