A Subthreshold SRAM Memory Cell Circuit Solving the Half-selection Problem
A storage unit circuit and sub-threshold technology, which is applied in information storage, static memory, digital memory information, etc., can solve the problem of affecting the potential of storage points, the limited improvement of 6T unit read and write capabilities, and the reduced stability of read half-select and write half-select And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
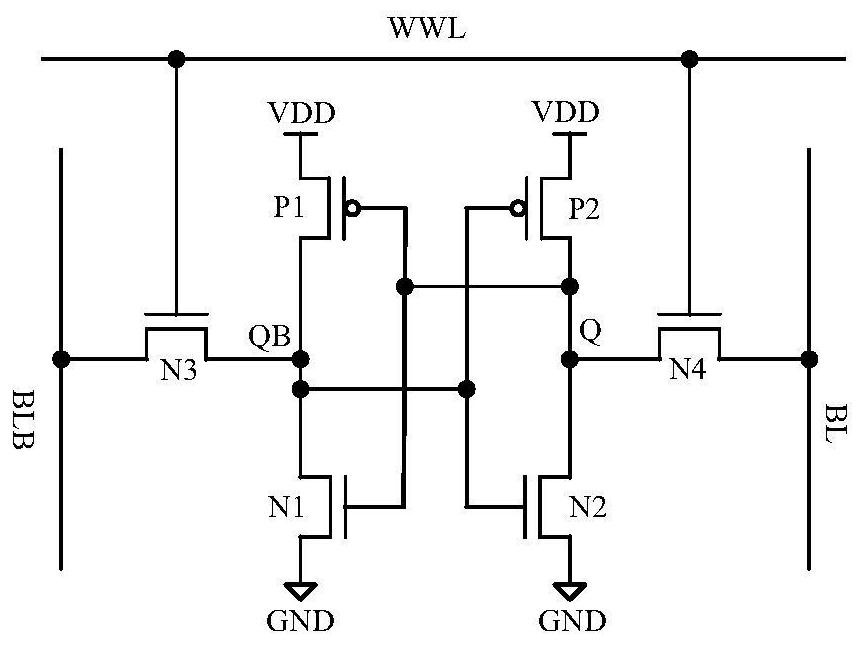
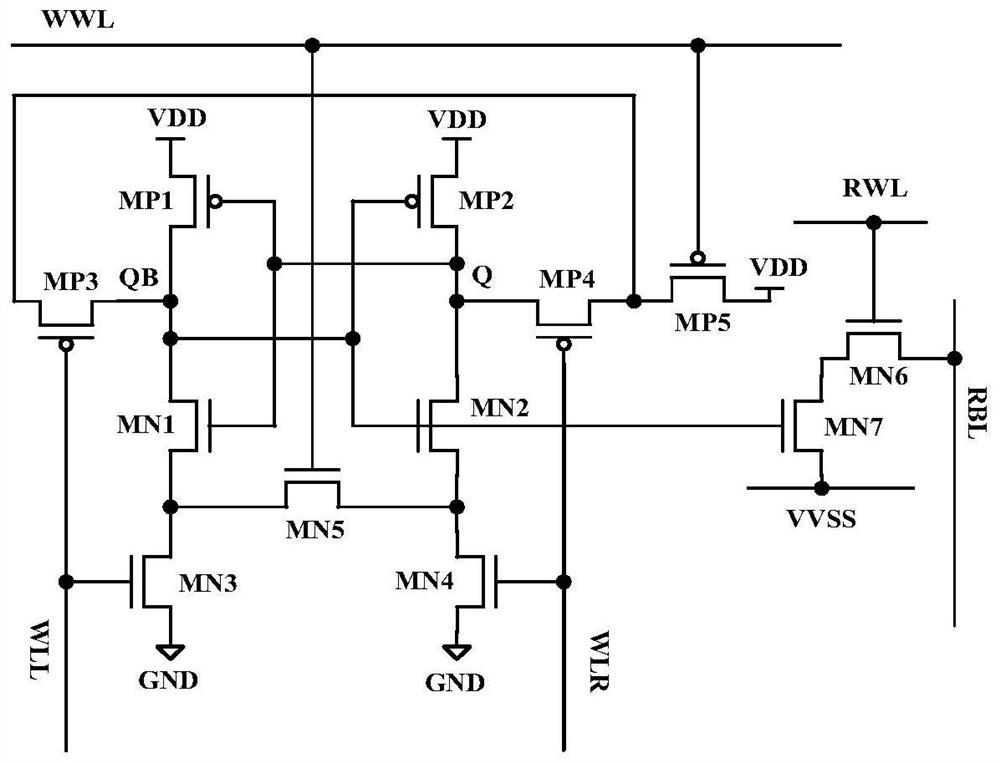
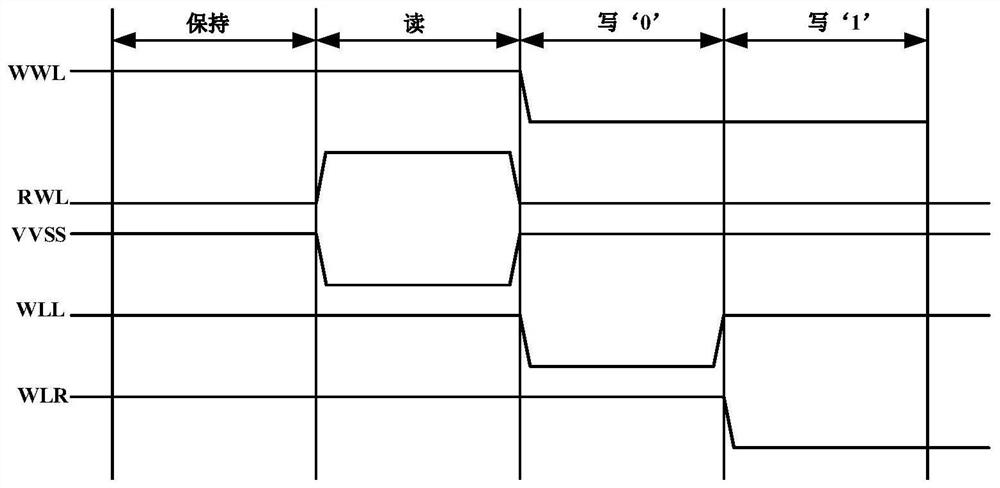
[0021] Such as figure 2 Shown is a schematic structural diagram of a sub-threshold SRAM memory cell circuit that solves the half-selection problem provided by the present invention, wherein the drain of the second PMOS transistor MP2 is the first storage point Q, and the drain of the first PMOS transistor MP1 is the second storage point QB; the first PMOS transistor MP1 and the first NMOS transistor MN1 constitute the first inverter, and the second PMSO transistor MP2 and the second NMOS transistor MN2 constitute the second inverter for storing opposite data, that is, storage points Q and To store the data of point QB, two inverters form a feedback structure, so that the data is stably latched. The first signal control line WLL, the second signal control line WLR and the third signal control line VVSS are used to control the circuit of the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com