An Adaptive Blind Equalization Method Based on Offset Compensation
An adaptive, blind equalization technology, applied in baseband systems, baseband system components, shaping networks in transmitters/receivers, etc., and can solve problems such as inability to implement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
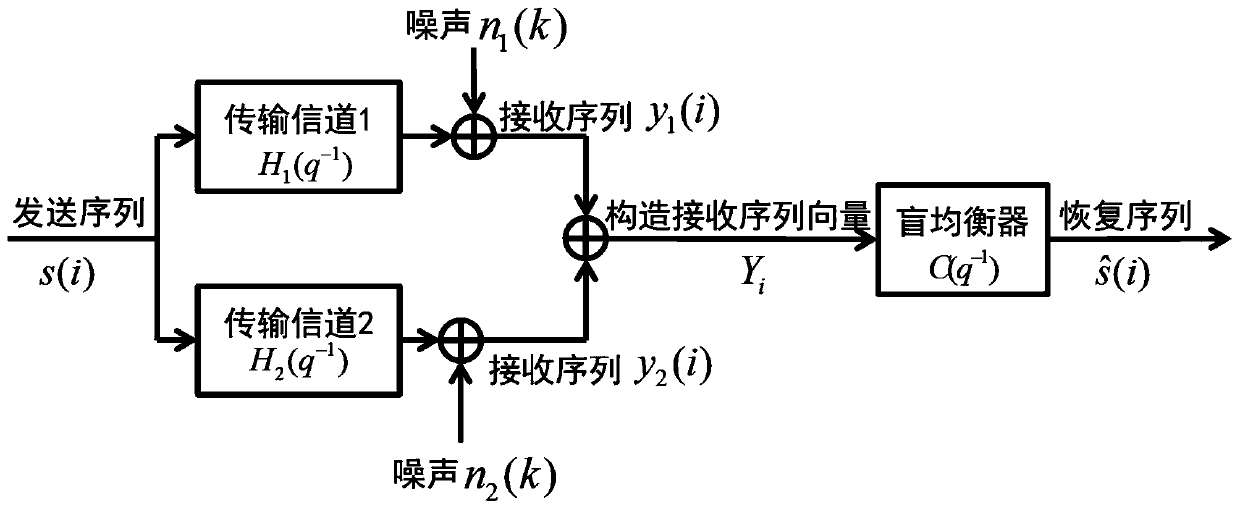
[0079] This embodiment describes the process of applying the "Adaptive Blind Equalization Method Based on Offset Compensation" of the present invention to the scenario of two transmission channels.
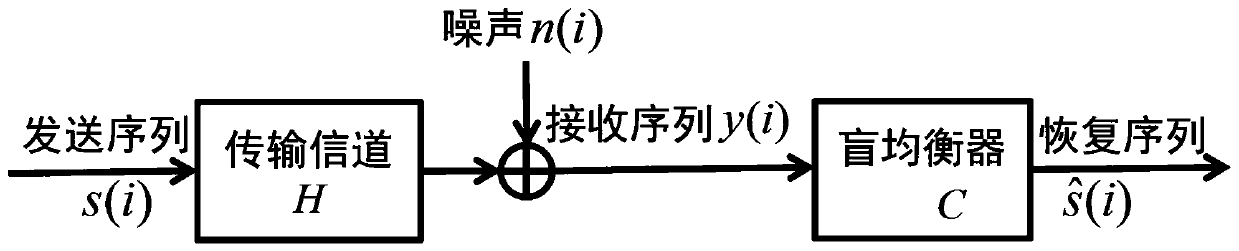
[0080] figure 1 is the transmission channel model adopted in this embodiment, figure 2 The schematic diagram of this method.
