Method and device for rapid identification of small fault of coal seam
A technology of small faults and coal seams, applied in the field of geological exploration, can solve the problems of inability to observe, understand, analyze, leak small faults and small structures, and small structures are easy to leak, so as to improve the speed and accuracy of interpretation, improve the precision of identification, Enhance the effect of discontinuity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
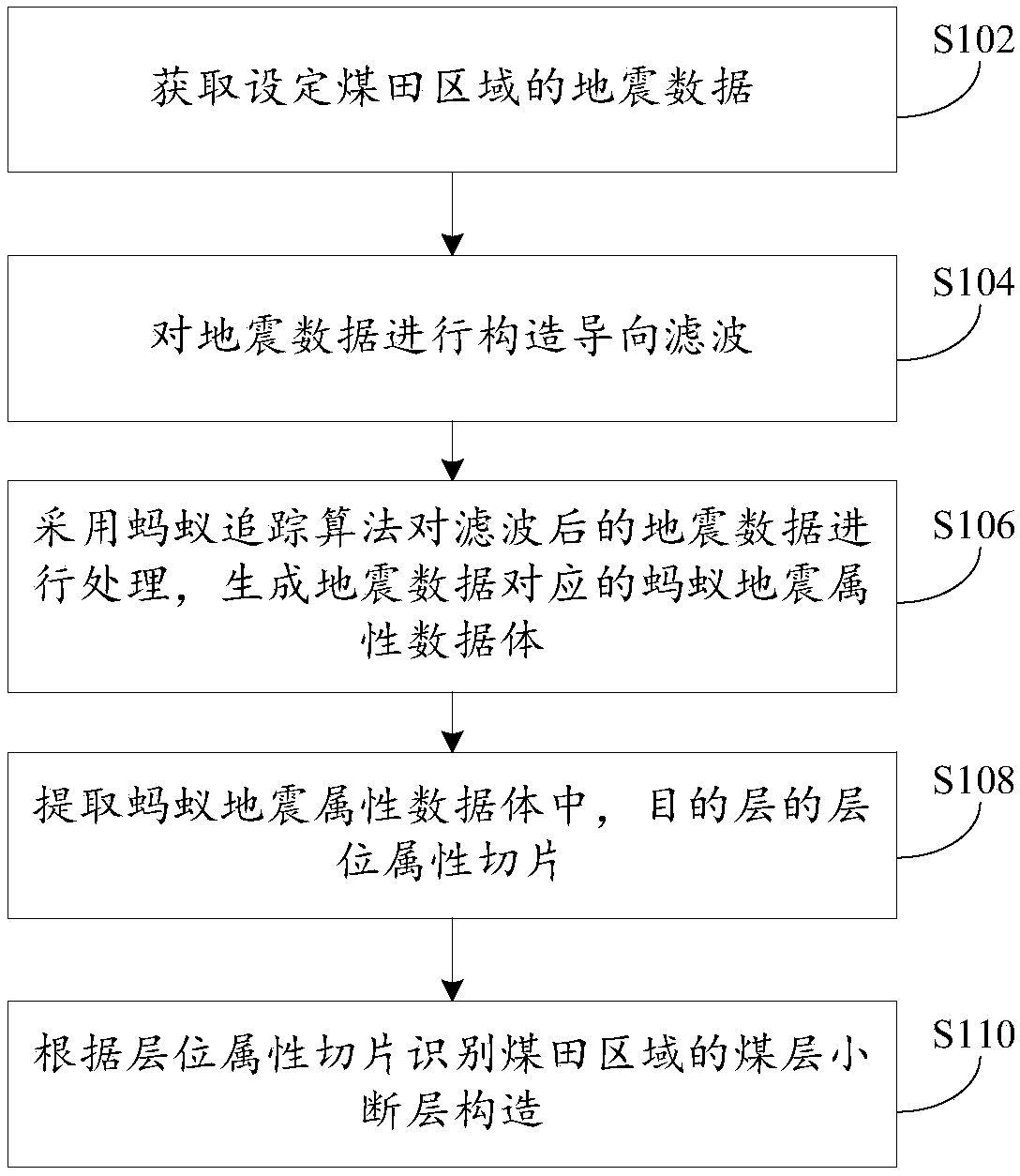
[0029] see figure 1 The flow chart of the rapid identification method of the first shown small coal seam fault; The method comprises the following steps:
[0030] Step S102, acquiring the seismic data of the set coalfield area;
[0031] Specifically, the seismic data may be 3D seismic data, 3D data volume, 3D seismic volume or 3D seismic data, etc.; the above seismic data may belong to the same geological unit, or may belong to different geological units; in order to facilitate processing and improve identification accuracy, When the seismic data above belong to different geological units, the seismic data may be divided into geological units in advance, and the different geological units are processed separately.
