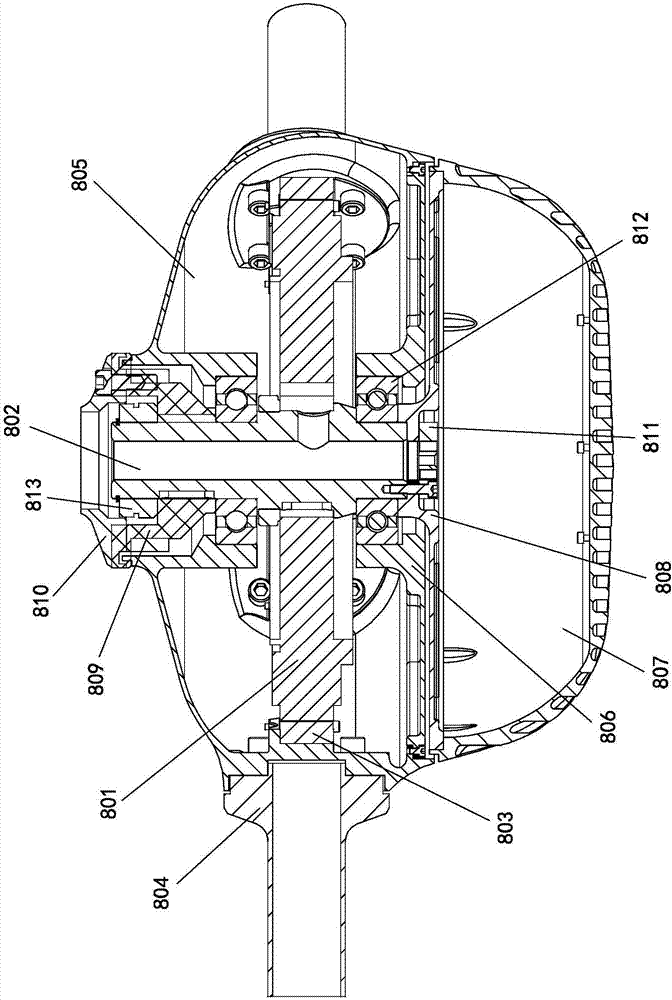
Direct drive ceiling fan
A technology for driving ceiling fans and ceiling fans, which is applied in the field of direct-drive ceiling fans, and can solve the problems of high-torque motors amplifying noise
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
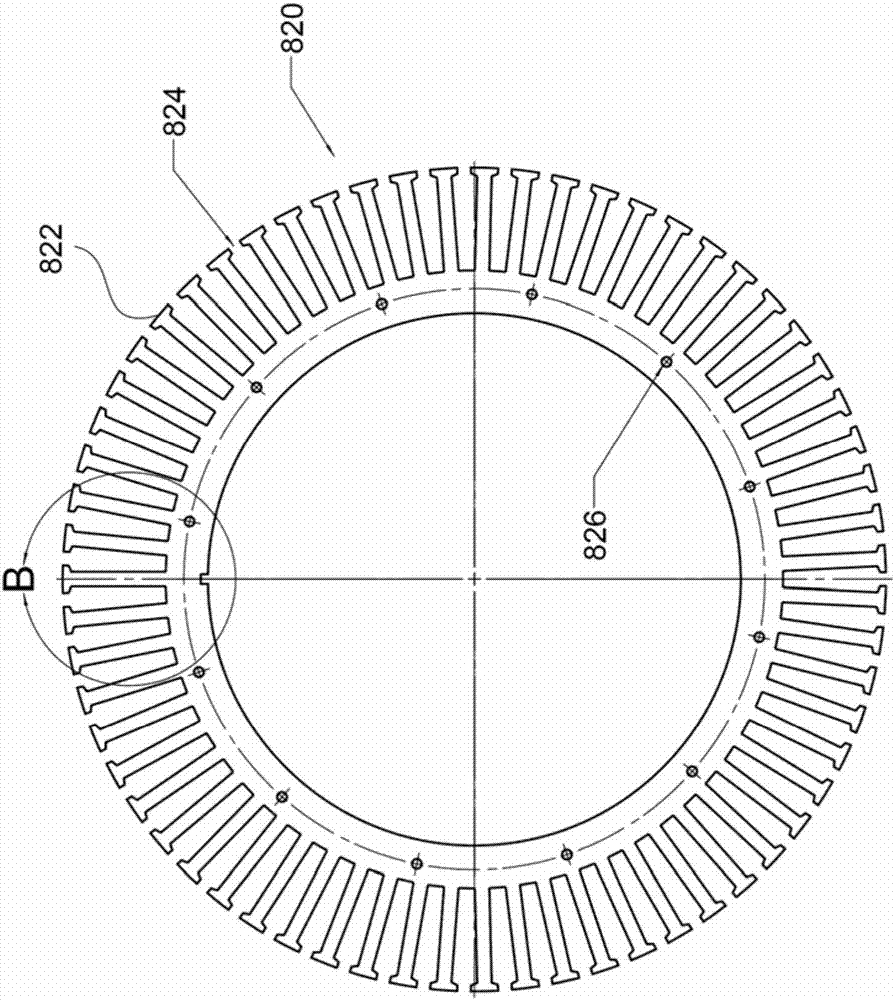
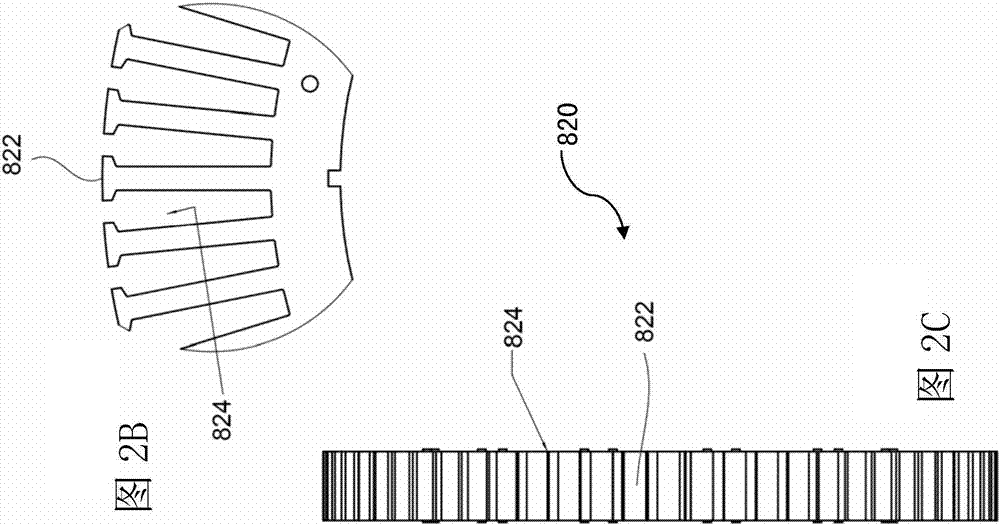
[0072] Figure 4A Shown is a stator according to a first embodiment and a stator winding pattern with a symmetrical winding configuration. The stator is used in a PMSM with 63 slot structures (the slots are numbered 1-63 individually and consecutively along the circumference of the stator for reference) and 70 slot poles. It can be seen that the value of q in the equation is less than 1:
[0073]
[0074] More specifically, 63÷70÷3=3 / 10. The wire is used to form a coil around each tooth of the stator, and it is a copper wire with a diameter of 0.9mm, with an enamelled insulation grade of G2 and a temperature resistance index of 180°C. Each coil on the stator consists of 110 turns of wire. The winding directions of each of the 63 coils of the stator are shown in Table 2 below and explained in detail below. numbered in table 2 below and in Figure 4A The 63 coils shown in , starting from coil 101, are respectively consecutively numbered to the 63rd coil, ie, coil 163.
...
Embodiment 2
[0088] Following the method and discussion of Example 1, Figure 5A Another example of a stator is shown that can also be used with a 70 pole rotor to provide a PMSM. Such as Figure 5A As shown, the stator 200 includes sixty (60) teeth 270 separated by sixty (60) slots 201 - 260 , with an exemplary number marked therein. Each