Smart shopping cart and using method thereof
A smart shopping cart and shopping cart technology, applied in the direction of vehicle position/route/height control, non-electric variable control, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increasing labor costs and shopping time, and achieve the goal of improving shopping efficiency and saving labor costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] Embodiment 1, return a single shopping cart:
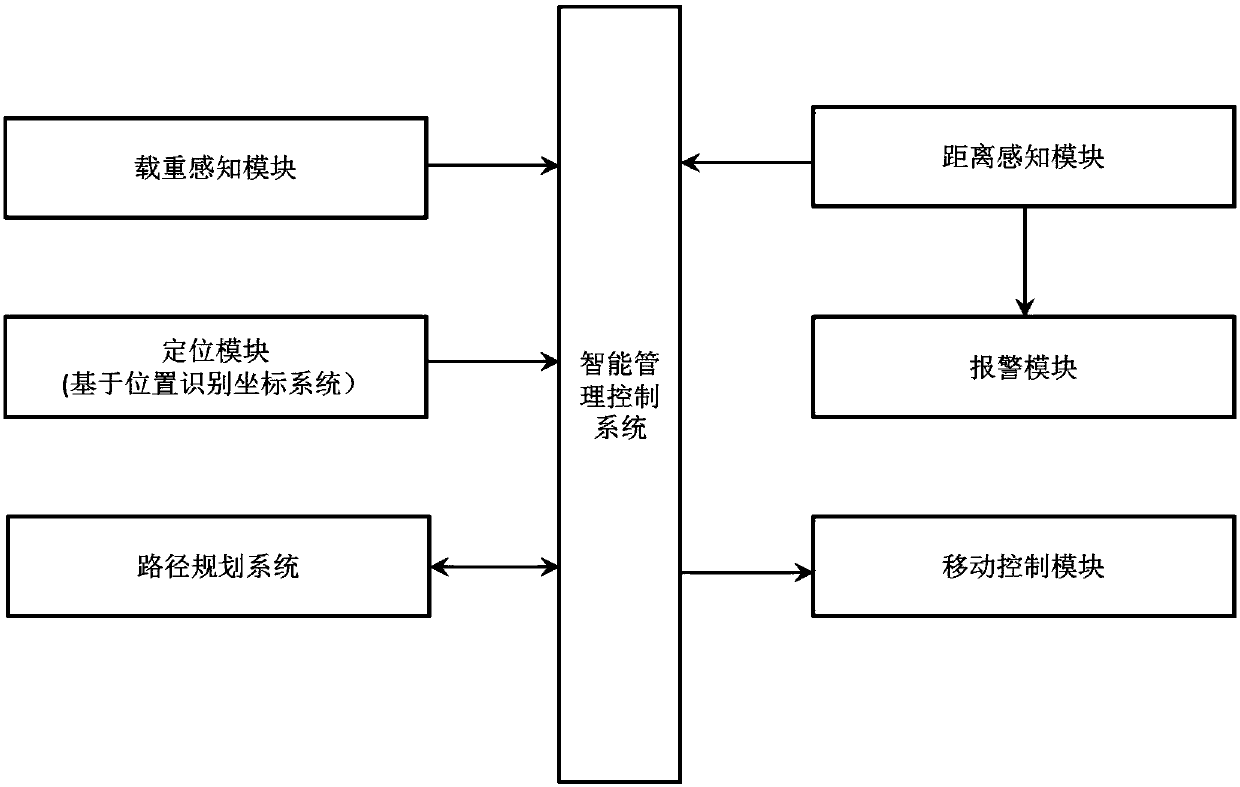
[0046] In this embodiment, the shopping place uses recognizable two-dimensional code images placed at intervals on the ground as location identification marks. The load module of the shopping cart contains pressure sensors, which can sense whether there are items placed on the shopping cart. An image sensor is installed directly under the shopping cart to recognize position identification marks on the floor of the shopping place. The positioning module can obtain the definite position information of the shopping cart through identification of the mark and GPS positioning. The distance perception module is installed around the shopping cart. There are image sensors and radar sensors in the module to detect surrounding obstacles, and then the obstacle information is identified through the recognition algorithm in the module: the dynamic and static state of the obstacle, category: human Or items. The mobile control module c...
Embodiment 2
[0054] Embodiment 2, returning multiple shopping carts:
[0055] In this example, there are two shopping carts A and B in the return state at the same time. In order to avoid collisions of shopping carts, the intelligent management control system coordinates the path planning system to plan their own return routes for each shopping cart. The return routes of shopping carts A and B do not overlap, but there is an overlapping point P.
[0056] Therefore, the path planning system plans that car A passes through the coincidence point P at time t1, and car B passes through the coincidence point P at time t2. The moving speed of both cars is v, and the time difference between the two cars passing through point P is:
[0057] |t1-t2|>m*n;
[0058] m is the safety multiple, n is the safety time, and is the safety distance / v.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com