[0032] Step S104, performing structure-guided filtering on the seismic data;
[0033]Generally, small fault information is displayed on the event axis of coal seam reflection waves, and the above-mentioned wire filtering method will not perform smoothing processi...
Embodiment 2
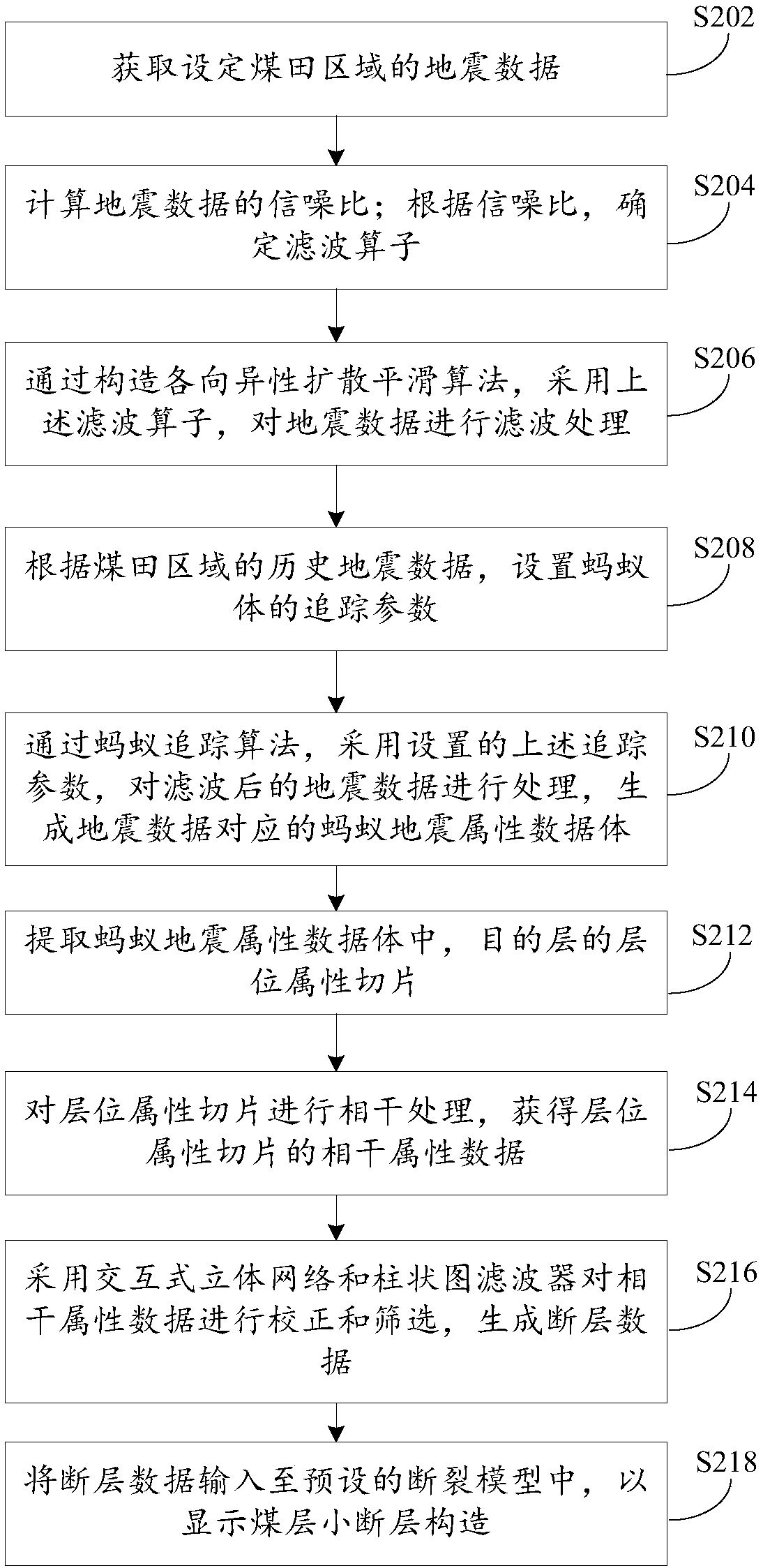
[0041] see figure 2 The flow chart of the rapid identification method of the second small coal seam fault shown; the method is realized on the basis of the rapid identification method of the small coal seam fault provided in embodiment one; the method comprises the following steps:
[0042] Step S202, acquiring the seismic data of the set coalfield area;
[0043] Step S204, calculating the signal-to-noise ratio of the seismic data; determining the filter operator according to the signal-to-noise ratio;
[0044] Generally, the larger the filter operator, the rougher the filter, and the less obvious the filtering effect; and the smaller the filter operator, the more noise can be filtered out, but it is possible to filter out weak effective signals (for example, smaller faults). Therefore, in actual implementation, appropriate filter operators can be determined according to the signal-to-noise ratio of different geological units in seismic data, so as to effectively filter out ...