tooth 270 is wound by a U-phase conductor, or a V-phase conductor, or a W-phase conductor according to the q1 winding pattern shown in Table 1 . The rotor is a 70-pole rotor, specifically, as Figure 5B The rotor 292 shown, the resulting motor is a PMSM, which generates almost zero radial force during operation. Figure 5A The winding patterns of the stator shown include the symmetrical winding patterns shown in Table 3 below. For simplicity, Table 3 only shows the winding pattern for the first phase (U phase) of the 3-phase motor. There are 60 coils, and the U-phase coil includes two coils every three groups, specifically, one group includes coils ...
Embodiment 3
[0094] Following the method and discussion of Example 1, Figure 6A A stator comprising 54 symmetrically wound teeth is shown for use with a 66-pole rotor to form a PMSM that exhibits almost zero radial force. Every third wire, one for each phase, is wound on a corresponding set of teeth. The winding pattern follows the q3 winding pattern shown in Table 1 above. The fifty-four teeth (54) of the stator 400 are wound individually and continuously to form coils designated 501-554, in Figure 6A The example numbers of the coils are marked in . The fifty-four slots (54) of the stator 400 are individually and consecutively designated 401-454, at Figure 6A The example number of the slot is marked in . The winding pattern for the U-phase conductor is shown in Table 4 below. The U-phase, V-phase, and W-phase described here are respectively equivalent to the A-phase, B-phase, and C-phase referred to in the winding mode shown in Table 1 above.
[0095] Table 4
[0096]
[0097...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com