Resistance-variable type non-volatile memory and operating method thereof
A non-volatile memory technology, applied in static memory, read-only memory, information storage, etc., can solve the problem of deterioration of flat panel display aperture ratio, resolution performance index, hindering memory size reduction and storage density improvement, unit size Large and other problems, to achieve the effect of compact structure, low power consumption and fast working speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
[0021] Implementation Mode 1
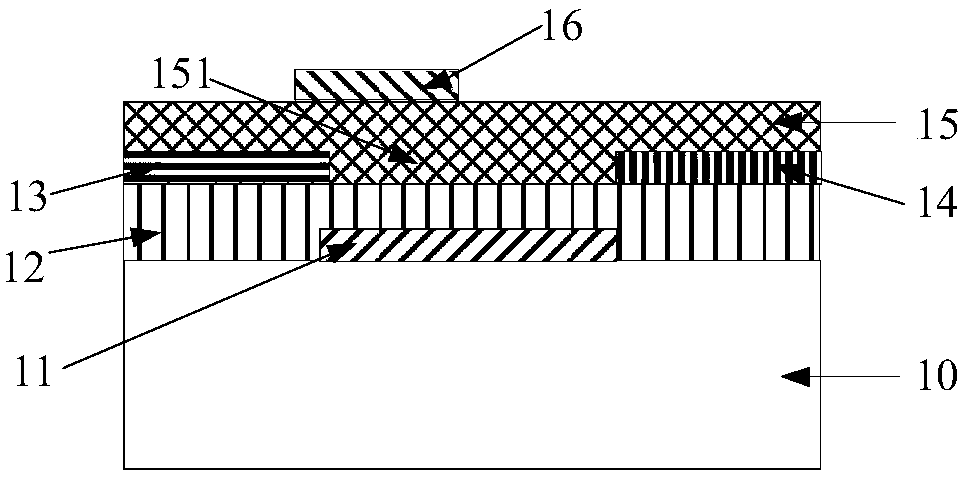
[0022] like figure 1 As shown, a resistive nonvolatile memory is composed of a bottom-gate bottom-contact thin film transistor and a resistive memory. The resistive memory includes a top gate 16, an InGaZnO semiconductor layer 15, a source 13 and a drain 14, and the top gate 16 is arranged on the InGaZnO semiconductor layer 15, the convex part below the InGaZnO semiconductor layer 15 is a channel 151, and the source 13 and the drain 14 are respectively arranged on both sides of the channel 151, and the top gate 16 overlaps with the source 13. The length of the overlapping region is 0.5 μm to 5 μm, the vertical distance between the top gate 16 and the source 13 and the drain 14 is 10 nm to 50 nm, the length of the channel 151 below the InGaZnO semiconductor layer is less than 10 m, and the channel of the InGaZnO semiconductor layer 15 The length of the track 151 is 1-5 times the length of the overlapping region of the top gate 16 and the source 1...
Example Embodiment
[0030] Implementation Mode Two
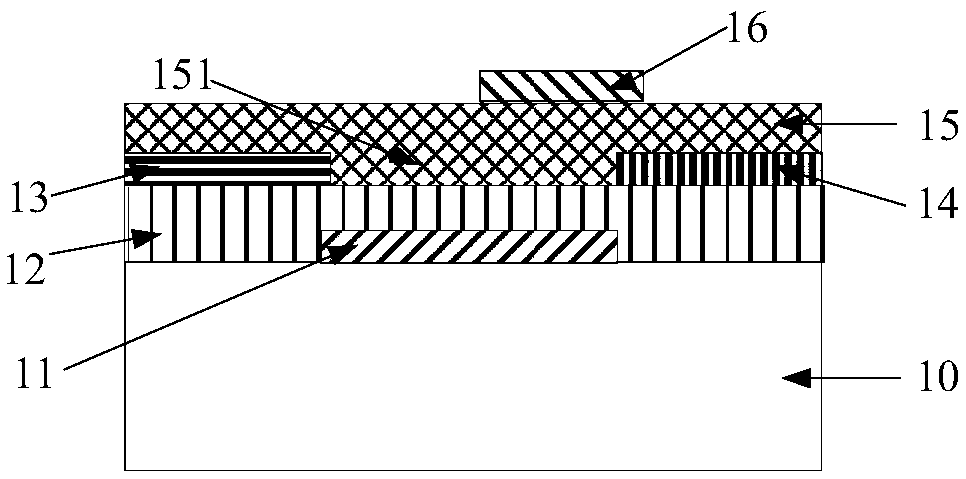
[0031] like figure 2 As shown, a resistive nonvolatile memory is composed of a bottom-gate bottom-contact thin film transistor and a resistive memory. The resistive memory includes a top gate 16, an InGaZnO semiconductor layer 15, a source 13 and a drain 14, and the top gate 16 is arranged on the InGaZnO semiconductor layer 15, the convex part below the InGaZnO semiconductor layer 15 is a channel 151, and the source electrode 13 and the drain electrode 14 are respectively arranged on both sides of the channel 151, and the top gate 16 overlaps with the drain electrode 14. The length of the overlapping region is 0.5 μm to 5 μm, the vertical distance between the top gate 16 and the source 13 and the drain 14 is 10 nm to 50 nm, the length of the channel 151 below the InGaZnO semiconductor layer is less than 10 m, and the channel of the InGaZnO semiconductor layer 15 The length of the track 151 is 1-5 times the length of the overlapping region of ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com