A photoresponsive surface molecularly imprinted material and its preparation method and application
A technology of surface molecular imprinting and light response, applied in the fields of chemistry and material and molecular separation, can solve the problems of expensive separation and purification of chromatographic columns, low industrial output, etc., and achieve difficult elution of template molecules, remarkable separation effect, and good identification. performance effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
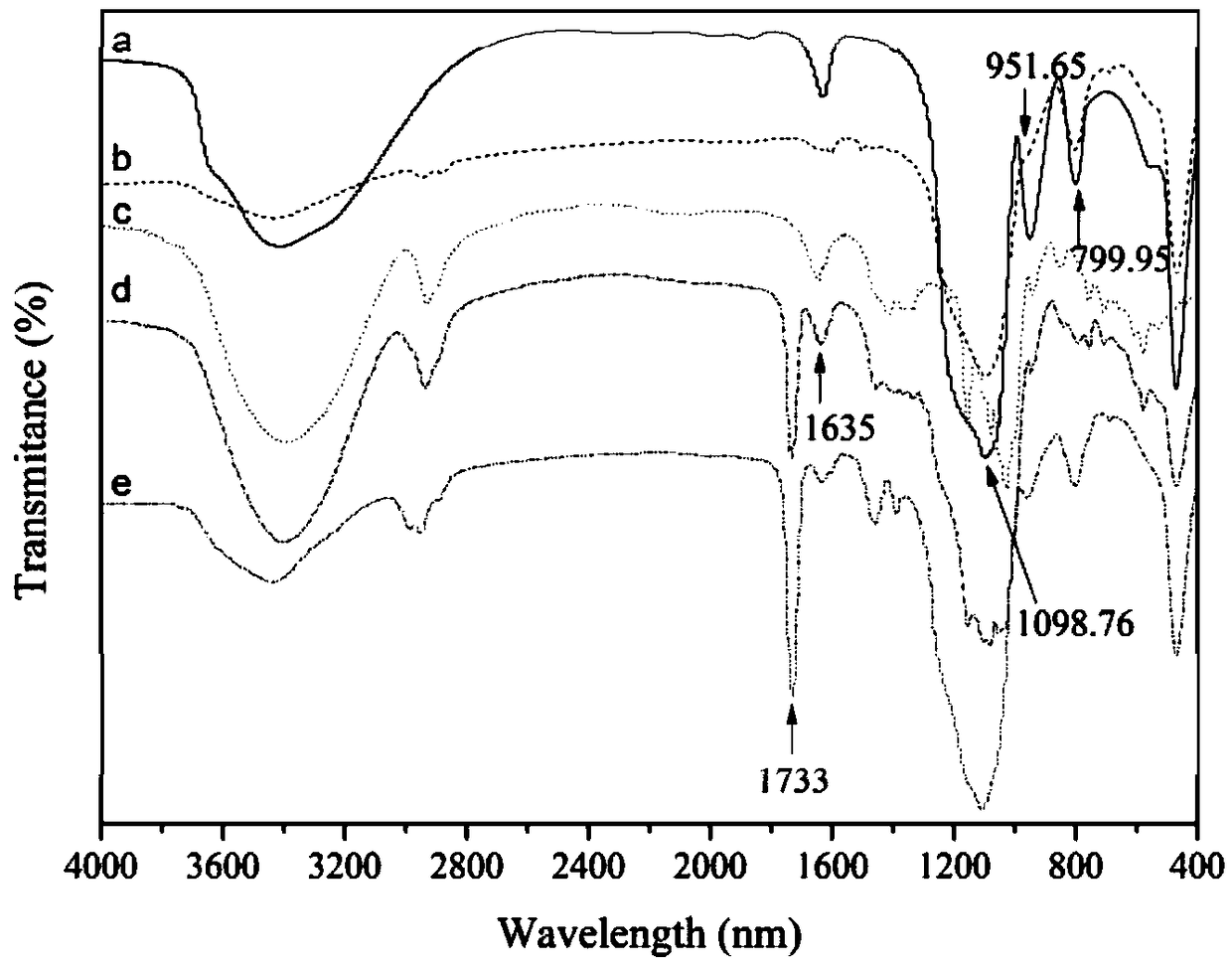
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
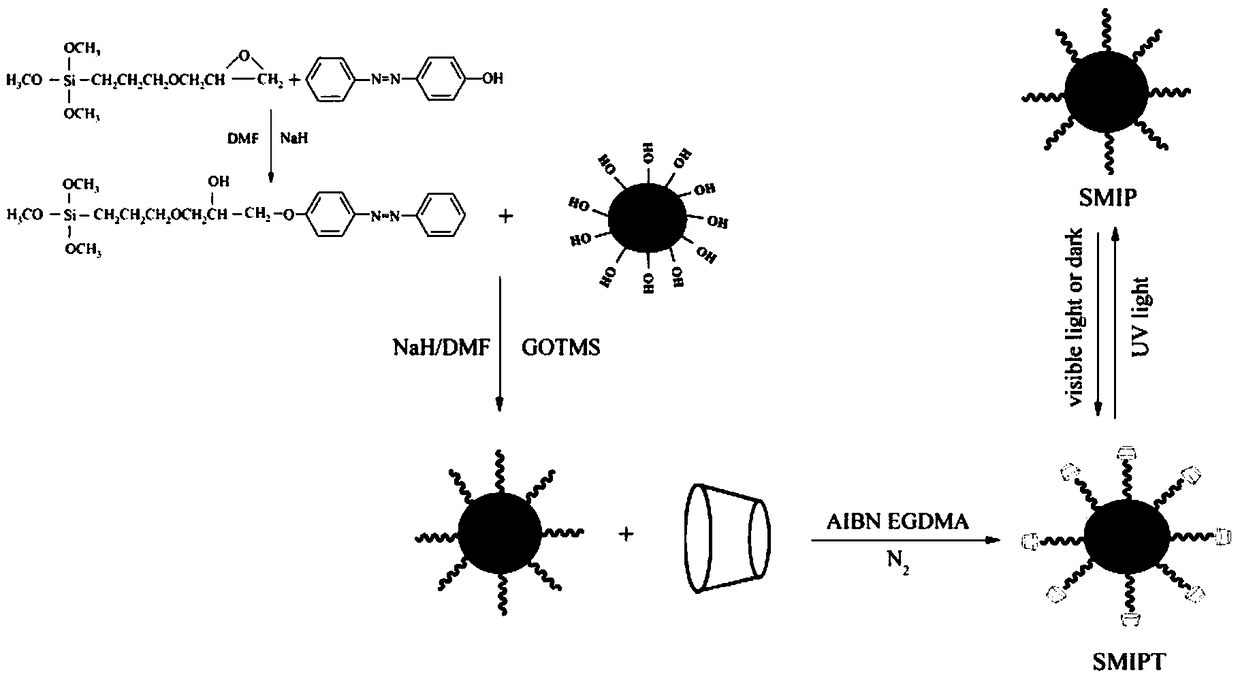
[0036] (1) Preparation of azobenzene derivatives: 4-hydroxyazobenzene (0.3964g) was dissolved in 50.0ml of anhydrous, N,N'-dimethylformamide (DMF), and 0.20g of NaH was added thereto. The mixture was stirred at room temperature until no bubbles evolved. The excess NaH was then filtered off, and the filtrate was transferred to a three-necked flask. After 1.0ml of γ-glycidyltrimethoxysilane (GOTMS) was slowly added dropwise to the filtrate, the reaction mixture was reacted at 50°C for 8h under the protection of nitrogen. Through this reaction, 4-hydroxyazobenzene is covalently bonded to the epoxy group of GOTMS.
[0037] (2) Preparation of silica gel particles: add 0.5mL tetraethoxysilane to 11.35mL ethanol solution, then quickly add 2mL ammonia solution (mass fraction: 12%), stir at room temperature for 48h, centrifuge, filter, and wash with water for several times Dry under vacuum.
[0038] (3) Activation of silica gel: take 2.0 g of silica gel particles, add 20.0 mL of hyd...
Embodiment 2
