System and program for cognitive skill training
A skill and training module technology, applied in the field of cognitive skill training systems and programs, can solve problems such as it is difficult for users to repeatedly manage brain activities for a long time, neurofeedback will not be isolated, and training is time-consuming and laborious.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
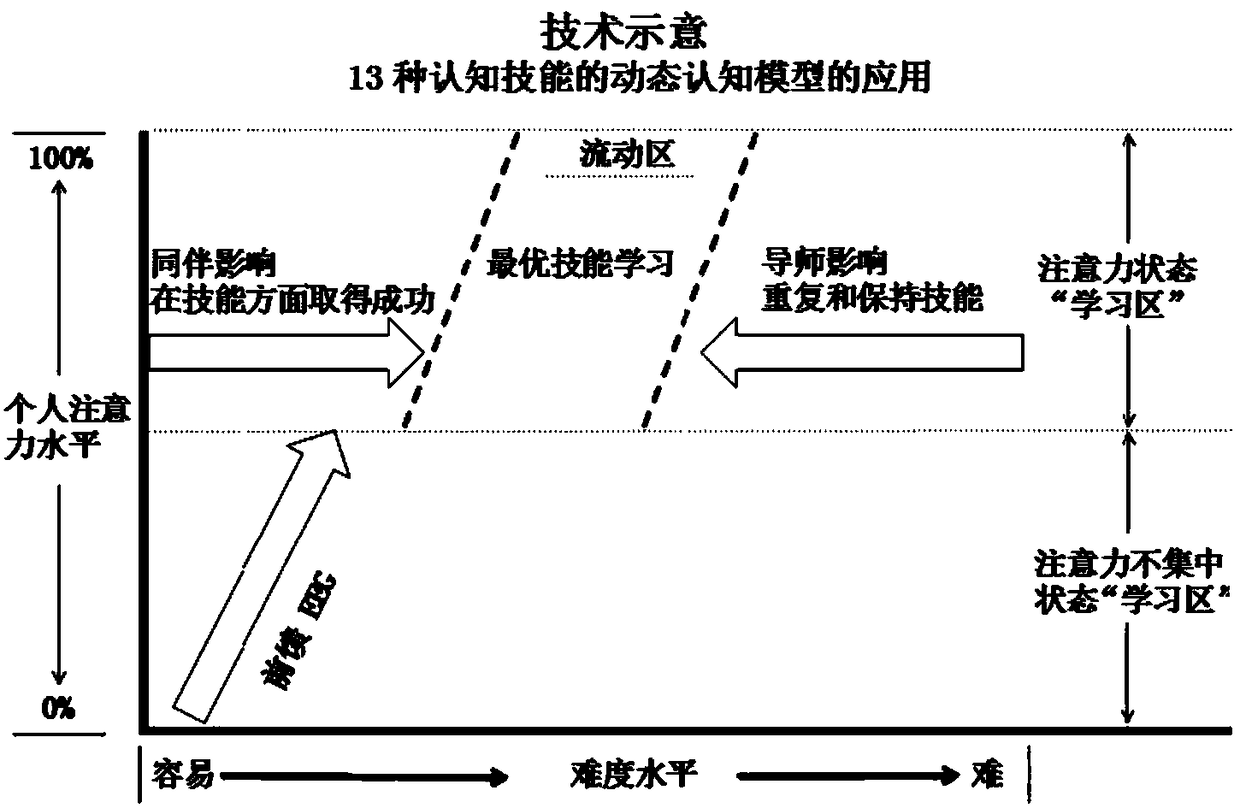
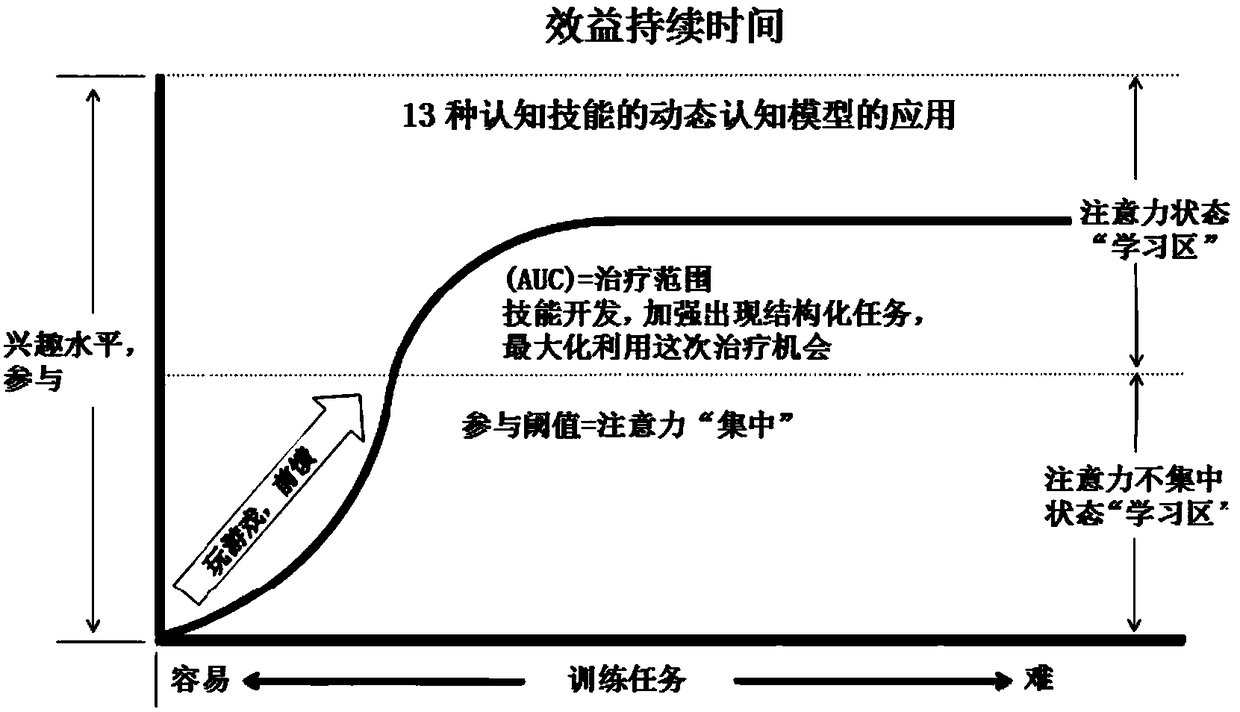
Image
Examples
example 1
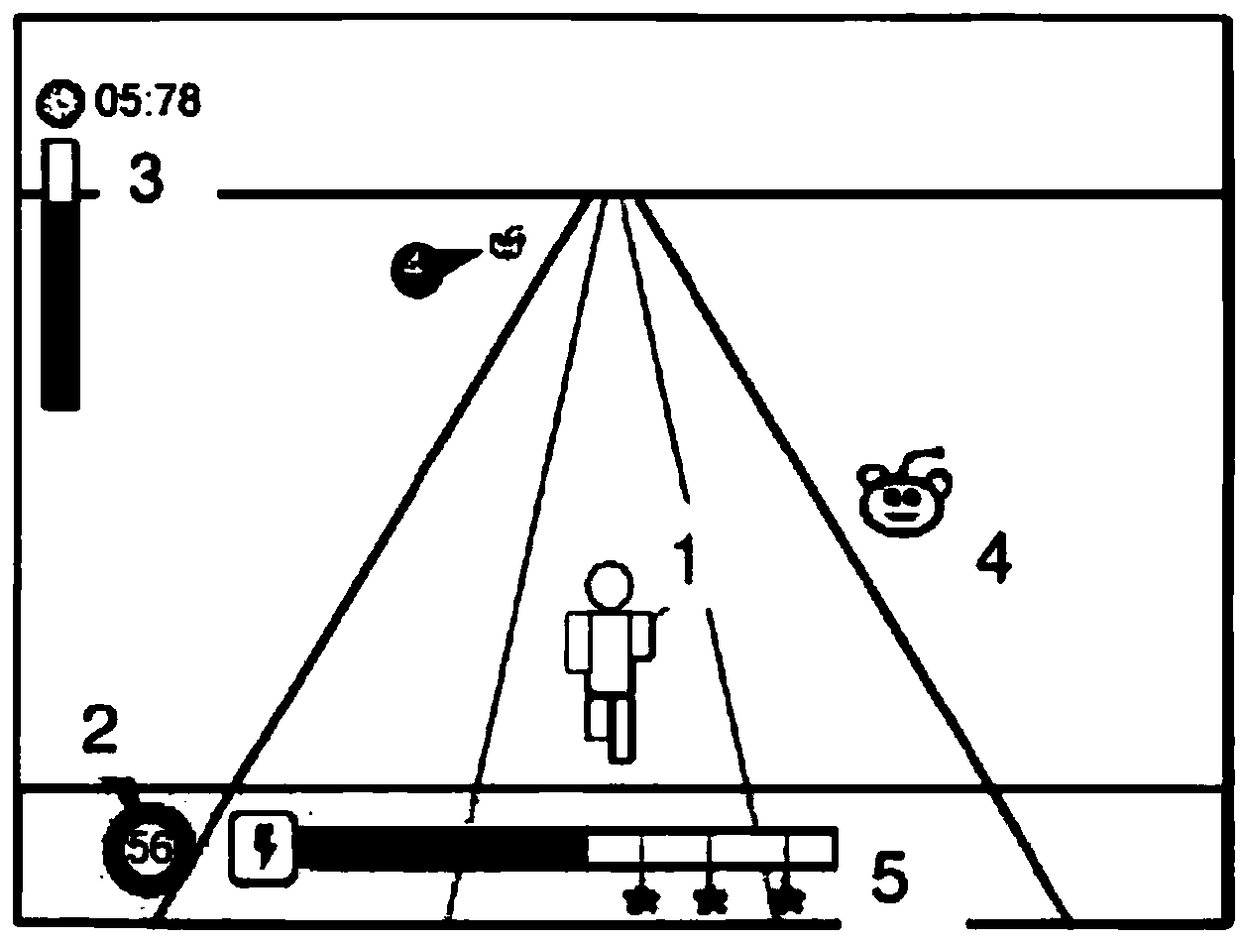
[0167] Example 1 Attention Hold Game Component
[0168] image 3 An example of the environment and task type in which "attention retention" skills are trained and assessed is provided. The user avatar 1 advances along the path at a velocity derived from the user's attention state level measured by the EEG headset and transmitted to the computer or tablet 2 . A timer 3 records the duration of the journey and a progress meter shows the distance to the end of the path. In this example, the user must use self-regulation to persevere until the end of the path and focus hold to achieve a faster completion