Embodiment 3
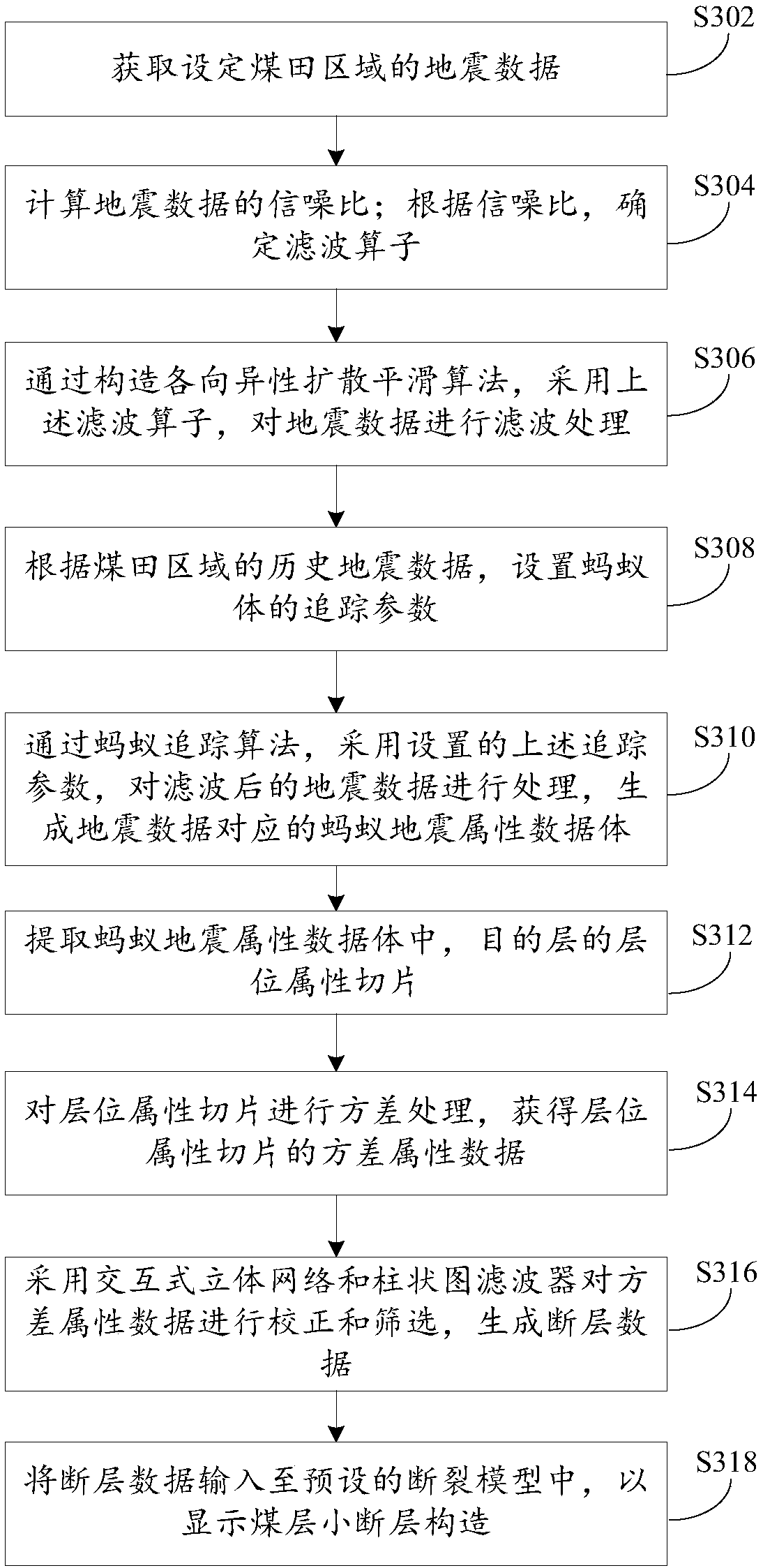
[0086] see image 3 The flowchart of the quick identification method of the third kind of coal seam small fault shown; This method realizes on the basis of the quick identification method of coal seam small fault that provides in embodiment one or embodiment two; The method comprises the following steps:
[0087] Step S302, acquiring the seismic data of the set coal field area;
[0088] Step S304, calculating the signal-to-noise ratio of the seismic data; determining the filter operator according to the signal-to-noise ratio;
[0089] Step S306, filter the seismic data by constructing an anisotropic diffusion smoothing algorithm and using the above filter operator;
[0090] Step S308, according to the historical seismic data of the coalfield area, set the tracking parameters of the ant body; wherein, the tracking parameters include the seed point, the angle of the foraging path, the search step size, the illegal range, the legal range, the search termination threshold and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com