[0043] (1) Preparation of azobenzene derivatives: 4-hydroxyazobenzene (0.9911g) was dissolved in 100.0ml of anhydrous, N,N'-dimethylformamide (DMF), and 0.50g of NaH was added thereto. The mixture was stirred at room temperature until no bubbles evolved. The excess NaH was then filtered off, and the filtrate was transferred to a three-necked flask. After 2.0 ml of γ-glycidyltrimethoxysilane (GOTMS) was slowly added dropwise to the filtrate, the reaction mixture was reacted at 80° C. for 5 h under the protection of nitrogen. Through this reaction, 4-hydroxyazobenzene is covalently bonded to the epoxy group of GOTMS.
[0044] (2) Preparation of silica gel particles: add 3mL tetraethoxysilane to 11.35mL ethanol solution, then quickly add 15mL ammonia solution (mass fraction: 16.7%), stir at room temperature for 24 hours, centrifuge, filter, wash with water several times, and then pour Vacuum dry.
[0045] (3) Activation of silica gel: Take 10.0 g of silica gel particles, add 1...
Embodiment 3
[0050] (1) Preparation of azobenzene derivatives: 4-hydroxyazobenzene (1.9822g) was dissolved in 250.0ml of anhydrous, N,N'-dimethylformamide (DMF), and 1.0g of NaH was added thereto. The mixture was stirred at room temperature until no bubbles evolved. The excess NaH was then filtered off, and the filtrate was transferred to a three-necked flask. After 5.0ml of γ-glycidyltrimethoxysilane (GOTMS) was slowly added dropwise to the filtrate, the reaction mixture was reacted at 100° C. for 2 h under the protection of nitrogen. Through this reaction, 4-hydroxyazobenzene is covalently bonded to the epoxy group of GOTMS.
[0051] (2) Preparation of silica gel particles: Add 6 mL of tetraethoxysilane to 11.35 mL of ethanol solution, then quickly add 30 mL of ammonia solution (20% by mass), stir at room temperature for 12 hours, centrifuge, filter, wash with water several times, and then pour Vacuum dry.
[0052] (3) Activation of silica gel: Take 20.0 g of silica gel particles, add...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com