Magnetic transmission
A speed changer and magnet technology, applied in the field of radial spaced magnetic speed changers, can solve the problems of not being able to change the speed ratio continuously, changing the speed ratio discontinuously, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
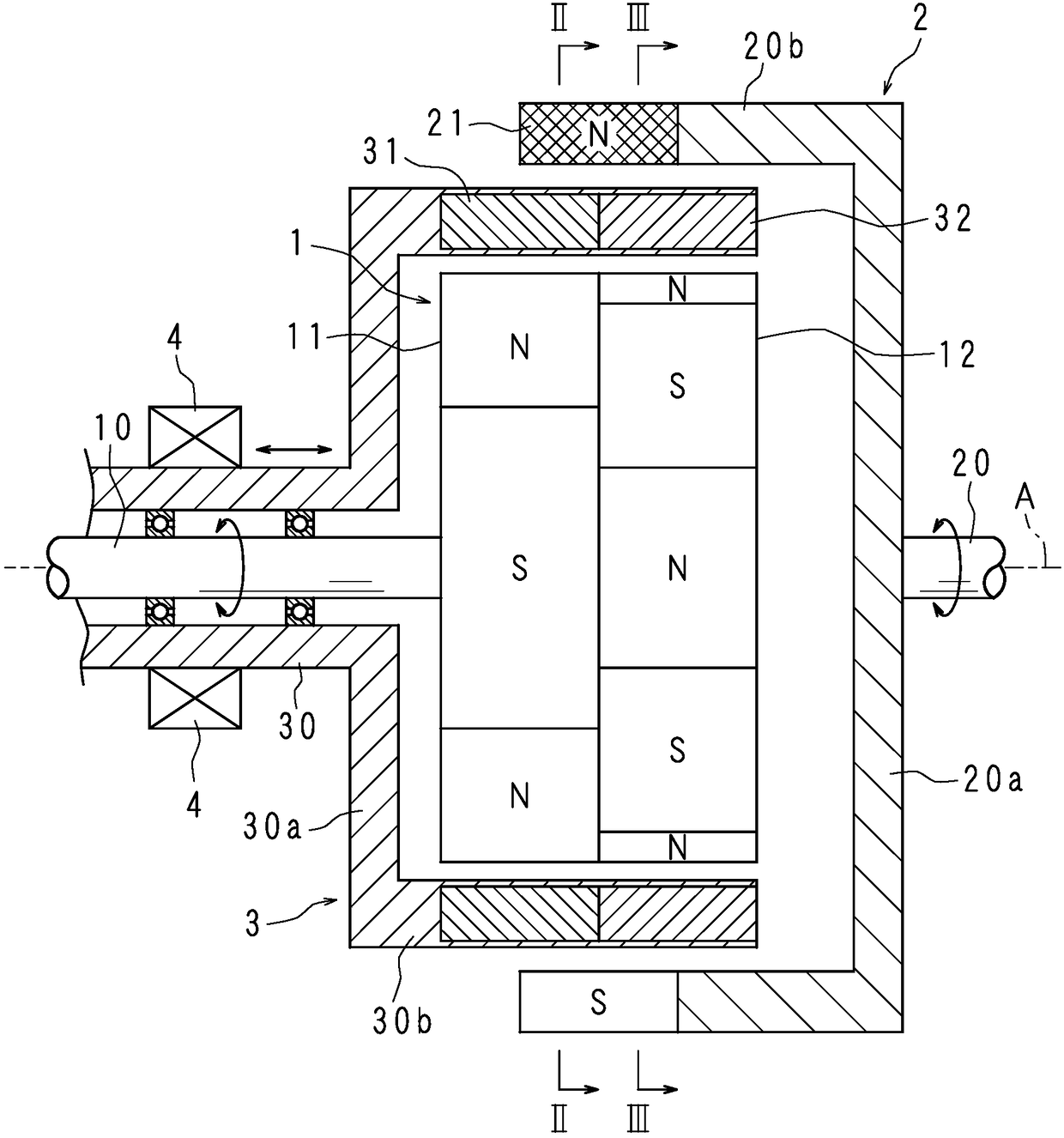
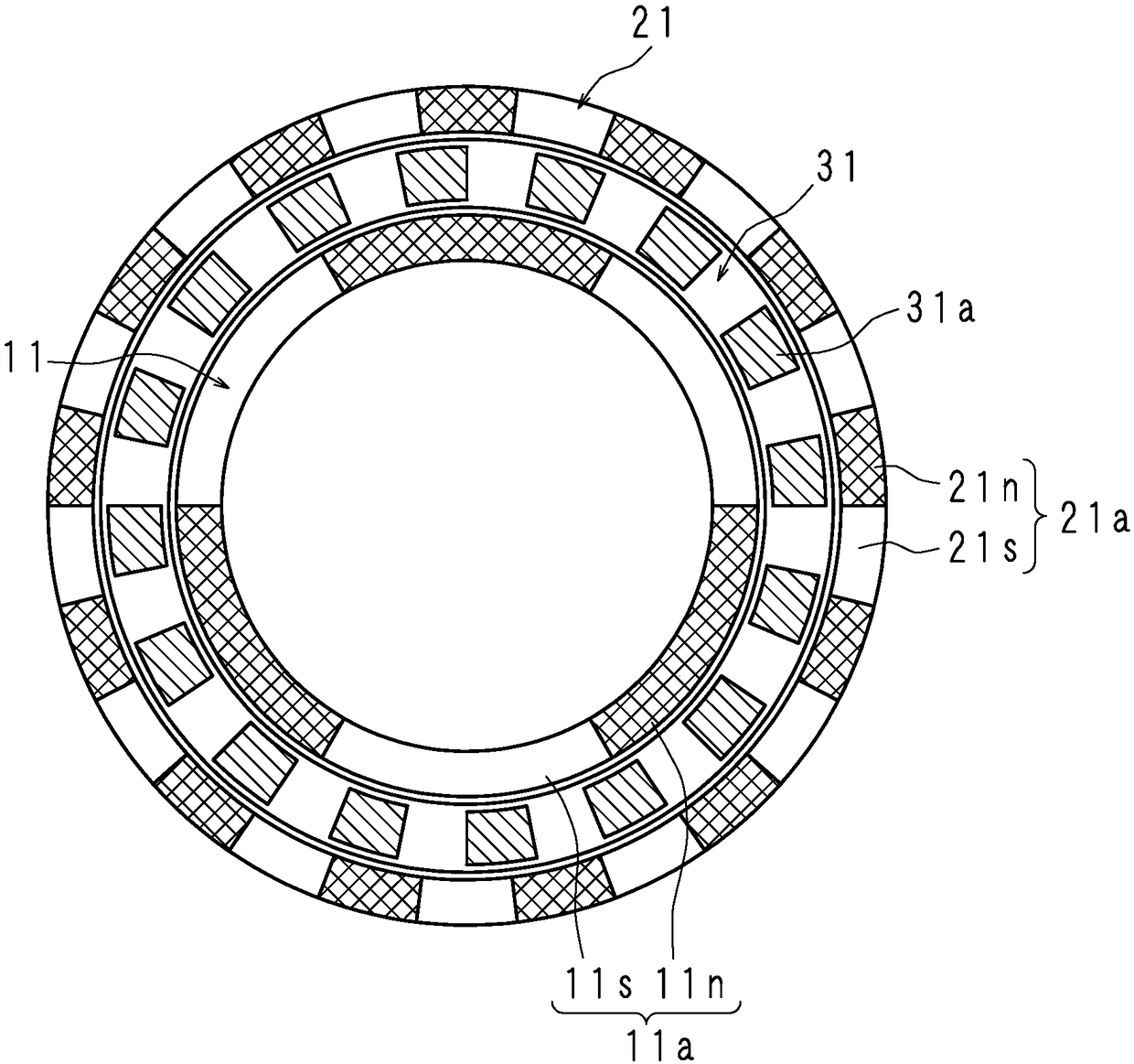
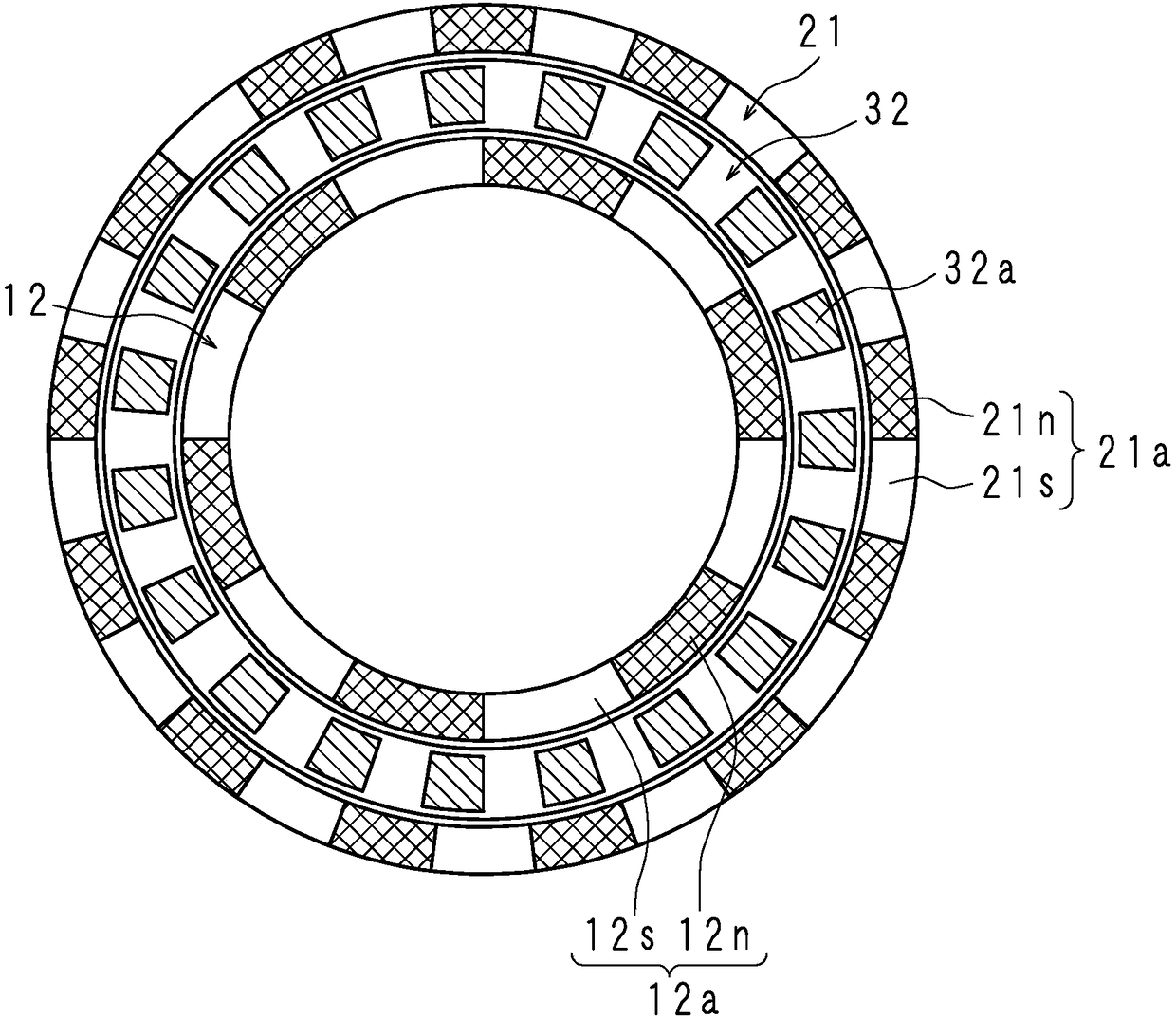
[0033] figure 1 It is a side sectional view showing the structure of the magnetic transmission of Embodiment 1, figure 2 It is the II-II line sectional view of the magnetic speed changer, image 3 It is the III-III line sectional view of the magnetic transmission. The magnetic variator according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention is a radially spaced magnetic gear device for outputting