Sparse laser observation-based image depth estimation method
A depth estimation and laser technology, applied in image enhancement, image analysis, image data processing, etc., can solve problems such as monocular image depth estimation deviation, and achieve the effect of reducing global deviation and high reliability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] In order to better understand the technical solution of the present invention, further description will be made below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings. Figure 1 shows an example of depth estimation, where the input is Figure 1a For the monocular image shown, it is required to estimate Figure 1b Depth of scene shown.
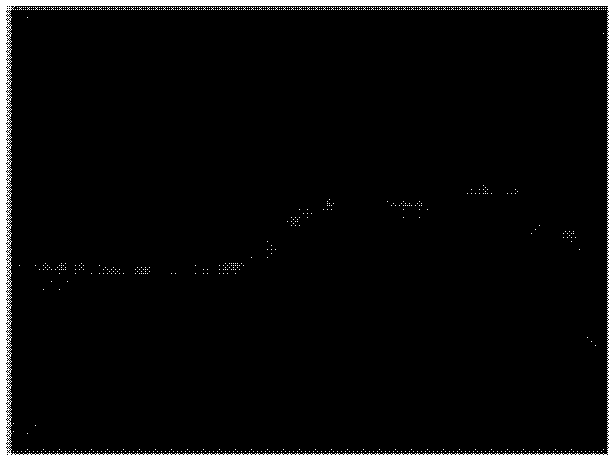
[0024] Step 1: Construct a reference depth map and a residual depth map based on the single-line laser. Figure 2a The known single-line laser information in Figure 1 is shown, and it can be seen that the single-line laser information is very sparse and limited. In order to densify the sparse single-line laser information, each laser point is stretched in the direction perpendicular to the ground in three-dimensional space to obtain a reference depth plane perpendicular to the ground. According to the calibration information of the monocular camera and the single-line laser, the reference depth plane obtained in three dimensions is corresp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com