A method for breeding japonica rice varieties resistant to herbicide imazethapyr using molecular markers
A molecular marker-assisted, herbicide-resistant technology, applied in the direction of biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve problems affecting crop growth and development, affecting harvesting efficiency, economic losses, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
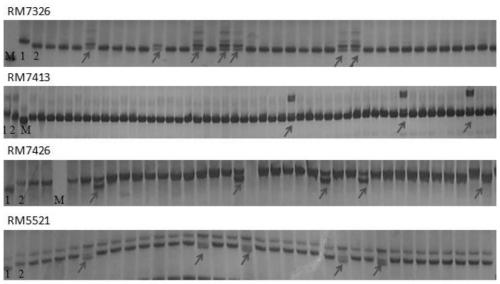
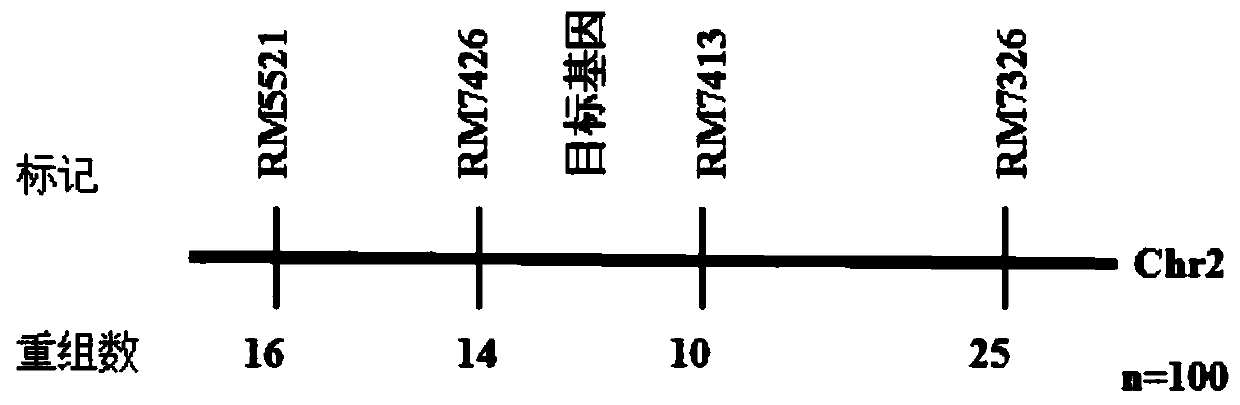
[0039] Example 1. Acquisition of the SSR molecular marker RM7413 linked to the herbicide resistance of japonica rice
[0040] The research group of the present invention screened out a rice material "Jinjing 818" which is resistant to imazethapyr from 7403 rice variety resource materials. After identification, it was found that the variety Jinjing 818 was resistant to the herbicide Imazethapyr, but its genetic mechanism was unknown. Therefore, the genetic mechanism of this variety was first studied, and the resistance gene mapping was carried out.
[0041] 1) Genetic analysis of Jinjing 818 resistance to the herbicide Imazethapyr
[0042] The japonica rice variety Jinjing 818 resistant to the herbicide imazethapyr was used as the donor, and the popularized japonica rice variety Suken 118 sensitive to the herbicide imazethapyr was used as the acceptor to obtain F. 1 10 plants, to F 1 When the seedlings grow to 2 leaves and 1 heart, the recommended concentration of imazethapyr i...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2. Application of molecular markers in assisted breeding of imazamox-resistant japonica rice varieties
[0053] 1) The present invention uses imazethapyr-resistant variety Jinjing 818 as the donor parent, and imazethapyr-sensitive Nanjing 9108 as the recipient parent. Both parents are currently the main popular varieties with good yield and adaptability. The two parents are crossed and assembled to harvest F 1 Substitute seeds.
[0054] 2)F 1 F was obtained by selfing the progeny plant 2 Substitute seeds, plant F 2 50 seeds to get F 2 Substitute plants. Take leaves from each individual plant, extract DNA, and use the SSR marker RM7413 in Example 1 for amplification. The amplification system, conditions and detection methods are the same as those shown in Example 1. Individual plants that are completely consistent with the resistant parent's banding pattern are selected.
[0055] 3) Put F 2 Generation-selected plants were continuously selfed to F 7 At th...
Embodiment 3
[0056] Example 3. Application potential of the marker RM7413 linked to the japonica resistance herbicide imazethapyr in the currently popular japonica rice varieties
[0057] Conventional japonica rice varieties usually do not have the ability to resist the herbicide imazethapyr. If the marker RM7413 has the polymorphisms in Examples 1 and 2 in the herbicide-sensitive conventional japonica rice varieties and the resistant variety Jinjing 818, then RM7413 can be used in conventional japonica rice varieties. Herbicide resistance improvement of japonica rice to obtain new herbicide-resistant varieties. In the present invention, 91 japonica rice varieties mainly promoted in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River are selected for polymorphism identification, and the SSR marker RM7413 in Examples 1 and 2 is used for amplification. The amplification system, conditions and detection methods are the same as those shown in Example 1. . The identified varieties include Lianji...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com