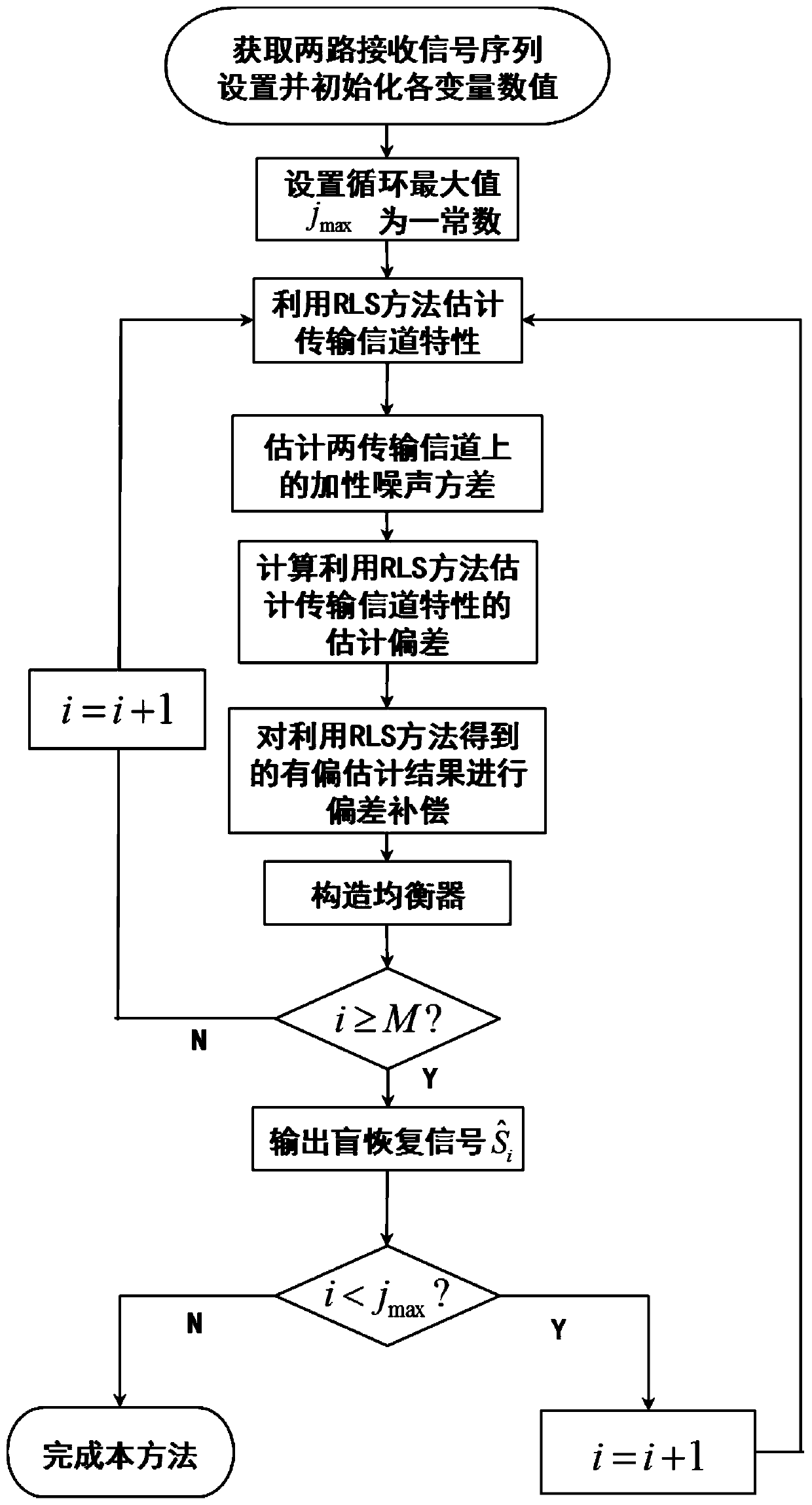
[0081] image 3 It is the algorithm flowchart of this method and the flowchart of this embodiment; As can be seen from the figure, this method comprises the following steps:
[0082] Step A: Obtain two received signal sequences, set and initialize the value of each variable in this method;
[0083] Specifically in this embodiment, the loop count value j is initialized to 1; the loop maximum value is j max ; The channel order L is 3, and the loop count value i is initialized to L+2; P L+1 = δ -1 I L , δ is a very small positive number, and δ=10 in this embodiment -6 ; Smoothing factor M=50; take t / 2 as the sampling interval, alternately sample ...
Embodiment 2
[0117] According to the noise estimation method in Embodiment 1, this embodiment specifically explains the output effect of the noise variance estimation part of this method when the unknown additive noise variances on the two transmission channels are not equal or equal, and the results are as follows Figure 4 shown.
[0118] Among them, case 1 means that when the unknown additive noise variances on the two transmission channels are different, and Estimation of the noise variance; case 2 means when the unknown additive noise variance on the two transmission channels is the same, and An estimate of the noise variance. Depend on Figure 4 In the two cases, we can see that this method can realize the real-time estimation of the additive noise variance on each transmission channel, and no matter whether the additive noise on each transmission channel has the same statistical characteristics, this method can accurately estimate the unknown additive noise. Sexual noise varian...
Embodiment 3
[0120] According to the algorithm flow in embodiment 1, this embodiment further illustrates the effectiveness of the system and algorithm of the present invention through specific examples. Here, specific simulation examples and analysis are given:
[0121] The simulation experiment uses 16-QAM signal as the input signal, the channel noise uses Gaussian white noise, and The channel characteristics of the two transmission channels are shown in formulas (25) and (26) respectively:
[0122] h 1 (q -1 )=-0.6233+1.9054q -1 +(0.6064+0.75i)q -2 -0.6233q -3 (25)
[0123] h 2 (q -1 )=0.2699-0.1558i+(2.1749+0.4764i)q -1 +(-0.8251+0.4763i)q -2 +(0.2699-0.1558i)q -3
[0124] (26)
[0125] The number of iterations of the simulation is set to 15000, and the number of independent experiments is set to 100.
[0126] Figure 5 What is given is the estimation accuracy comparison between the RLS method without offset compensation and the RLS method based on offset compensation to...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com