A routing method for least-cost spectrum allocation and fragmentation awareness in elastic optical networks
An elastic optical network and spectrum allocation technology, applied in the field of least-cost spectrum allocation and fragment-aware routing, can solve problems such as the inability of spectrum to serve services, limit spectrum utilization, and reduce network service quality, optimize network spectrum, maintain continuous the effect of reducing the impact of debris
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
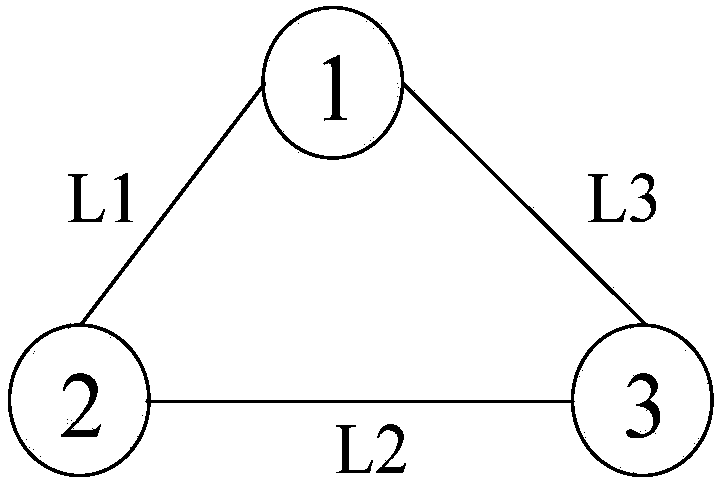
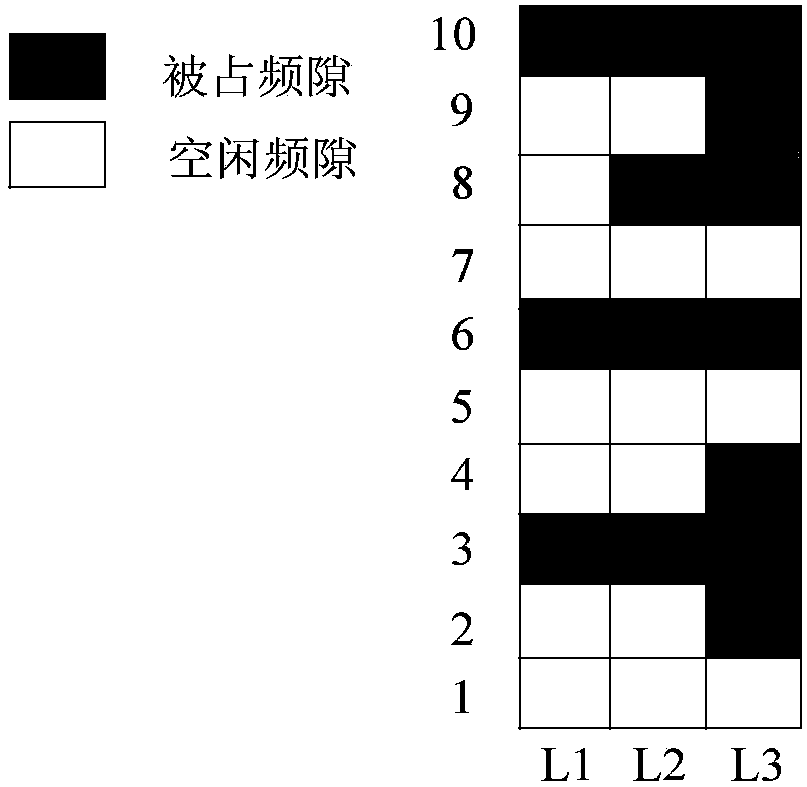
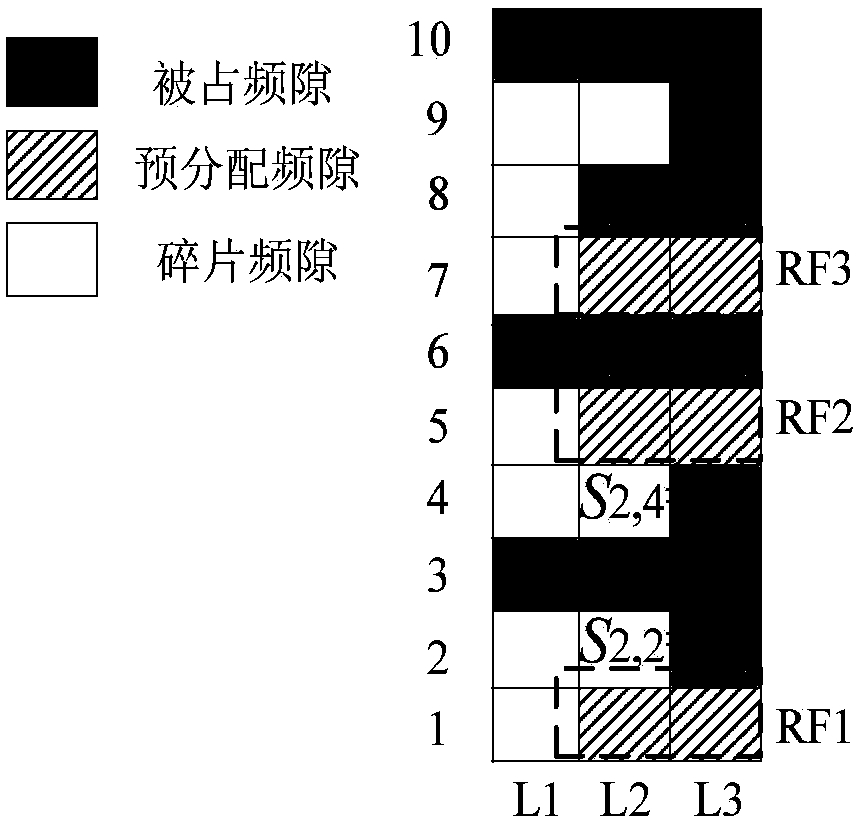
[0035] as attached figure 1 In the network topology shown, there are three links in the network, and the spectrum usage of each link is shown in the attached figure 2 , where the ordinate represents the frequency slot on each link, and the abscissa represents the network link number. Combined with this example, the routing method of minimum cost spectrum allocation and fragment awareness in the elastic optical network in the method of the present invention is described.
[0036] Since the request rates of services are different and the modulation formats selected are different, the frequency slots required by each service are also different. Spectrum fragments are isolated spectrum blocks that cannot meet any service bandwidth requirements. Let the network topology abstraction of the elastic optical network be G(V,E,F), V is the set of network nodes, E is the set of network links, F is the total frequency slot on each link, and the start and end range of each link frequency...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com