Linear actuator
A technology for linear actuators and driving motors, which is applied in the direction of transmissions, transmission parts, belts/chains/gears, etc., which can solve the problems of limited internal space and large space occupation of linear actuators, and achieve large thrust, The effect of increasing torque
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
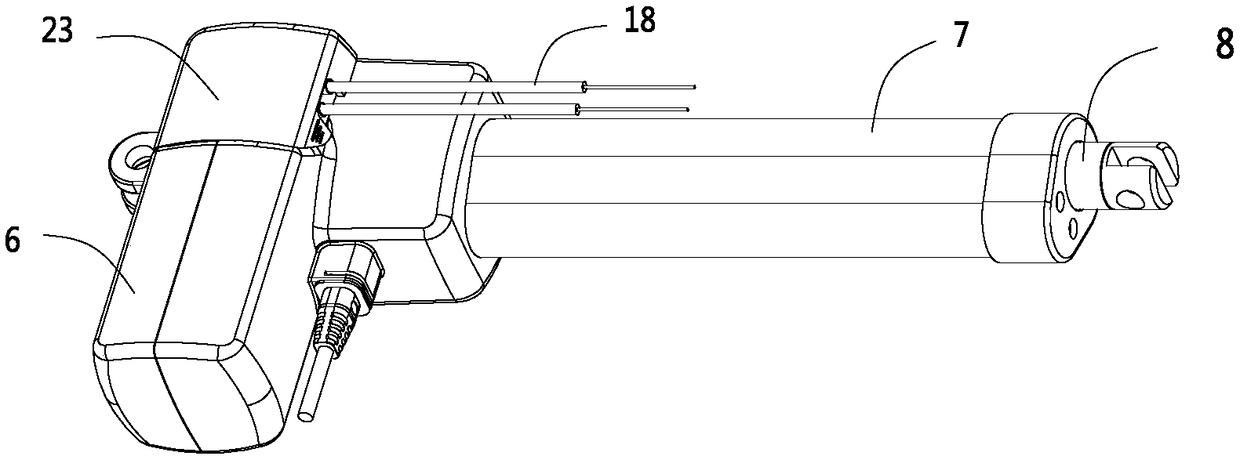
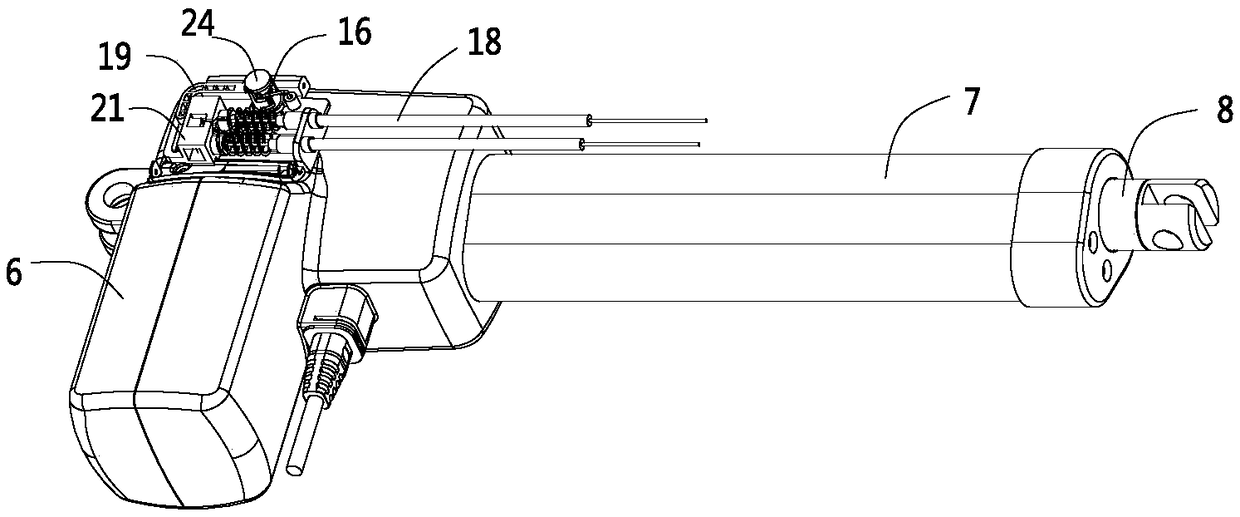
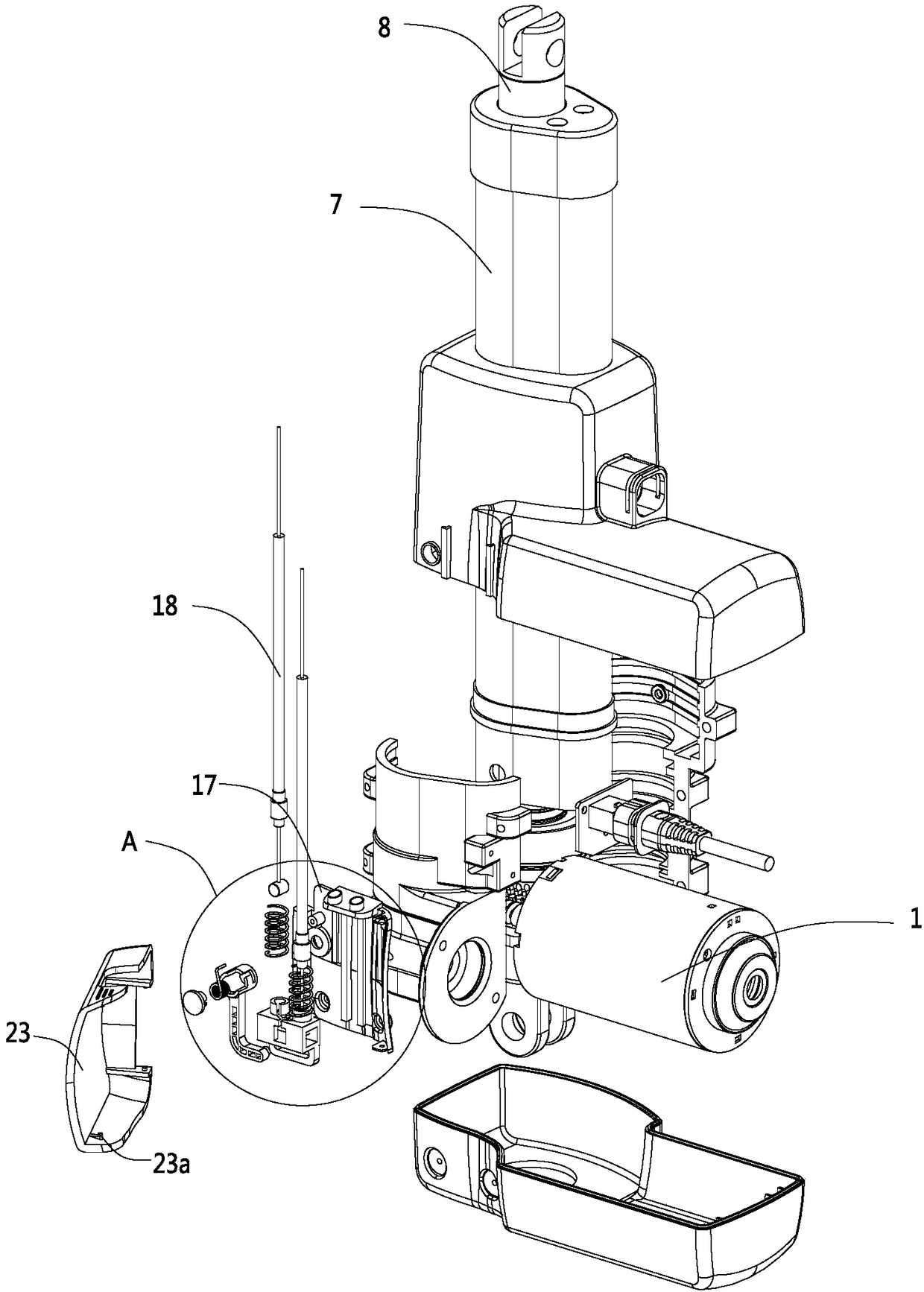
[0051] like Figure 1 to Figure 9 As shown, this embodiment is a linear actuator. In this embodiment, the linear actuator includes a driving motor 1, a transmission worm 2, a worm wheel 3, a screw 4, and a nut 5. The driving motor 1 is connected to the transmission worm 2, and the transmission The worm 2 drives the worm wheel 3 to rotate, the worm wheel 3 rotates to drive the screw 4 to rotate, and the screw 4 rotates to drive the nut 5 to move axially. In addition, the present embodiment also includes a casing 6, an outer tube 7, and an inner tube 8. The nut 5 It is connected with the inner tube 8, the shell 6 is connected with the outer tube 7, the driving motor 1 is fixedly installed in the shell 6, and the axial movement of the nut 5 is ultimately expressed as the axial relative displacement between the inner tube 8 and the outer tube 7.
[0052] In this embodiment, a planetary gear 12 assembly is also provided between the worm wheel 3 and the screw rod 4, for details, see...
Embodiment 2
[0104] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that, in the first embodiment, a brake worm is used to brake the inner ring gear. A suit of an inner ring gear outer torsion spring, directly pulls the inner ring gear outer torsion spring through the cable to realize the radial contraction or radial expansion of the inner ring gear outer torsion spring, when the inner ring gear outer torsion spring radially contracts , will brake the ring gear, which is an alternative to the brake in the first embodiment.
Embodiment 3
[0106] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that the structure of the one-way locking coupling between the worm and the screw is different. In this embodiment, the transmission torsion spring is set between the first dial and the second dial In the sheet, the damping ring is set inside the transmission torsion spring. In other words, the damping ring is located on the innermost side, the first paddle and the second paddle are located on the outermost side, and the transmission torsion spring is located on the damping ring and the first paddle. , between the second paddle.
[0107] The bending pins of the transmission torsion spring in this embodiment are bent radially outward. When the first paddle transmits torque to the transmission torsion spring, the bending pins are moved toward the direction of loosening the transmission torsion spring. And when the second paddle transmits torque to the transmission torsion spring, the bent pin is moved towards the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com