Liquid crystal display device
A liquid crystal display device and liquid crystal layer technology, applied in static indicators, nonlinear optics, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as panel flicker, cost increase, and system output capacity doubled
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 example
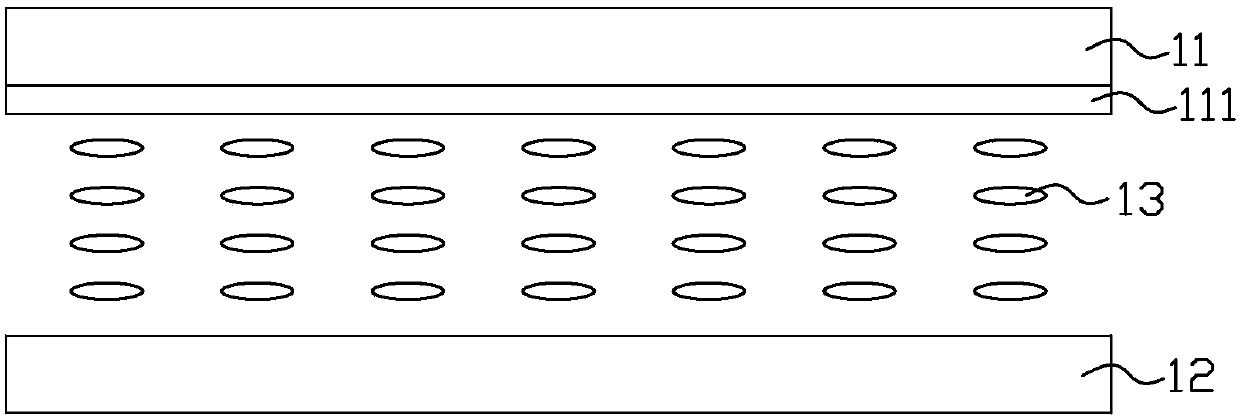
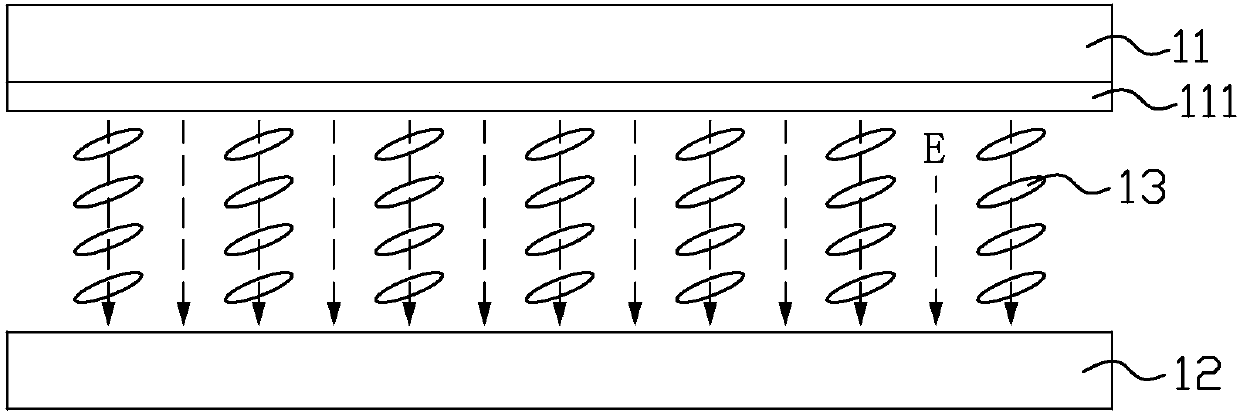
[0034] image 3 It is a schematic diagram of part of the circuit structure of the liquid crystal display device in the first embodiment of the present invention, Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of the plane structure of the viewing angle control electrodes and the black matrix on the color filter substrate of the liquid crystal display device in the first embodiment of the present invention, Figure 5 for image 3 Schematic cross-section along the A-A line in , please refer to image 3 As shown in FIG. 4 , the liquid crystal display device includes a color filter substrate 21 , an array substrate 22 disposed opposite to the color filter substrate 21 , and a liquid crystal layer 23 located between the color filter substrate 21 and the array substrate 22 .
[0035] The liquid crystal display device provided in this embodiment is suitable for liquid crystal display devices of In-Plane Switching (IPS), Fringe Field Switching (FFS) and other modes, and the common electrode and...
no. 2 example
[0063] Figure 9 The waveform diagrams of the first AC control voltage applied to the first electrode portion and the second AC control voltage applied to the second electrode portion in the second embodiment of the present invention, please refer to Figure 9 , the voltage output to the common electrode 225 is the DC common voltage 30 (ie DCVcom) when the liquid crystal display device is displayed (whether under a wide viewing angle or a narrow viewing angle). The difference between this embodiment and the first embodiment is that, when an AC voltage is applied to the viewing angle control electrode 210 , a periodic first AC control voltage 31 is respectively applied to the first electrode portion 211 and the second electrode portion 212 , respectively. (ie com1) and the second AC control voltage 32 (ie com2), and the potential difference between the first AC control voltage 31 and the second AC control voltage 32 and the DC common voltage 30 is equal.