input torque at a variable speed. The magnetic speed change machine includes: a disc-shaped inner rotor (inner magnet row) 1 coaxially arranged, an outer rotor (outer magnet row) 2, and a magnetic field modulation stator (magnetic field adjusting stator) arranged between the inner rotor 1 and the outer rotor 2. body row) 3. The magnetic transmission further includes an input shaft (input member) 10 for inputting torque to the magnetic transmission and an output shaft (output member) 20 for outputting the shifted torque. The input shaft 10 and the output shaft 20 are formed of non-magn...
Embodiment approach 2
[0069] Figure 5 It is a side sectional view showing the structure of the magnetic transmission of Embodiment 2. The magnetic transmission of Embodiment 2 includes the same inner rotor 1, outer rotor 2, and field modulating stator 3 as Embodiment 1, and further includes an input rotation speed detection unit 51 for detecting the rotation speed of the input shaft 10, and a unit for detecting the rotation speed of the output shaft 20. The output rotation speed detection part 52 and the control part 6 which controls the operation|movement of the actuator 4 based on the detected rotation speed are output.
[0070] The input rotational speed detection part 51 includes, for example: a magnetic pickup that sends a signal proportional to the rotational speed of the input shaft 10, a non-contact sensor including a Hall element, and a counting circuit that measures the number of pulses from the non-contact sensor. The detection unit 51 calculates the rotational speed of the input shaft...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com