Receiver and assembly process thereof
An assembly process and technology for receivers, applied in the field of receivers, can solve the problems of inability to achieve modularization and complicated installation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
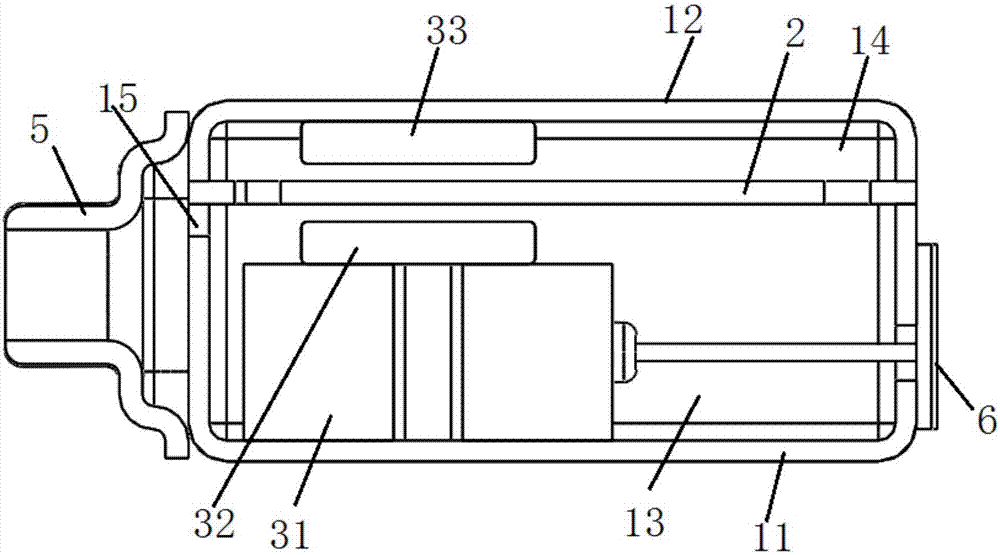
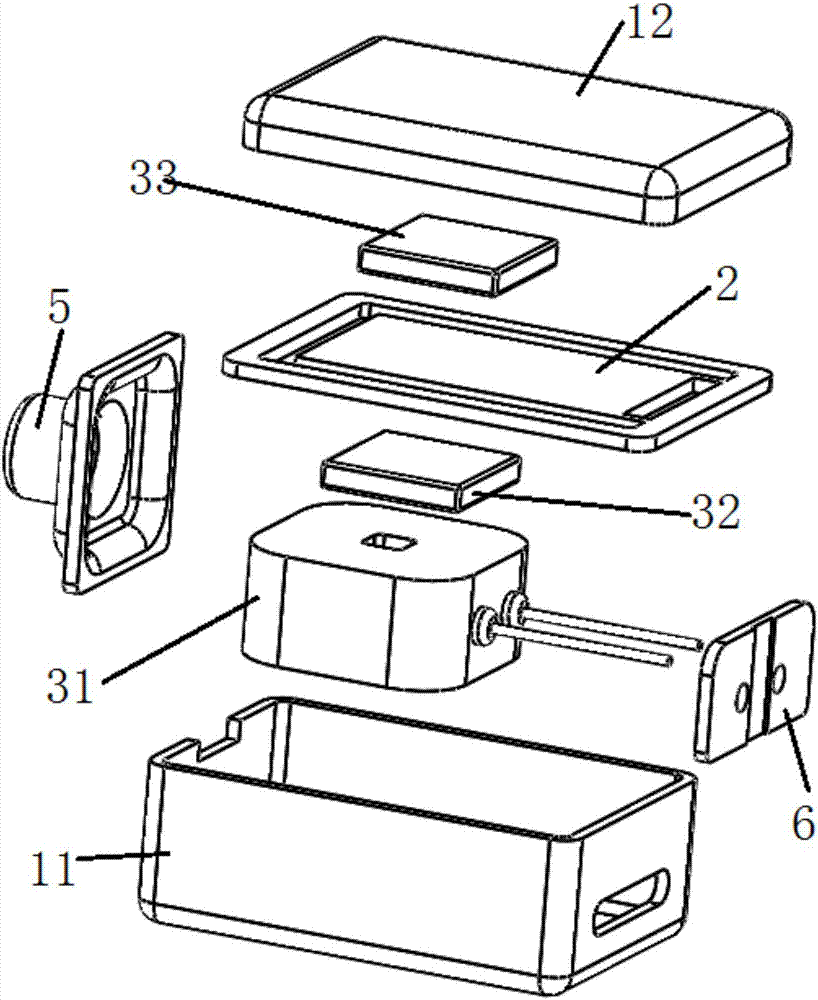
[0089] This embodiment provides a receiver, such as Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, it includes a housing 1 , a diaphragm mechanism 2 and an electromagnetic drive mechanism 3 .
