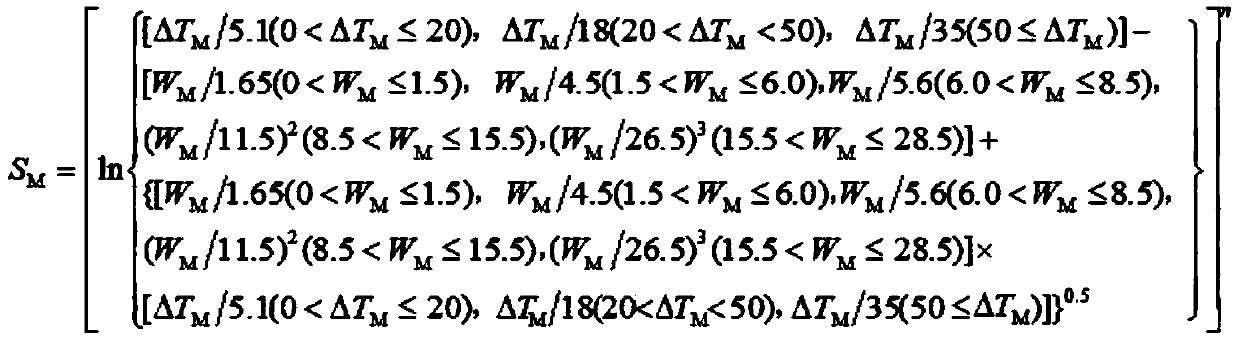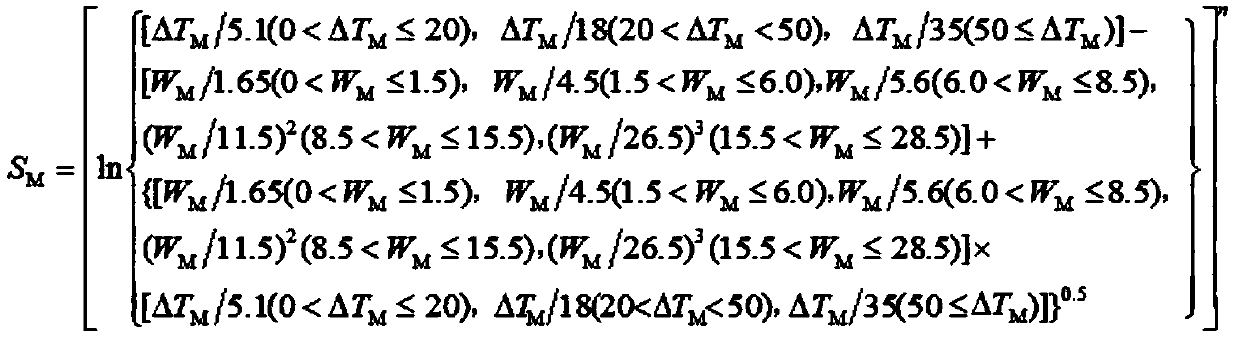A method to predict the wettability of brazing filler metals controlled by low melting point elements
A technology with low melting point and wettability, applied in chemical property prediction, analytical materials, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, low test efficiency, low efficiency, etc., achieve high numerical calculation accuracy and reduce test workload , the effect of reducing the test cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] Example 1: A method for predicting the wettability of Sn-regulated silver solder (AgCuZnSn, Sn content not exceeding 6.5%) on the surface of 304 stainless steel, which includes the following steps:
[0026] Step 1: Use XRF-1800 X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF) to determine the content of Sn in the solder W M % (Mass score);
[0027] Step 2: Use STA449F3 thermal analyzer (DSC) to determine the melting temperature range of solder ΔT M ;
[0028] Step 3: Change the content of the low melting point element W in Step 1 M % Expand 100 times and the melting temperature interval data of step 2 ΔT M Substitute into predictive mathematical model S M .
[0029]
[0030] Since it contains a low melting point element, n=1.
[0031] Step 4: According to Step 3 S M The size of the value determines the law of the influence of Sn element on the wettability of the solder. The smaller the value, the better the wettability of the solder, and vice versa.
[0032] In order to verify the accuracy o...
Embodiment 2
[0035] Example 2: A method for predicting the wettability of In element-regulated silver solder (AgCuZnIn, with an In content of not more than 5.5%) on the surface of 316 stainless steel. The steps are the same as in Example 1.
[0036] The specific data is shown in Table 2 below:
[0037]
[0038] According to Table 2, as the In content increases, the S of AgCuZnIn solder on the surface of 316 stainless steel M The value gradually decreases, indicating that its wettability is getting better and better; the test results show that as the In content increases, the wetting area of the solder gradually increases. The test results are consistent with the predicted results of the present invention.
Embodiment 3
[0039] Embodiment 3: A method for predicting the wettability of a silver solder (AgCuZnGa, Ga content not exceeding 6.5%) on the surface of H62 brass with Ga element regulation, and the steps are the same as in Embodiment 1.
[0040] The specific prediction data and test results are shown in Table 3 below:
[0041]
[0042]
[0043] According to Table 3, with the increase of Ga content, the S of AgCuZnGa solder on the surface of H62 brass M The value gradually decreases, indicating that its wettability is getting better and better; the test results show that as the Ga content increases, the wetting area of the solder gradually increases. The test results are consistent with the predicted results of the present invention.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap