System and method for beam-based physical random-access
A random access and beam technology, applied in transmission systems, radio transmission systems, diversity/multi-antenna systems, etc., can solve complex problems and achieve the effects of improved coverage, reduced power consumption, and improved waiting time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] The following with reference to the attached Figure 7-12 To describe specific embodiments, the same reference numerals are used for the same and corresponding parts of the various drawings.
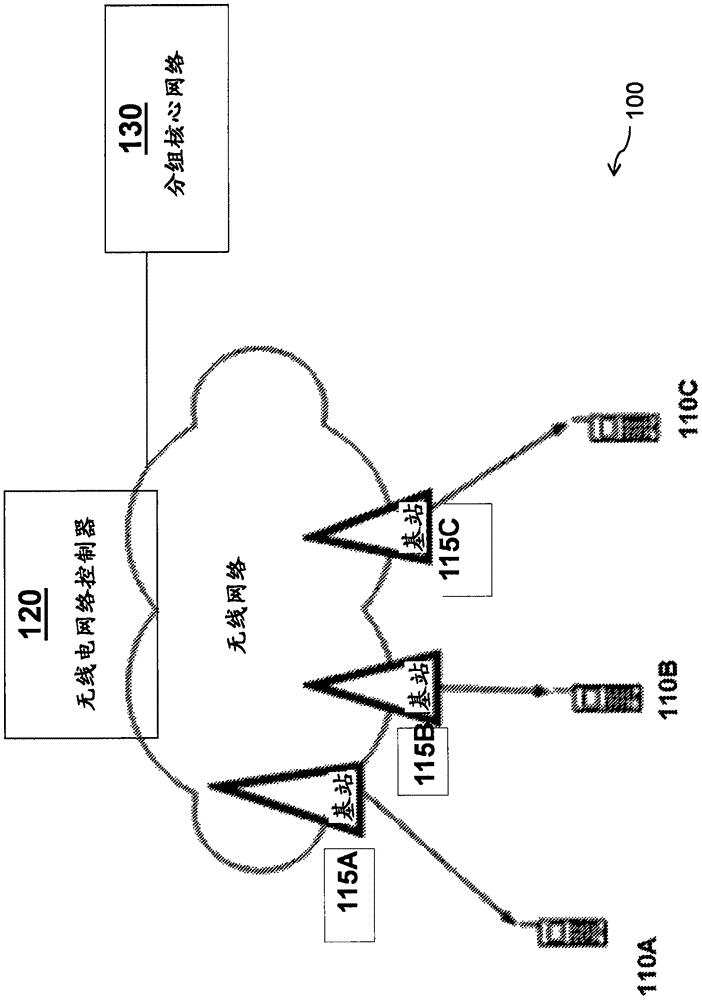
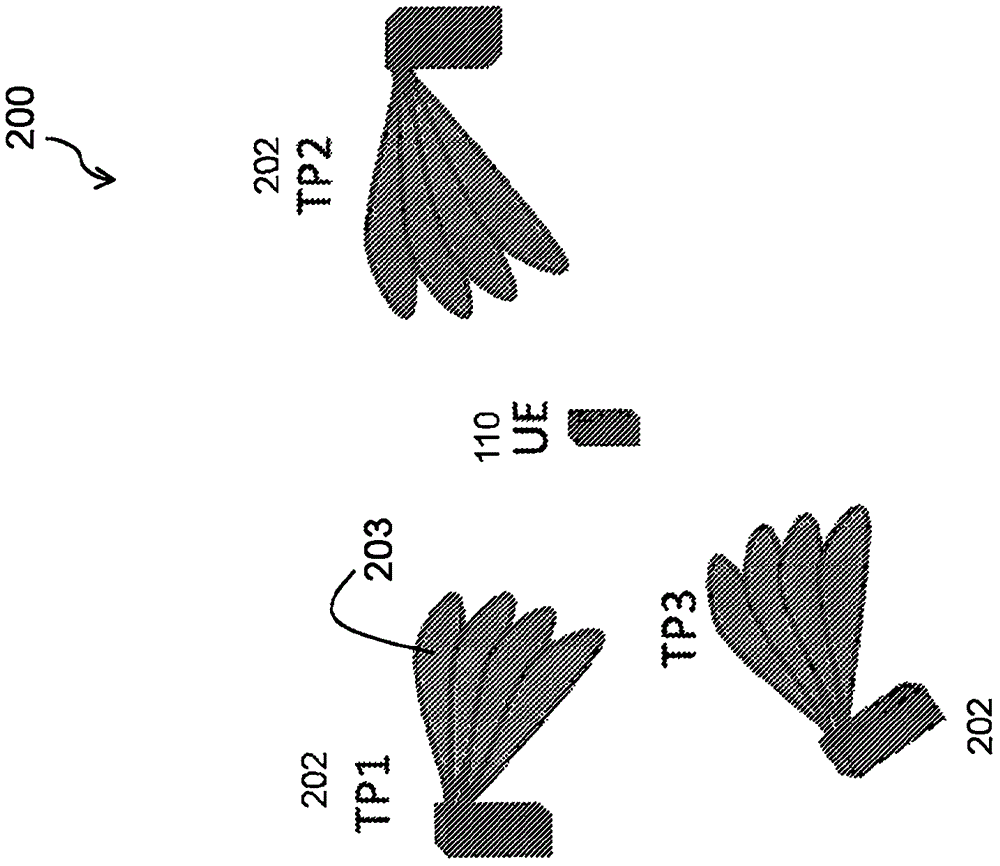
[0046] Figure 7 A system 700 according to some embodiments is shown, the system 700 includes a wireless device 110 (in Figure 7 Shown as "terminal" in ), the wireless device 110 is operable to select the beam 704 based on the received signal strength in the downlink (DL). As shown in the figure, the system 700 includes a plurality of network nodes 115A and 115B, and each node transmits a reference signal unique to each beam. In a specific embodiment, the two network nodes 115A, 115B may be two transmission points (TP) capable of performing multi-beam transmission in the same cell (same physical cell ID), or they may be nodes belonging to different cells .
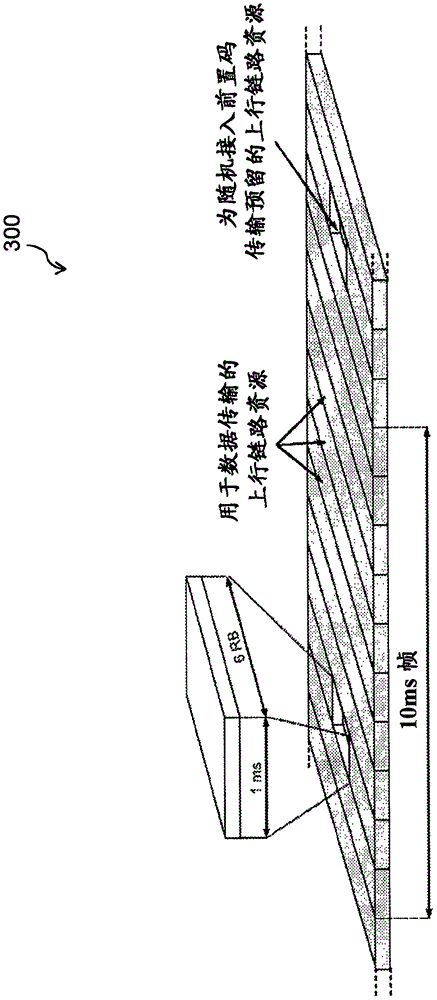
[0047] In a specific embodiment, the wireless device 110 can detect the preferred downlink beam (and ultimately the network no...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com