Blind verifiable cryptographic signature method based on block chain
A blockchain and signer technology, applied in the field of information security, can solve problems such as the inability to obtain digital signatures and the inability to obtain signer public key information
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
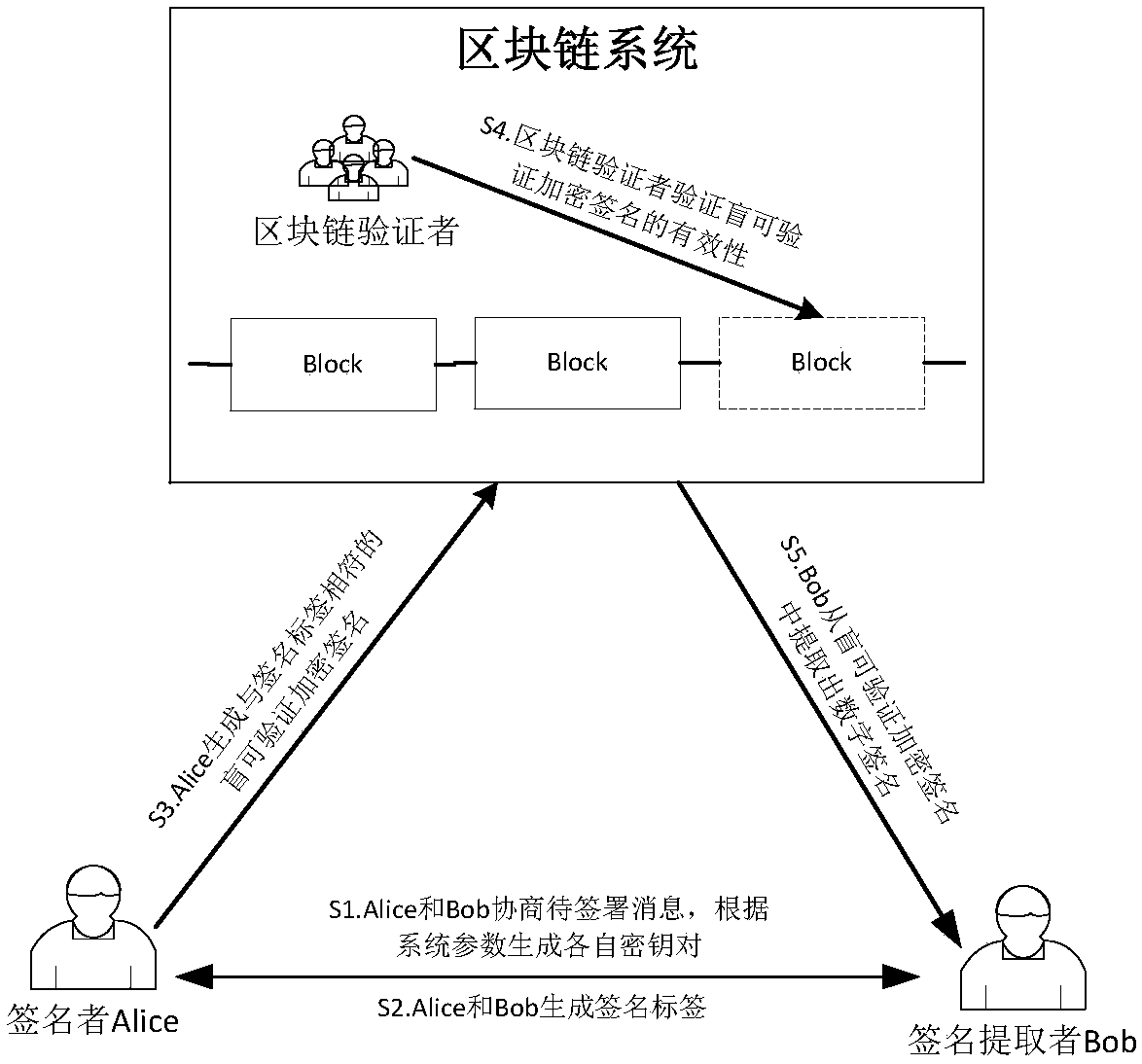
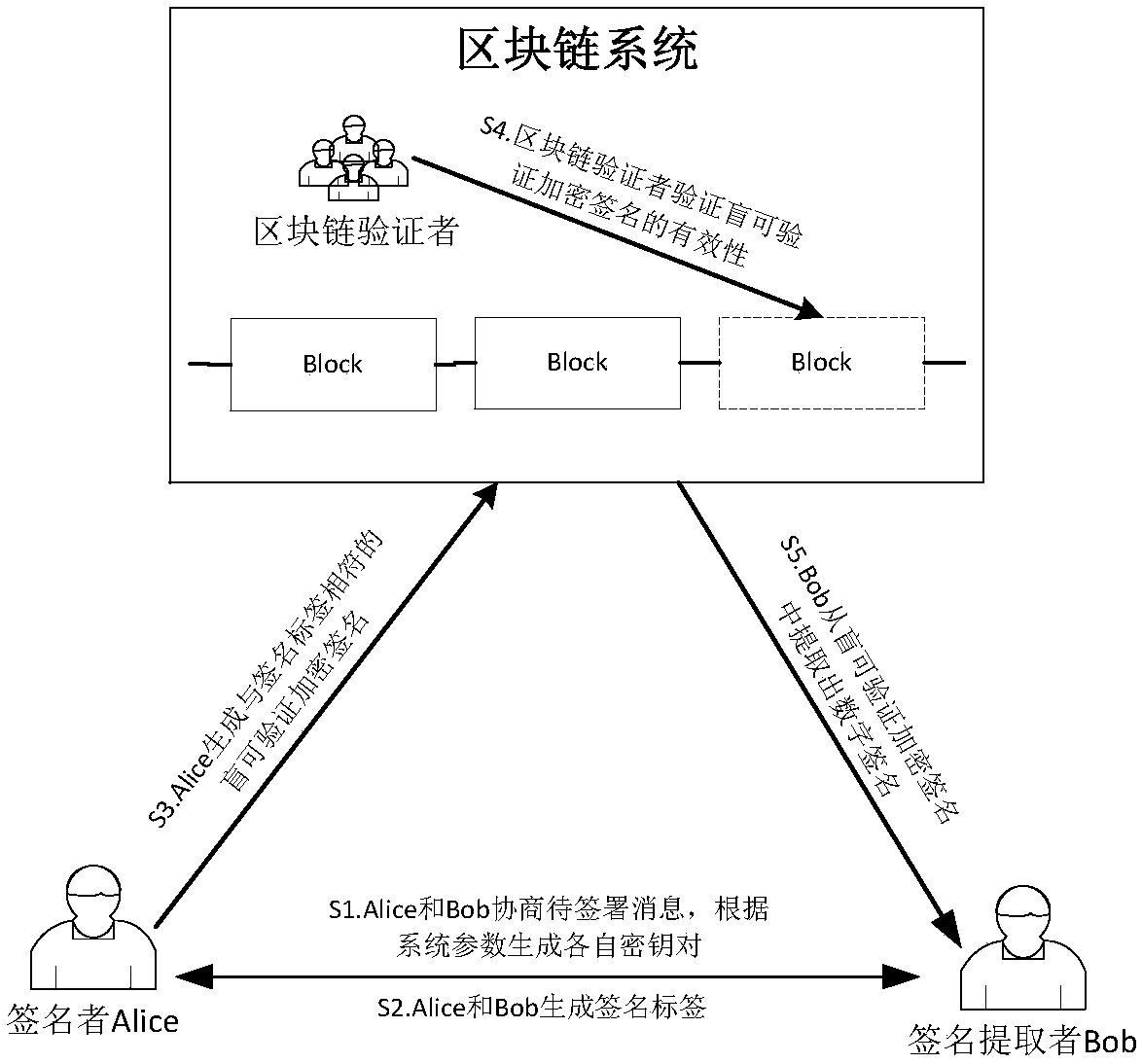
[0034] Assuming that Zhang San and Li Si have negotiated an electronic contract m, Zhang San needs to sign the contract and then publish it to the blockchain network. The blockchain verifier obtains the signature and verifies the validity of the signature. After the verification is passed, Li Si can extract Zhang San's real digital signature on m from this signature. The participants in this example are: Zhang San (Alice), Li Si (Bob) and blockchain verifiers.
[0035] The implementation process to complete the above requirements is as follows:
[0036] 1. Zhang San and Li Si negotiate the message to be signed, and the steps to generate their respective key pairs according to the system parameters include:
[0037] 1) Zhang San and Li Si negotiate the message object m to be signed;
[0038] 2) The system parameters are generated by using the type a parameter in the JPBC library, including a bilinear pairing operation e:G 1 ×G 1 →G 2 , where G 1 is a cyclic additive group...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com