Routing Methods in Opportunistic Networks
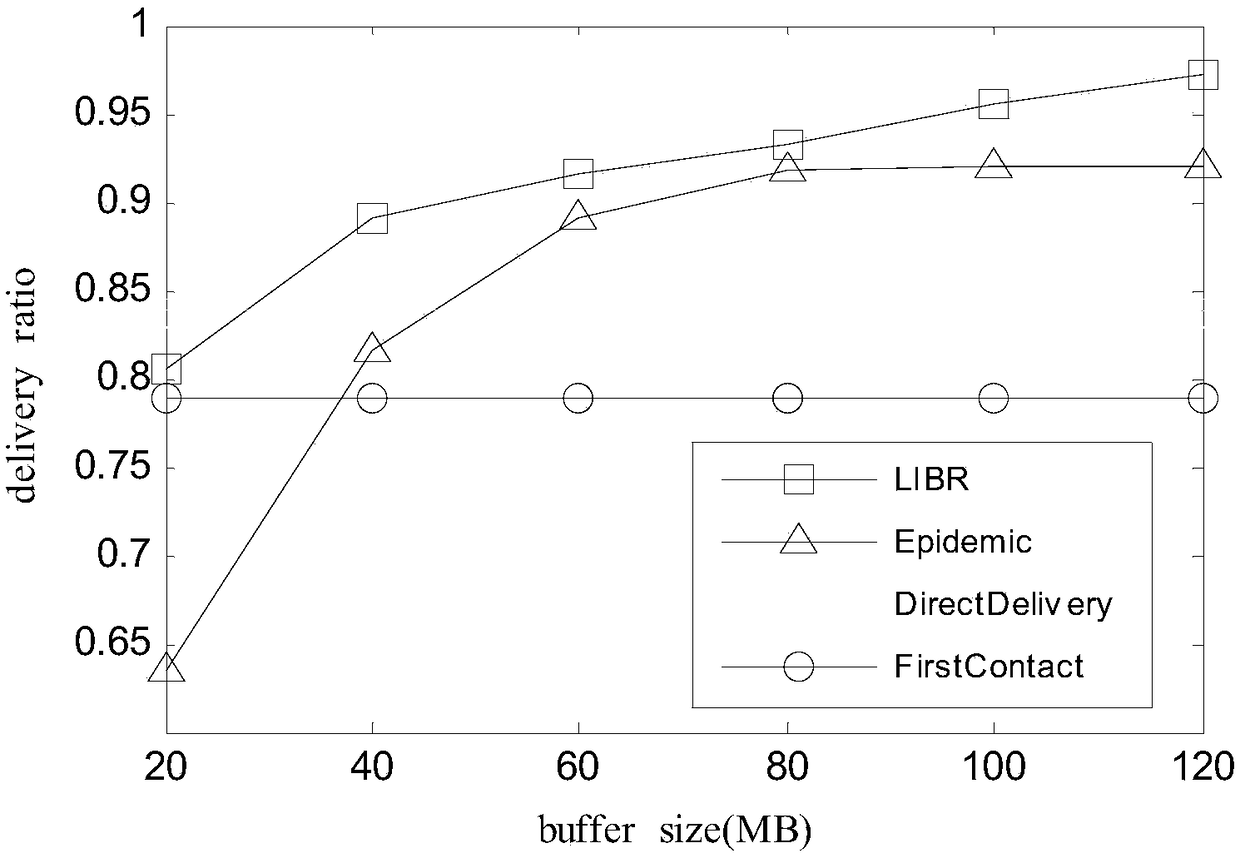
A network and routing technology, which is applied in the field of routing based on node meeting position prediction, can solve the problems of inaccurate prediction of destination node location and other information, poor routing accuracy, and algorithm performance degradation, so as to improve message delivery rate, Effect of reducing network overhead and reducing overhead ratio and average transmission delay
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
