A Time-Frequency Two-Dimensional Sparse Code Multiple Access Method for Narrowband Internet of Things
A sparse code multiple access, narrowband IoT technology, applied in the field of multiple access, can solve problems such as lack of multiple access methods, and achieve the effect of increasing the number of users, improving performance, and increasing the number of user connections
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
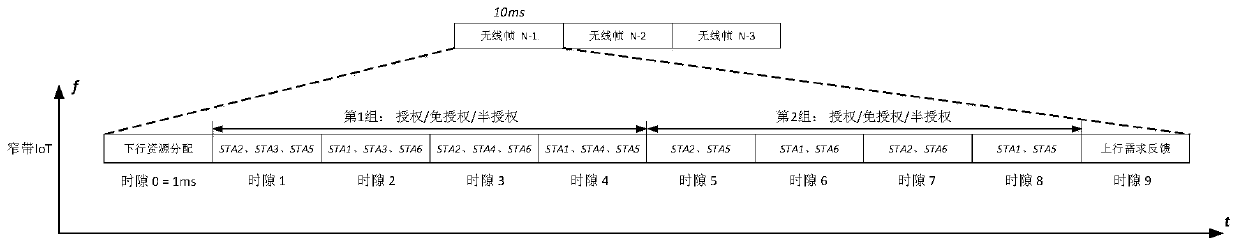
[0044] Such as figure 2 As shown, Embodiment 1 describes the pure time-domain SCMA method when the 5G cellular network has only one narrowband IoT channel. The narrowband IoT is divided into multiple time slots, and N time slots form an SCMA resource block, which is used by the UE Block transfer data.
[0045] Step 1: Divide each frame of narrowband IoT into time slots, and use N time slots as an SCMA resource block for a group of UEs.
[0046]Specific steps are as follows:
[0047] Step 1.1: Divide each frame on narrowband IoT into time slots, figure 2 In the example, 10 time slots are divided based on the frame structure of the fourth generation mobile communication system (4G). As a typical configuration, the present invention supports other flexible time slot division methods, which are determined by specific wireless network protocols.
[0048] Step 1.2: N time slots form a SCMA resource block, which is allocated to the UE. figure 2 Among them, Slot 0 is used for sche...
Embodiment 2
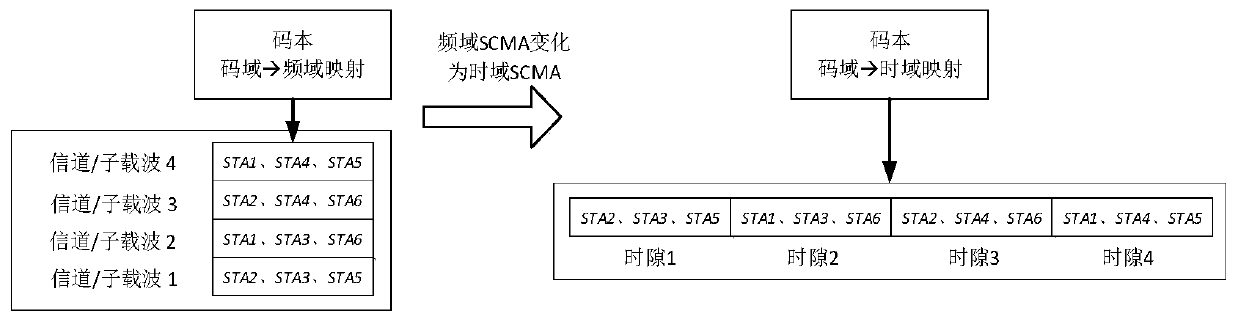
[0058] Such as image 3 As shown, Embodiment 2 describes the time-domain SCMA method in the case of multiple independent narrowband IoT channels in the 5G cellular network, that is, extending Embodiment 1 to the situation of multiple independent narrowband channels, and multiple narrowband IoT channels are divided into multiple time slots, and N time slots on each narrowband constitute a SCMA resource block, different narrowband channels are independent of each other, and the UE uses resource blocks to transmit data.
[0059] Step 1: Divide each narrowband IoT frame into time slots, and use N time slots on each narrowband as an SCMA time-frequency resource block for a group of UEs.
[0060] Specific steps are as follows:
[0061] Step 1.1: Divide each frame on the narrowband into time slots, image 3 In the example, 10 time slots are divided into 2 channels based on the 4G frame structure as a typical configuration, and the time slot division method is determined by the spec...
Embodiment 3
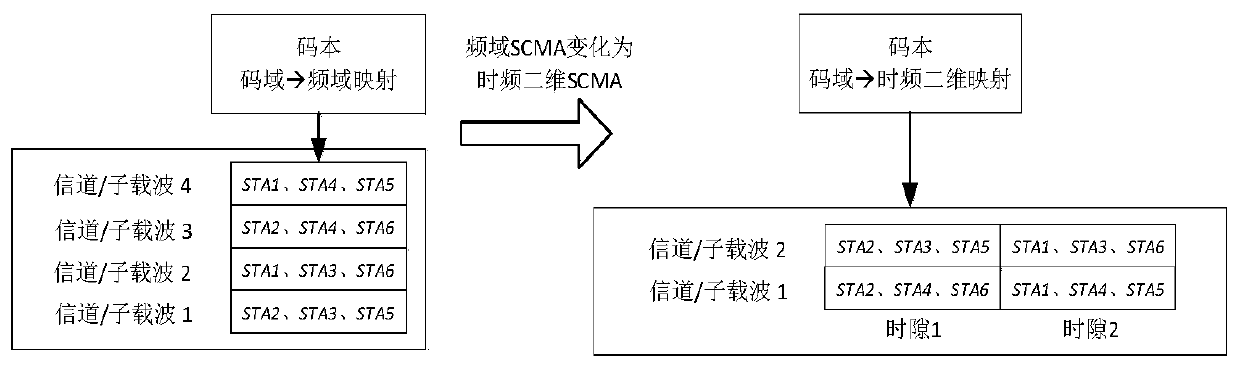
[0073] Such as Figure 4 As shown, embodiment three describes the time-frequency two-dimensional SCMA method in the case of multiple narrowband channels in the 5G cellular network, which is to change the channel in embodiment two into a non-independent case, and multiple time slots and multiple channels together An SCMA resource block is formed, and the UE uses this resource block to transmit data.
[0074] Step 1: Divide narrowband channels into time slots, and use N time slots on multiple narrowbands together as an SCMA time-frequency resource block, and assign them to a group of UEs.
[0075] Specific steps are as follows:
[0076] Step 1.1: Divide each frame on the narrowband into time slots, figure 2 The two channels are divided into 10 time slots respectively as a typical configuration, but the present invention supports other flexible time slot division methods, which are determined by specific wireless network protocols.
[0077] Step 1.2: N time slots on multiple n...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com