[0064] Specifically ...
no. 3 example
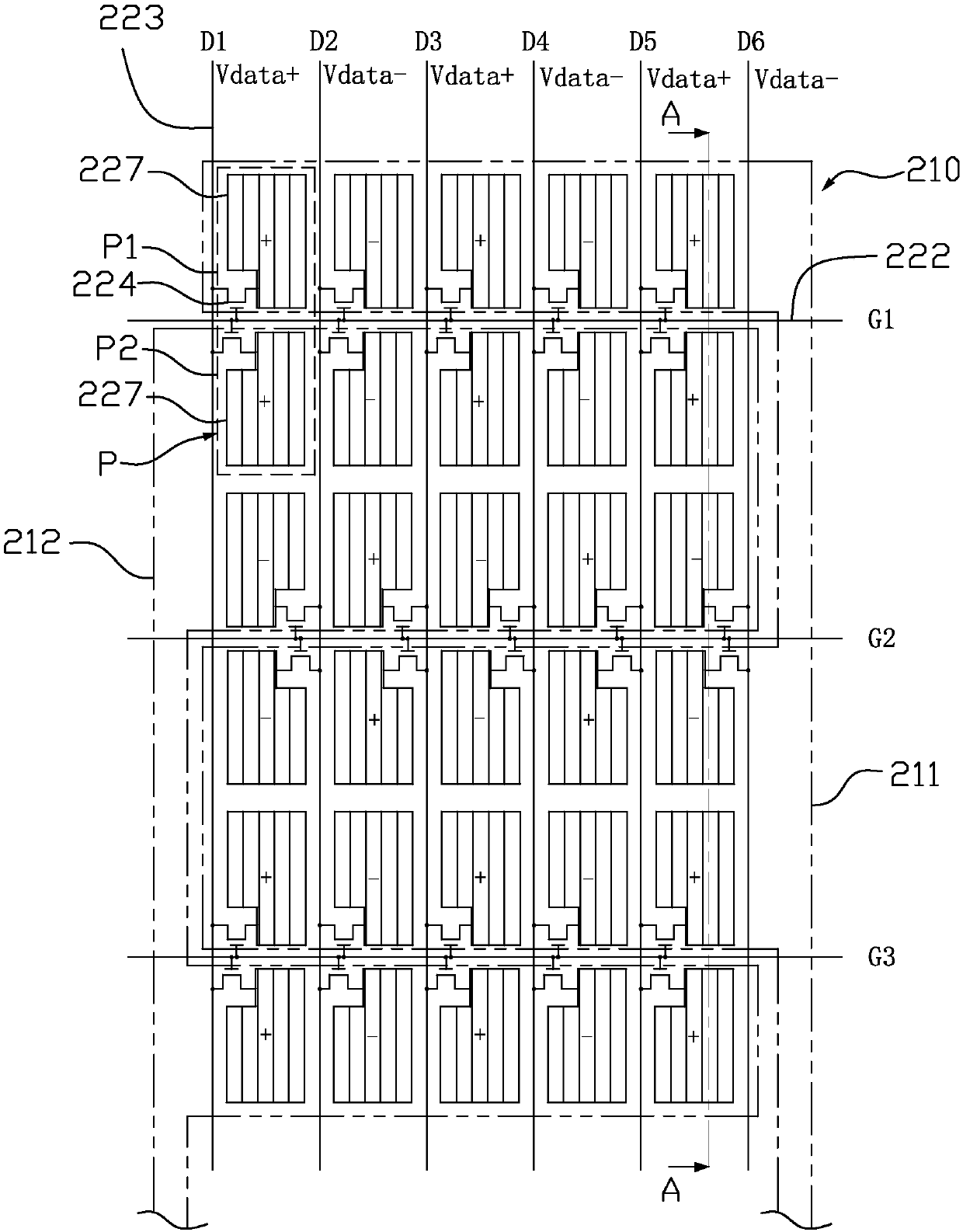
[0070] Figure 10 It is a schematic diagram of the partial circuit structure of the liquid crystal display device in the third embodiment of the present invention, please refer to Figure 10 The difference between this embodiment and the above-mentioned first embodiment is that, in this embodiment, a pixel electrode 227 is arranged in each pixel unit P, and the pixel electrode 227 is arranged in the first sub-pixel P1 and the second sub-pixel P1 at the same time. The pixel P2 is electrically connected to the scan line 222 and the data line 223 in the pixel unit P through a thin film transistor 224 . For the rest of the content of this embodiment, reference may be made to the description of the first embodiment above, and details are not repeated here.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com