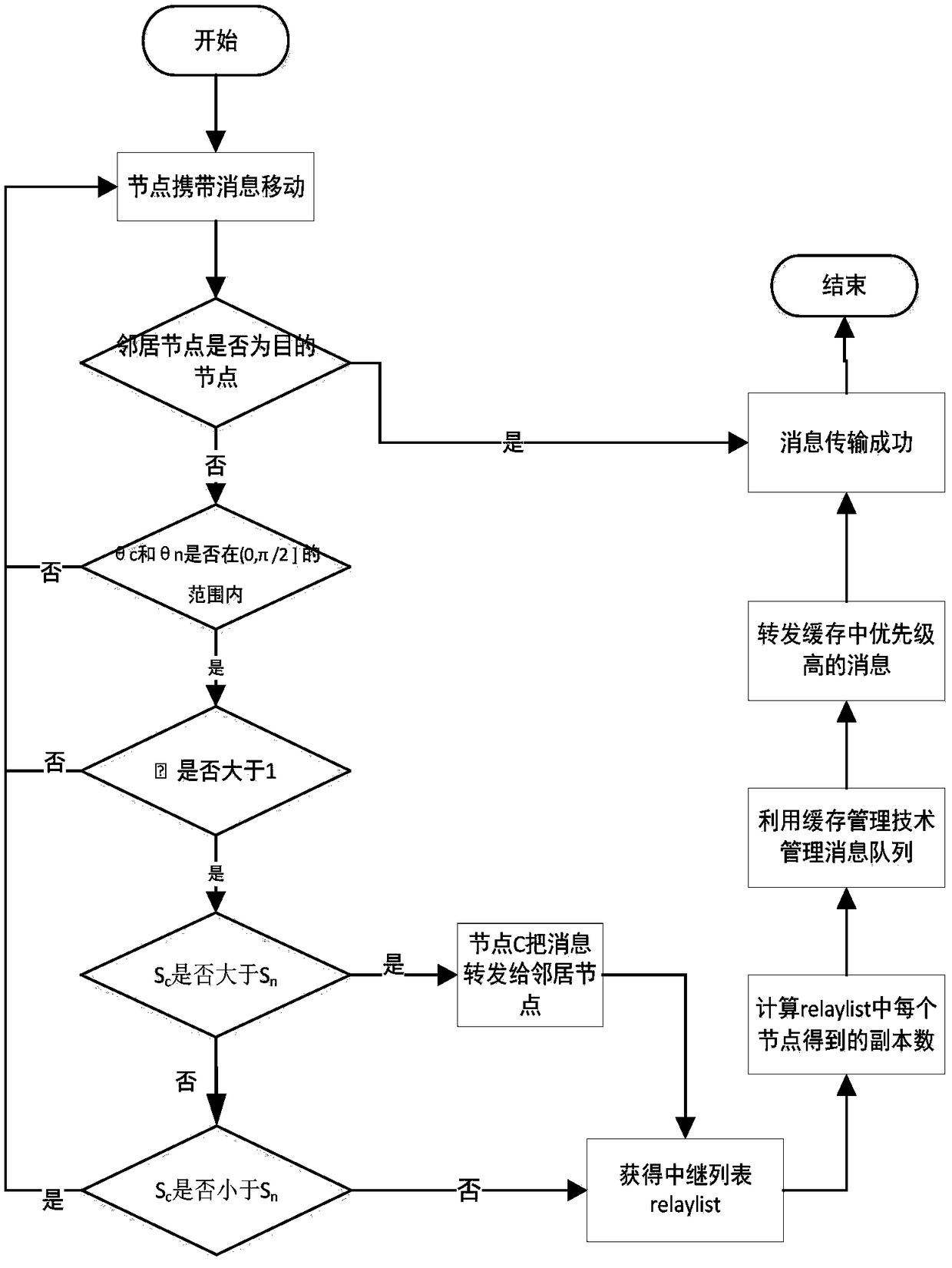
[0055] Take the establishment of a second-order Markov model as an example, such as figure 1 As shown, the route selection method in the opportunistic network consists of the following steps:
[0056] (1) Before sending, determine all its neighbor nodes for node C that currently carries a message. When nodes meet each other, they exchange message lists to determine all neighbor nodes N that do not carry messages. i .
[0057] This embodiment determines its neighbor node N and destination node D for the node C currently carrying the message.
