Heat dissipation system of rail lamp
A technology for heat dissipation systems and lamps, which is applied to cooling/heating devices of lighting devices, lighting and heating equipment, semiconductor devices of light-emitting elements, etc. The effect of reducing heat dissipation volume and light weight
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0021] Specific embodiments of the present invention will be described in further detail below based on the accompanying drawings. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only examples, and are not intended to limit the protection scope of the present invention.
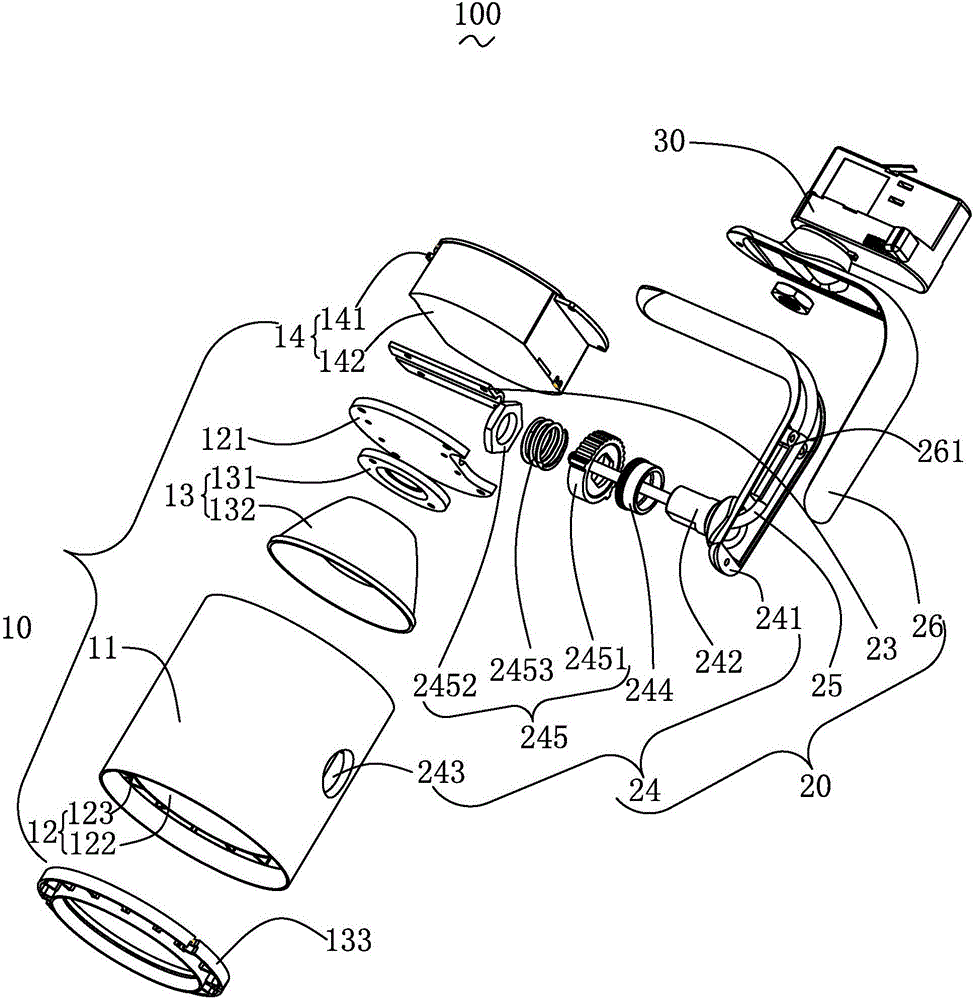
[0022] see figure 1 and figure 2 , which is a structural schematic diagram of a heat dissipation system 100 for a track light fixture provided by the present invention. The heat dissipation system 100 of the track lamp includes a lamp head 10 , a rotating handle 20 rotatably connected with the lamp head 10 , and a power plug 30 . It is conceivable that, in order for the track lamp to work normally, it should also have an electrified track, which is a well-known technology in the art and will not be described in detail here.
