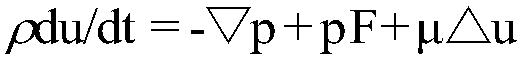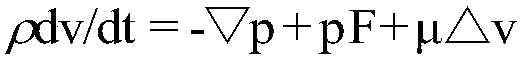Deposition numerical-value simulation method of fine-grain sediments
A numerical simulation and sediment technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of many human factors and the inability to judge the distribution characteristics and deviations of fine-grained sediment deposits in detail
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
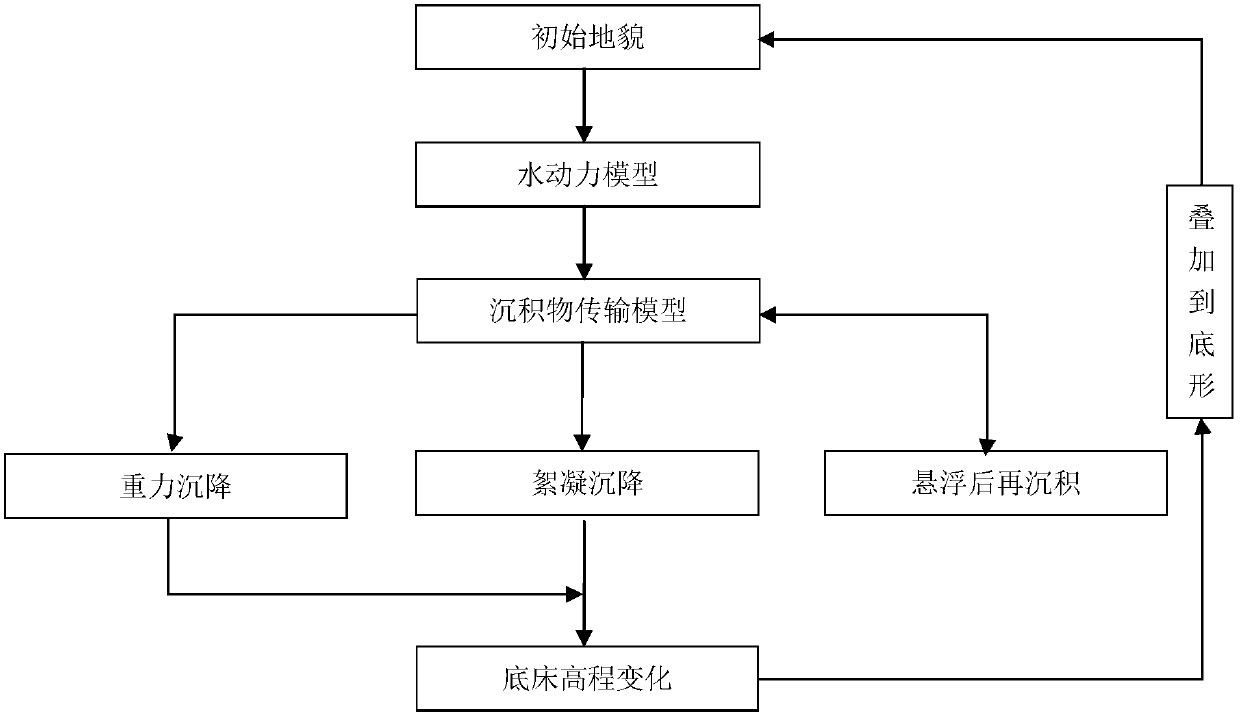
[0071] Such as figure 1 Shown: a numerical simulation method for deposition of fine-grained sediments, including the following steps:
[0072] 1) According to the data of the study area, grid the study area to construct a hydrodynamic model;
[0073] 2) Starting from the depositional dynamics characteristics of sedimentary fine-grained sedimentary rocks, carry out sedimentological investigation and research, and conduct dynamic simulations of different depositional environments to determine the geological structure characteristics of sedimentary fine-grained sedimentary rocks in the study area and the physical mechanism of fine-grained sedimentary rock formation. Conditions; its specific methods:
[0074] a. According to the parallel finite element algorithm of the Navier-Stocks equation to simulate the salinity distribution and ion component distribution in the study area, compare and analyze the salinity and ion component distribution data with the geological data, adjust t...
Embodiment 2
[0112] A method for numerical simulation of deposition of fine-grained sediments, the method of the present embodiment is basically the same as that of Example 1, except for step 3) and step 5), as follows:
[0113] 3) On the basis of step 2), according to the geological structure characteristics of sedimentary fine-grained sedimentary rocks and the physical conditions for the formation of fine-grained sedimentary rocks, the depositional methods of fine-grained sediments are divided into gravity mode deposition and flocculation mode deposition; according to the following differences Deposition mode, calculate the sedimentation rate v of fine-grained sediments in different deposition modes;
[0114] When the fine-grained sediment is deposited by gravity, for the sedimentary rock formed in the process of gravity settlement, on the basis of the dynamic simulation of the depositional environment in step 2), according to the gravity formula, calculate the sedimentation rate of the f...
Embodiment 3
[0144] A deposition numerical simulation method of fine-grained sediments, the method of the present embodiment is basically the same as that of embodiment 3, the difference being step 3), specifically as follows:
[0145] 3) On the basis of step 2), according to the geological structure characteristics of deposited fine-grained sedimentary rocks and the physical conditions for the formation of fine-grained sedimentary rocks, the deposition methods of fine-grained sediments are divided into three categories, namely, gravity deposition and flocculation deposition Suspended with fine-grained sediments and then deposited; according to different deposition methods, calculate the sedimentation rate v of fine-grained sediments in different deposition methods;
[0146] When the fine-grained sediment is deposited by gravity, for the sedimentary rock formed in the process of gravity settlement, on the basis of the dynamic simulation of the depositional environment in step 2), according ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com