time. Distracting objects and creatures 4 appear in the path, and the user must ignore the distracting objects to maintain his or her elevated attention state level and speed through the section. "Ability Table" 5 measures the user's level of attention-sustaining skill; this table is populated at a rate that reflects the combination between the level of attention state and perfo...
example 3
[0171] Example 3 Selective Attention Game Component
[0172] Figure 5 An example of the environment and task type in which the "selective attention" skill is trained and assessed is provided. A group of objects 6 with specific visual characteristics appears above the path and moves towards the user avatar. A target object list 7 appears in the user's display screen. In this example, the user has to utilize selective attention to identify an object in a group of objects that matches a certain goal, and then select that object. Ability Meter 5 in this context measures the user's level of selective attention skill; the ability meter fills up faster when the user makes correct actions on groups of objects, and when the user makes many consecutive correct actions. The ability sheet has the minimum success points required to advance to the next mission.
example 4
[0173] Example 4 Alternating Attention Game Component
[0174] Figure 6 and Figure 7 Examples of environments and task types are provided in which "alternating attention" skills are trained and evaluated. A group of objects 6 with specific visual characteristics appears above the path and moves towards the user avatar. A list of target objects appears in the user's display, sometimes showing one visualization parameter, such as a symbol 7, and other times showing a different visualization parameter, such as a shape 8 . In this example, the user must identify objects that match the parameters shown, and use alternating attention to select objects that match that relevant parameter, even if the relevant parameter changes rapidly. Ability Meter 5 in this environment measures the user's alternating attention skill level; the ability meter fills up faster when the user makes correct actions on objects, and when the user makes many consecutive correct actions. The ability shee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com