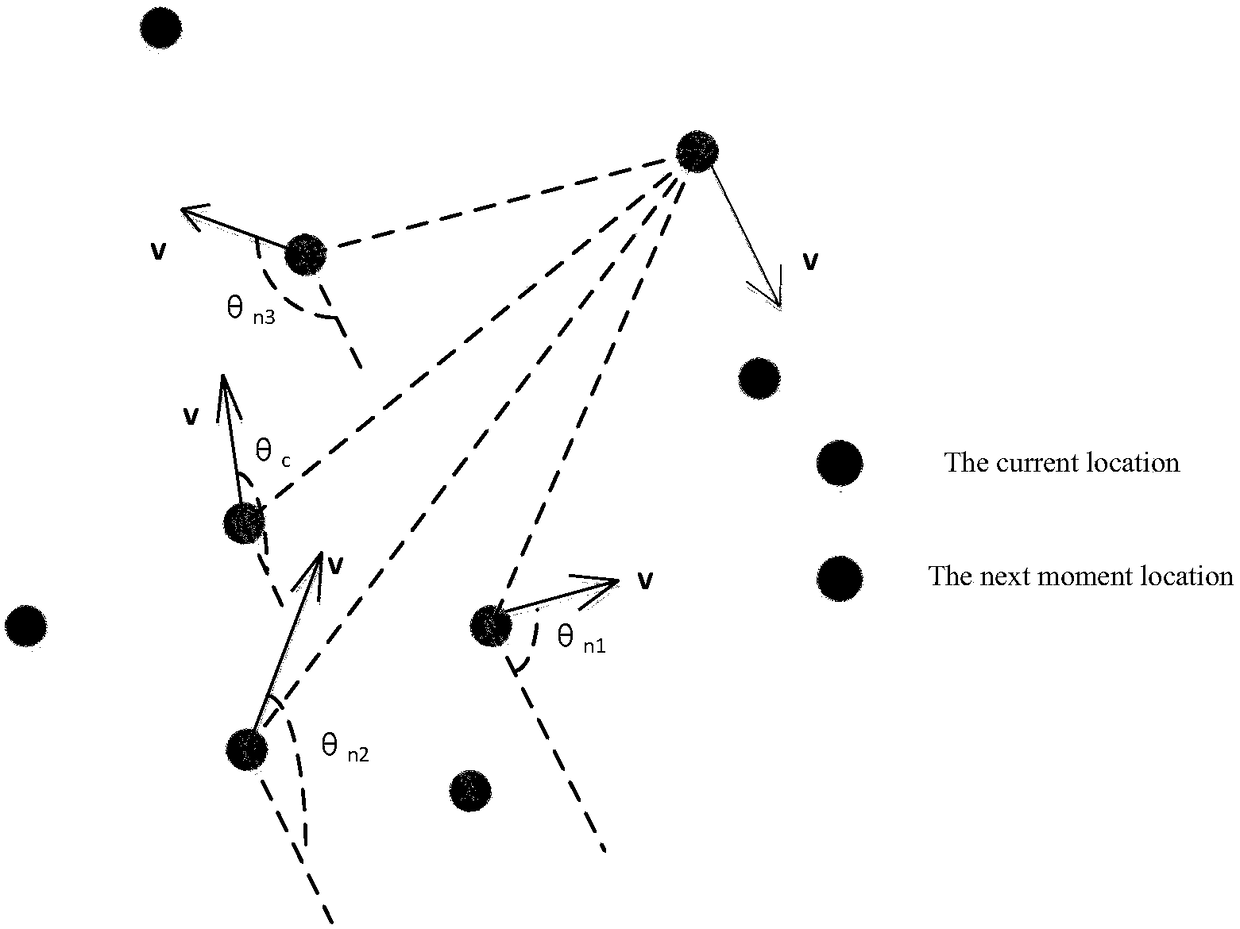
[0058] (2) Determine that the moving speeds of node C, all neighbor nodes N, and destination node D carrying the message at the current moment are respectively
[0059]
[0060]
[0061]
[0062] Where c1 x And c1 y Respectively represent the abscissa and ordinate of the position of the node C carrying the message at the previous moment, c x And c y Respectively represent the abscissa and ordinate of the current position of the node C carrying th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com