A visual microbial biochemical identification kit and identification method thereof
A biochemical identification and kit technology, applied in the field of microbial detection, can solve the problems of easy dripping of liquid, unstable drying and fixing, high accuracy, etc., and achieve the effect of easy storage and transportation, easy recording of results, and loose storage conditions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0053] The biochemical identification kit and identification method of embodiment 1 Shigella
[0054] The structure of the biochemical identification kit is as above.
[0055] The sugar fermentation reaction biochemical medium for identifying Shigella is configured according to the corresponding biochemical medium formula in GB 4789.5-2012-National Food Safety Standard Food-Microbiological Inspection-Shigella Inspection.
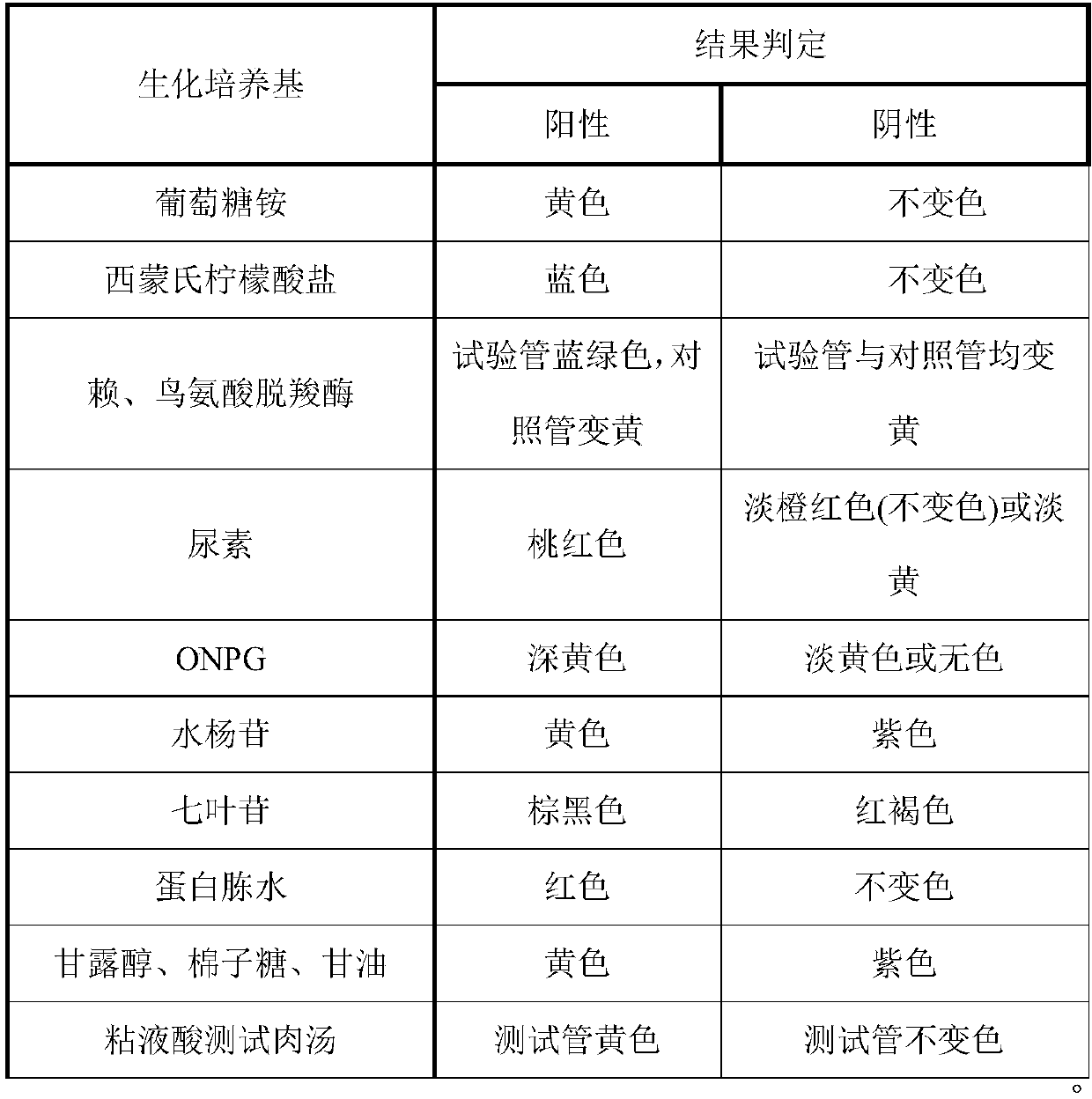
[0056] A biochemical identification kit for identifying Shigella, including at least 13 reaction components, and the fixed biochemical medium in each reaction tank is different, namely ammonium glucosamine, Simon's citrate lysate, ornithine decarboxylase , lysine decarboxylase, urea, ONPG, salicin, escin, peptone water, mannitol, raffinose, glycerin, mucus acid test broth. Add 0.3ml of liquid biochemical medium to each reaction branch tank, and dry at 50°C and vacuum degree of 133Pa for 50min. The biochemical medium forms a film and sticks to the bottom of ...
Embodiment 2
[0069] The biochemical identification kit and identification method of embodiment 2 Salmonella
[0070] The structure of the biochemical identification kit is as above.
[0071] The sugar fermentation reaction biochemical medium for identification of Salmonella is configured according to the corresponding biochemical medium formula in GB 4789.4-2016-National Food Safety Standard Food-Microbiological Examination-Salmonella Examination.
[0072] The biochemical identification kit for identifying Salmonella microorganisms includes at least 10 components, and the biochemical medium fixed in the reaction branch tank in each component is different, which are respectively lysine decarboxylase and lysine decarboxylase control (without Contains lysine), indigo base, urea, ONPG, malonate, mannitol, sorbitol, weimonol, salicin. Add 0.2ml of liquid biochemical culture medium to each reaction branch tank, and dry at 48°C and vacuum degree of 133Pa for 40min. The biochemical culture medium...
Embodiment 3
[0080] The biochemical identification kit and identification method of embodiment 3 Listeria
[0081] The structure of the biochemical identification kit is as above.
[0082] The sugar fermentation reaction biochemical medium for identifying Listeria is configured according to the corresponding biochemical medium formula in GB 4789.30-2016-National Food Safety Standard Food-Microbiological Examination-Listeria monocytogenes Examination.
[0083] The biochemical identification kit for identifying Listeria microorganisms includes at least 8 components. The biochemical media fixed in the reaction branch tanks in each component are different, which are hemolysin (hemolysis reaction), glucose, maltose, MR-VP, mannitol, rhamnose, xylose, escin. Add 0.2ml of liquid biochemical medium to each reaction branch tank, and dry at 50°C and vacuum degree of 133Pa for 60min. The biochemical medium forms a film and sticks to the bottom of the reaction tank.
[0084] The identification metho...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com