Walking type mower
A lawn mower, walking technology, applied in the direction of harvesters, cutters, agricultural machinery and implements, etc., can solve the problems of hindering the lawn mower to advance by hand, slow cutting speed of nylon rope, and scattering of small stones and other debris.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
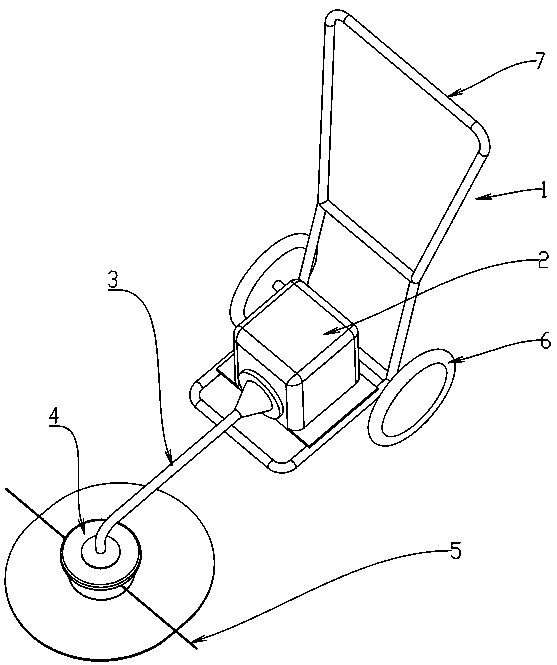
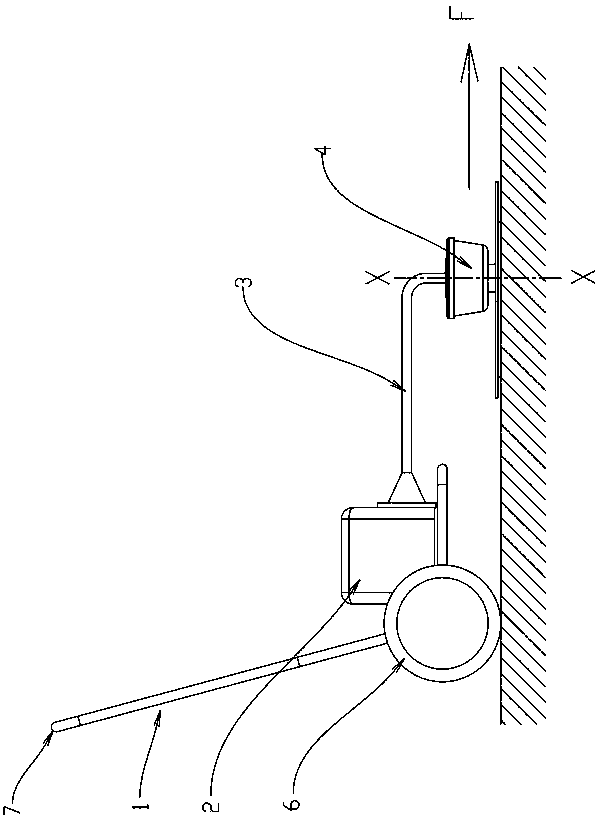
[0024] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 3 As shown, there is a lawn mower with a structure that transmits the rotational power generated by the engine and the motor to the rotary cutter equipped on the front end of the operating rod. The lawn mower is mounted on a frame with wheels and handles, and the operator walks and pushes Use the handle to move the mower along the ground for the desired mowing. One end of the frame 1 is provided with a power source 2 such as an engine or a motor, and the drive member inserted in the drive tube 3 rotates to transmit power to the front end of the drive tube 3 . The frame 1 is grouped with wheels 6, 7 that can freely rotate relative to the frame, and is a handle portion that constitutes a part of the frame.
[0025] On the front end of the drive pipe 3, the rotational power of the engine is transmitted to the nylon rope holding member 4, and the nylon rope holding member 4 rotates around the rotation axis X-X. The nylon string cutting blade 5 ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] In order to reduce the resistance between the weeds and the grounding member when the mower advances and mows, and prevent the weeds from lodging, the outer edge of the grounding member 14 is provided with a ring-shaped flange 17, Figure 5 In the above embodiment, the flange 17 is arranged as a raised ring structure on the top surface opposite to the ground surface of the guide member.
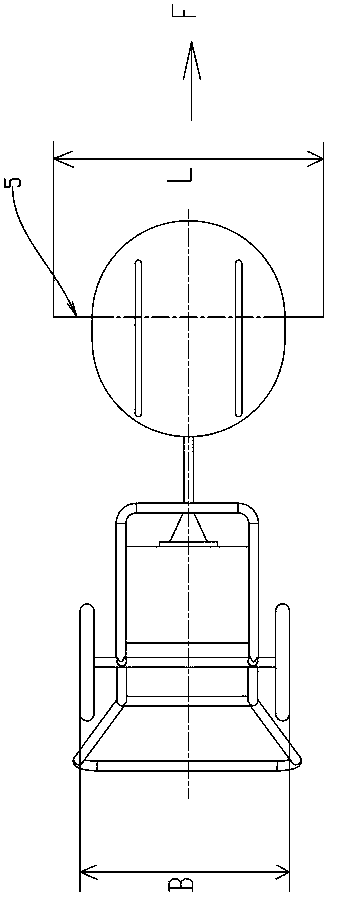
[0029] Such as image 3 As shown, the rotation diameter L of the front end portion of the nylon cord cutting tool 5 is larger than the axial width B of the wheel. Therefore, there will be no residue left over from cutting while mowing forward.
Embodiment 3
[0031] In this embodiment, the shape of the outer edge of the ground member 14 is not limited to a standard circle centered on the rotation axis X-X. For example in Figure 4 In the embodiment, with respect to the plane P-P including the rotation axis X-X, the area of one side of the ground member is larger than the area of the other side. A plurality of crowbars 16 are arranged symmetrically with respect to the plane P-P on the grounding surface of the grounding member, and the length of the crowbar is longer on the side of the larger area of the grounding member than on the side of the smaller area relative to the plane P-P. By the setting of the sled bar 16, when the lawn mower advances, the contact area between the ground plate and the ground is small, and the forward resistance becomes smaller.
[0032] In addition, with respect to the plane P-P, through the grounding parts with different grounding areas and the sled bars 16 with different lengths, when the lawn mo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com