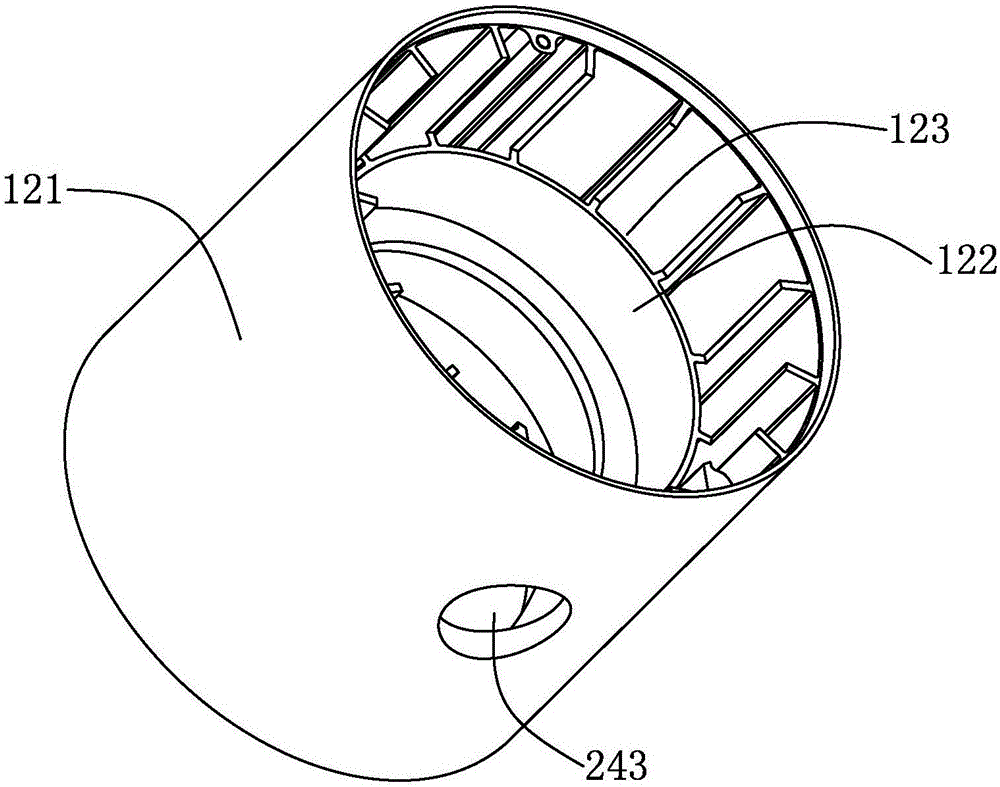
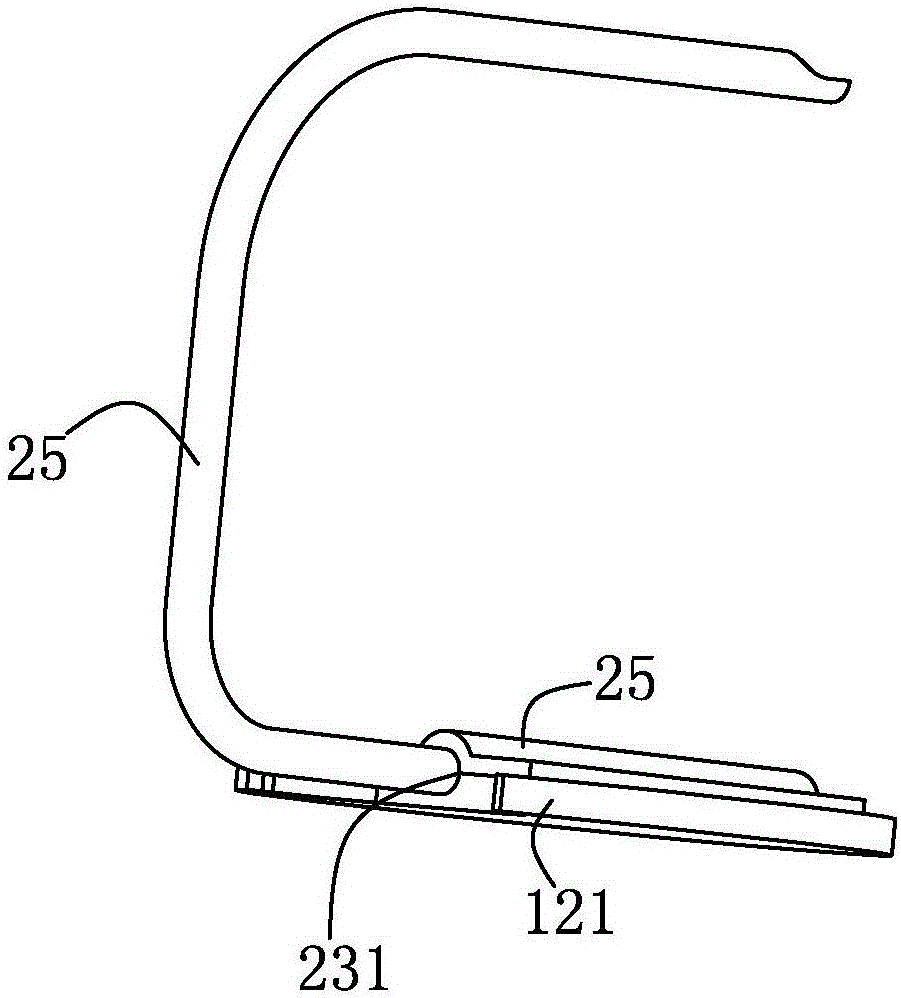
[0023] The lamp holder 10 includes a lamp tube 11, a lamp tube cooling subsystem 12 arranged in the lamp tube 11, a light source module 13 arranged in the la...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com