Mixed compensating type subaperture spliced surface shape detection method
A technology of surface shape detection and aperture splicing, which is applied to measuring devices, instruments, and optical devices, etc., can solve the problems of increased operation time cost of detection operation data, high manufacturing cost of lens compensator, and rising economic cost, so as to reduce splicing. The effect of error transmission and accumulation, time cost reduction, and economic cost reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] The present invention will be described in detail below with reference to the accompanying drawings and examples.
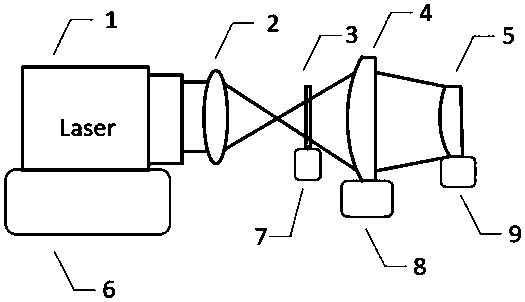
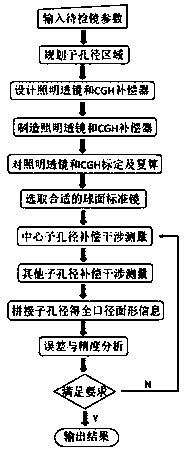
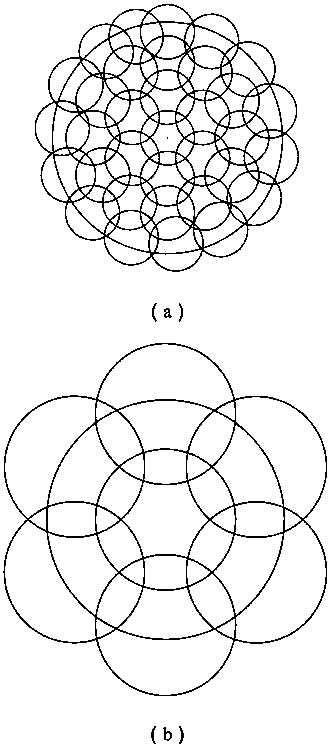
[0030] The present invention proposes a method for detecting the surface shape of a super-large-diameter convex aspheric surface (above 500 mm in diameter) mirror, and realizes surface shape detection based on sub-aperture splicing and compensation detection, and the compensation detection method of the present invention combines CGH compensation and lens compensation A hybrid compensation method formed in combination can expand the area of a single sub-aperture measurement under the condition of using a smaller CGH compensator 3, thereby effectively reducing the number of required sub-apertures, reducing the transmission of errors and reducing all The number of compensators required. The benefits brought by the reduction in the number of sub-apertures are: a. reducing the time cost required for optical element adjustment and subsequent splicing calculat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com