[0090] like figure 2 and image 3 As shown, the shell 1 has a first shell 11 made of a first bottom surface and a side wall, and a second shell 12 made of a second bottom surface and a side wall; the second shell 12 is detachably connected to the first shell 11 buckle and encircle the inner cavity. The diaphragm mechanism 2 is arranged in the inner cavity, and the inner cavity of the housing 1 is divided into an installation cavity 13 close to the first bottom surface and a sound emitting cavity 14 close to the second bottom surface; Figure 14 and Figure 15As shown, the diaphragm mechanism 2 includes a fixed frame 22 , a reed 21 and a sound diaphragm 23 . The fixed frame 22 has a hollow inner cavity, and one end of the reed 21 is connected to the fixed frame 22 through the fixed end 211 for th...
Embodiment 2
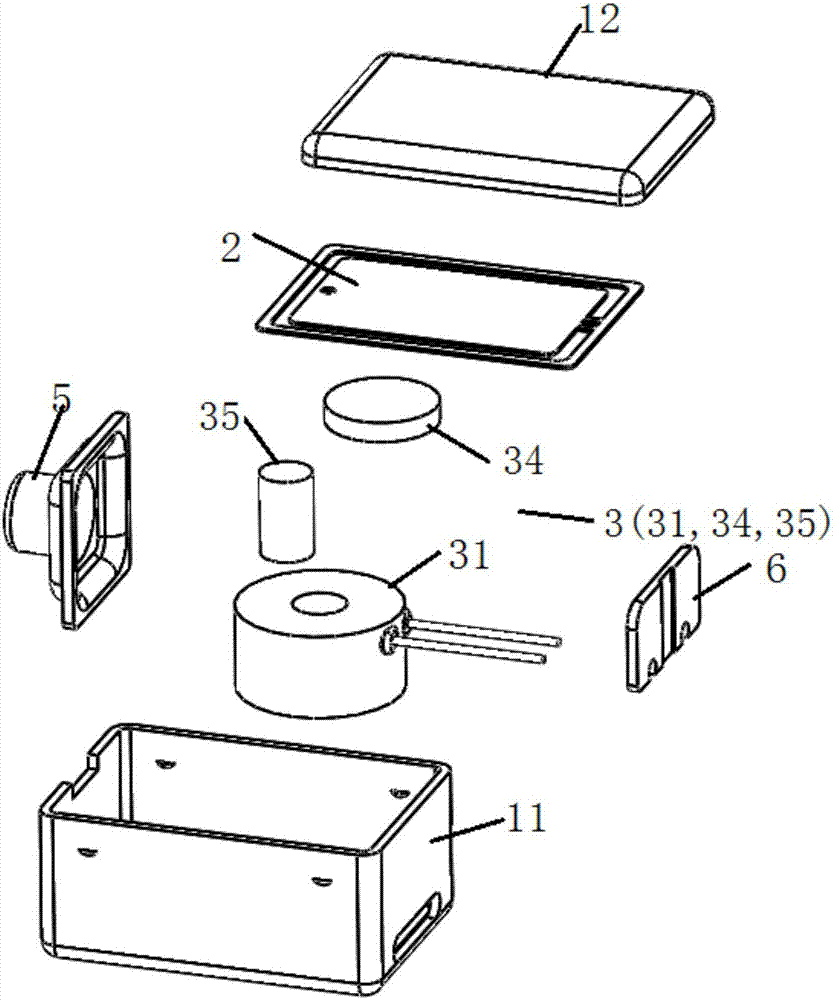
[0136]This embodiment provides a receiver, such as Figure 7 and Figure 8 As shown, compared with the receiver provided in Embodiment 1, the only difference is that the reed 21 is made of non-magnetic material, and the electromagnetic drive mechanism 3 is different from the electromagnetic drive mechanism 3 provided in Embodiment 1. The electromagnetic drive Mechanism 3 includes a coil 31 and a third magnet 34 is fixed on the side surface of the reed 21 facing away from the sound membrane 23; the coil 31 and the third magnet 34 are located in the same cavity, and the coil 31 and the third magnet 34 A gap is reserved between the ends facing each other, and a vibration space for the reed is formed between the top of the coil 31 and the second bottom surface of the second housing 12 .
[0137] The electromagnetic driving mechanism 3 of this structure is in the process of driving the reed 21 to reciprocate and vibrate: if the polarity of the third magnet 34 towards the end of th...
Embodiment 3
[0162] This embodiment provides a receiver, such as Figure 12 and Figure 13 As shown, compared with the receiver provided in Embodiment 2, the only difference is that one end of the third magnet 34 is fixed on the reed 21, and the other end extends vertically into the inner cavity of the coil 31 and is connected to the coil The inner wall surfaces of the magnets 31 are separated from each other, and a distance is reserved between the bottom of the third magnet 34 and the first bottom surface of the first housing 11 . The iron core is fixed in the inner cavity of the coil 31 , but there is a gap between the top of the iron core and the bottom of the third magnet 34 .
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Caliber | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com