Charging method and device
A charging method and charging device technology, which are applied to circuit devices, battery circuit devices, and secondary battery charging/discharging directions, can solve the problems of shortening battery life, shortening the duration of constant current charging, battery capacity attenuation, etc. Enhanced stability, shortened charging time, and reduced polarization effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
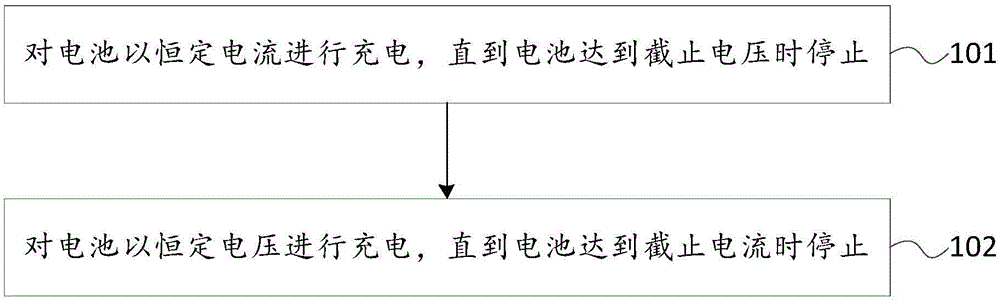
[0055] figure 1 The flow chart of Embodiment 1 of the charging method provided by the embodiment of the present invention is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the charging method of this embodiment may specifically include the following steps:
[0056] 101. Charge the battery with a constant current until the battery reaches the cut-off voltage and stop.
[0057] In the embodiment of the present invention, different positive electrode materials and negative electrode materials are used to make battery cells. Due to the different properties of the battery cell materials themselves, the performance of the battery is jointly determined. As the battery is charged and discharged many times, the chemical changes in the cells inside the battery will gradually accumulate. Therefore, in the case where the performance of the battery is difficult to change, in order to reduce the probability that the polarization phenomenon of the battery in the battery will damage the stability of the ba...
Embodiment 2
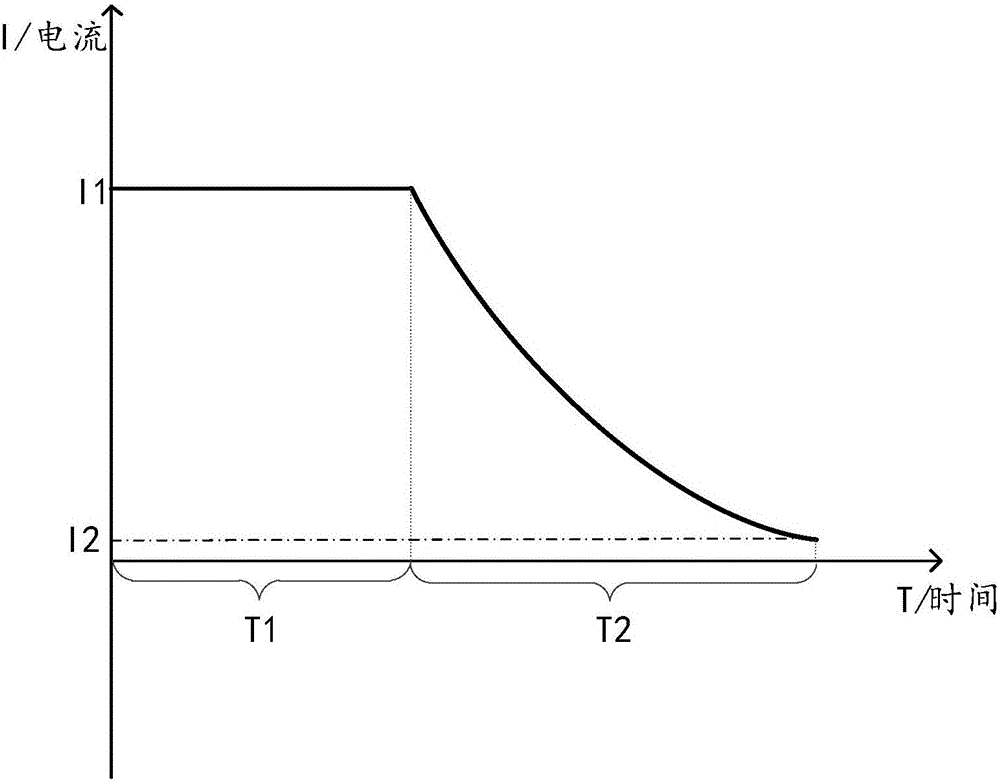
[0078] Figure 4 The flow chart of the second embodiment of the charging method provided by the embodiment of the present invention, such as Figure 4 As shown, the charging method of this embodiment may specifically include the following steps:
[0079] 201. Charge the battery with a constant current until the battery reaches the cut-off voltage and stop.
[0080] For the specific process of step 201, refer to the description of step 101 in the first embodiment above. The principle and implementation process are the same in the embodiment of the present invention, and will not be repeated here.
[0081] 202. Calculate the sum of the preset current adjustment value and the cut-off current used in each charging process in the i-th charging stage as the cut-off current used in each charging process in the i+1th charging stage.
[0082] It can be understood that the current adjustment value is a value used to adjust the cut-off current. In the embodiment of the present inventio...
Embodiment approach 1
[0094]Choose 4 batteries of the same type, numbered No. 1, No. 2, No. 3 and No. 4. Batteries 1 to 4 are charged with the same data during the constant current charging phase. In the constant voltage charging stage, the cut-off current of the No. 1 battery and the No. 2 battery is set to 0.025C, and the cut-off current of the No. 3 battery and the No. 4 battery is set to 0.05C. Perform 800 cycles on the 4 batteries respectively, and record the remaining capacity of each battery in each cycle.
[0095] Table 1 is a comparison table about cut-off current and remaining capacity in Embodiment 1, Figure 5 It is a comparison chart about the number of cycles and capacity retention in Embodiment 1, such as Figure 5 As shown in Table 1, as the cycle progresses, especially when the number of cycles increases, the remaining capacity of the battery with a larger cut-off current is greater than that of a battery with a smaller cut-off current. It can be seen from the data in Table 1 th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com