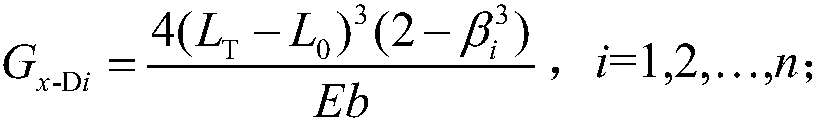Determination method for clamping end point force of end non-iso-structured small-blade variable-section plate springs
A non-isostructural, variable-section technology, applied in the direction of leaf springs, springs/shock absorbers, instruments, etc., can solve the problem that the clamping end point force of the non-equal-structured few-piece variable-section leaf spring at the end has not been given accurately and reliably, and cannot Satisfies the problems of suspension with few pieces of variable cross-section leaf springs, and achieves the effects of reducing design and test costs, improving design level, and speeding up development speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
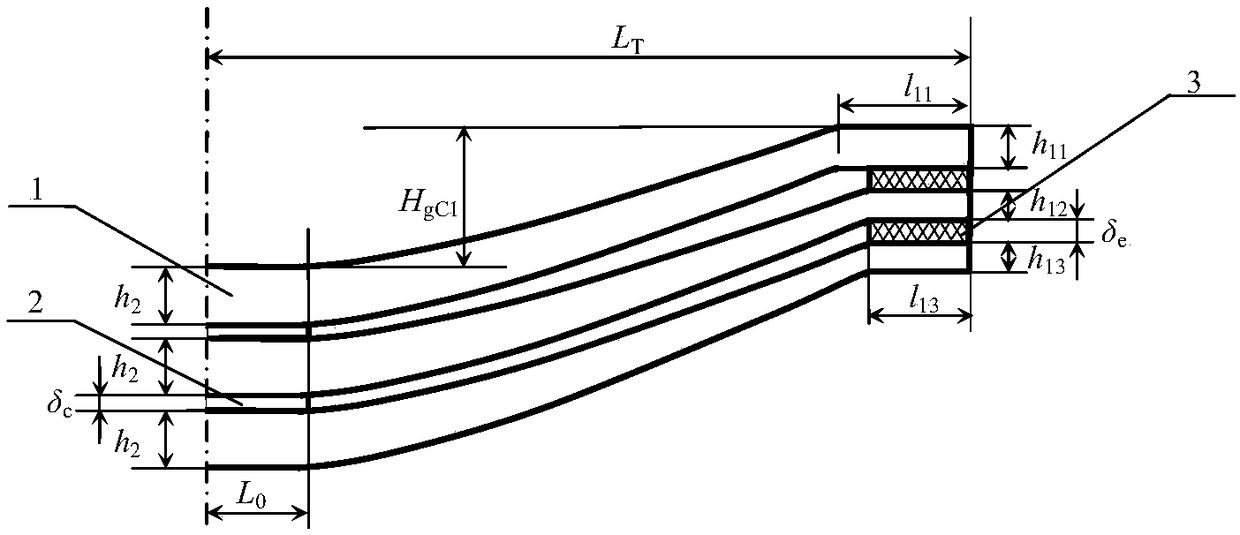
[0031] Example 1: The width of a few-piece parabolic variable section leaf spring with unequal structure at a certain end b=60mm, half of the span L T =570mm, half the length of the straight section of the root L 0 =50mm, elastic modulus E=200GPa. The number of leaf springs n=3, the thickness of the root straight section of each leaf spring is h 2 =18mm, the thickness of the flat end of each leaf spring h 11 = 9mm, h 12 =h 13 =8mm, the thickness ratio of the parabolic segment β 1 =h 11 / h 2 =0.5, β 2 = Β 3 =h 12 / h 2 =h 13 / h 2 = 0.444. Quota load P N =16000N, the allowable stress of the first leaf spring under the rated load [σ 1 ]=400MPa. According to the number of leaf springs, the structural parameters of each leaf spring, the elastic modulus, the rated load and the allowable stress of the first leaf spring under the rated load, for each leaf of the parabolic variable section leaf spring of this configuration The clamping end force of the leaf spring is determined.
[0032] ...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Example 2: The width of a parabolic variable cross-section leaf spring with a few pieces of unequal structure at an end is b=60mm, half the span L T =570mm, half the length of the straight section of the root L 0 =50mm, elastic modulus E=200Gpa. The number of leaf springs n=4, the thickness of the root flat section of each leaf spring is h 2 =16mm; the thickness of the flat end of each leaf spring h 11 = 8mm, h 12 =h 13 =h 14 =7mm, the thickness ratio β of the parabolic segment of each leaf spring 1 =h 11 / h 2 =0.5, β 2 = Β 3 = Β 4 =h 12 / h 2 = 0.4375. Quota load P N =16800N, the allowable stress of the first leaf spring under the rated load [σ 1 ]=400MPa. According to the number of leaf springs, the structural parameters of each leaf spring, the elastic modulus, the rated load and the allowable stress of the first leaf spring under the rated load, for each leaf of the parabolic variable section leaf spring of this configuration The clamping end force of the leaf spring ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com