A reflective star sensor
A star sensor, reflective technology, applied in celestial navigation and other directions, can solve the problems of chromatic aberration of magnification, increase of star point image spot size, limitation of stray light elimination ability, reduction of star sensor sensitivity, etc., to eliminate uncertainty Error, spectral type range expansion, overcoming the effect of low tolerance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
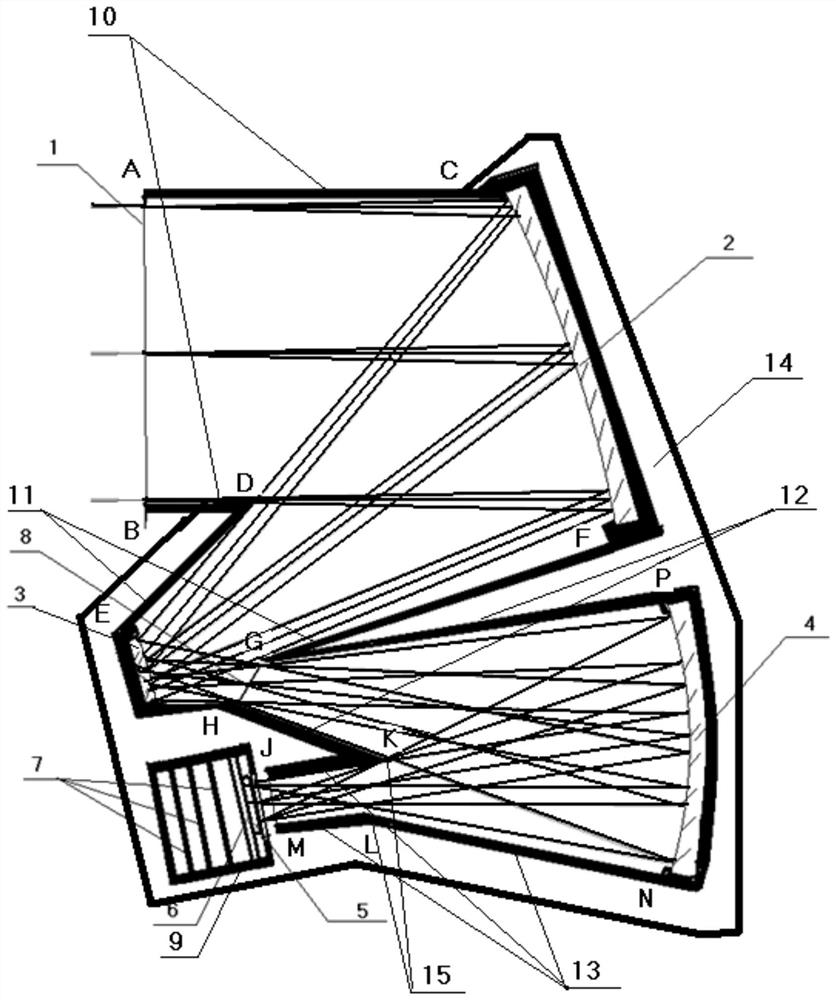
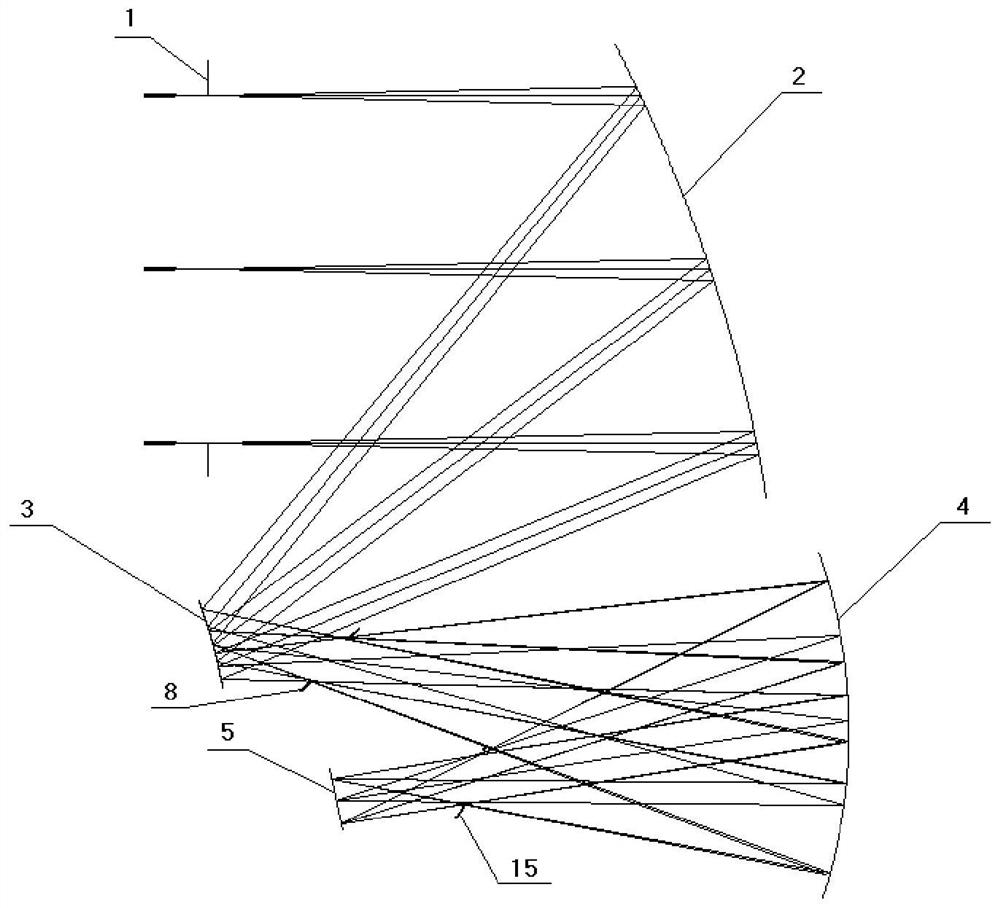
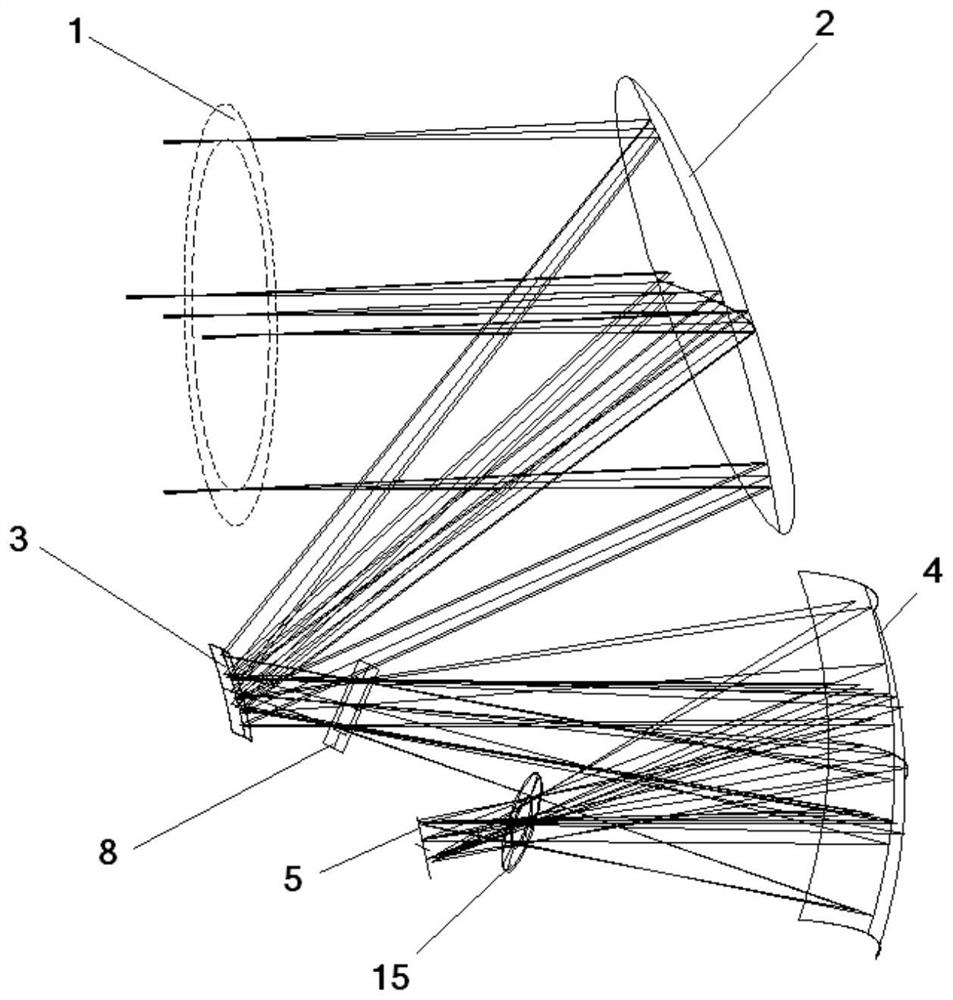
[0041] The scheme of reflective star sensor: consists of aperture diaphragm 1, main mirror 2, secondary mirror 3, third mirror 4, photodetector 5, detector circuit 6, information processor circuit 7, intermediate image diaphragm 8. The information processor 9, the first section of the light shield 10, the second section of the light shield 11, the third section of the light shield 12, the fourth section of the light shield 13, the supporting structure 14, and the Leo diaphragm 15.
[0042] The stellar target light first passes through figure 1 The aperture stop 1 of the lens passes through the first section of the hood 10, enters the main reflector 2, and then passes through the second section of hood 11, reaches the secondary reflector 3, and then passes through the intermediate image stop 8 and the third section of hood in turn 12. Reach the third reflector 4, then pass through the third section of the light shield 12 to the third reflector 4, and then go through the Leo diaphra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com