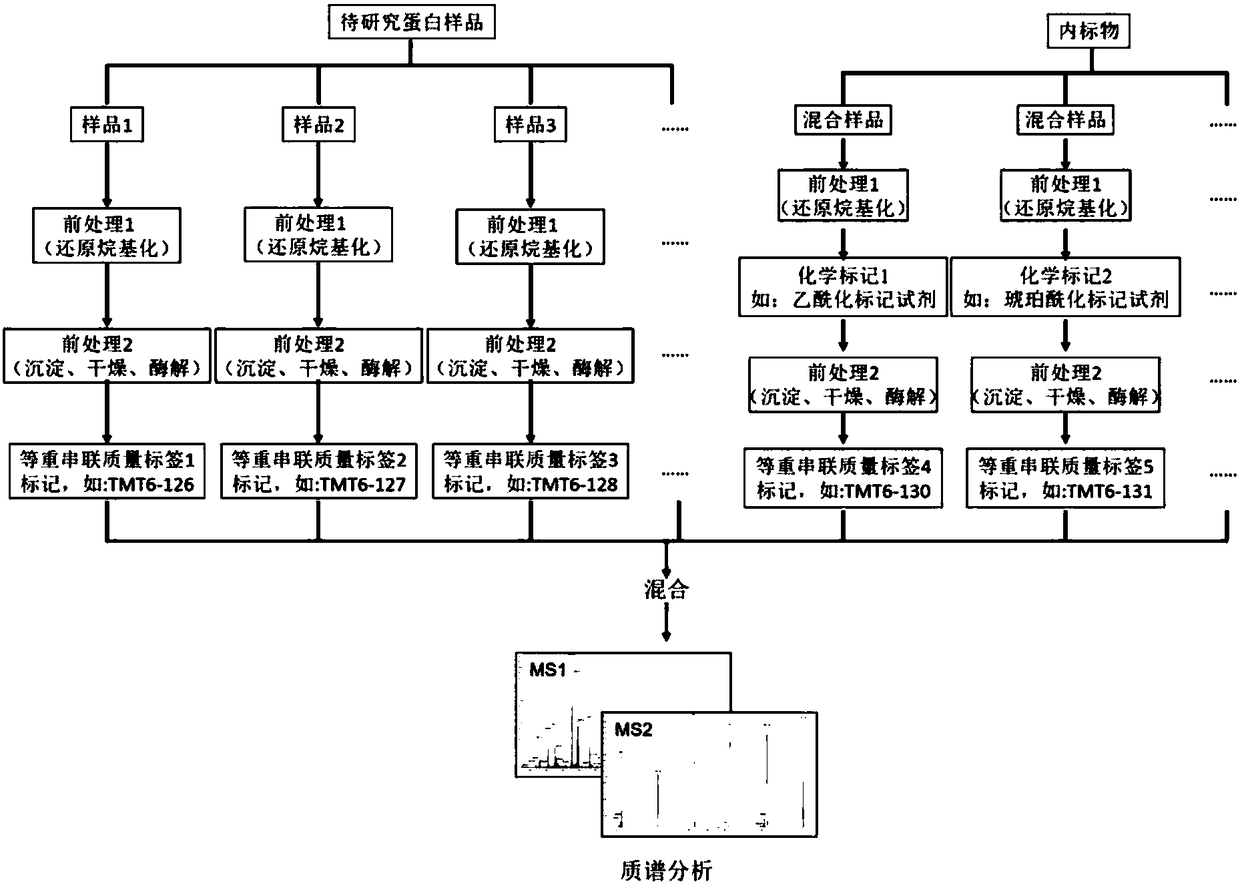
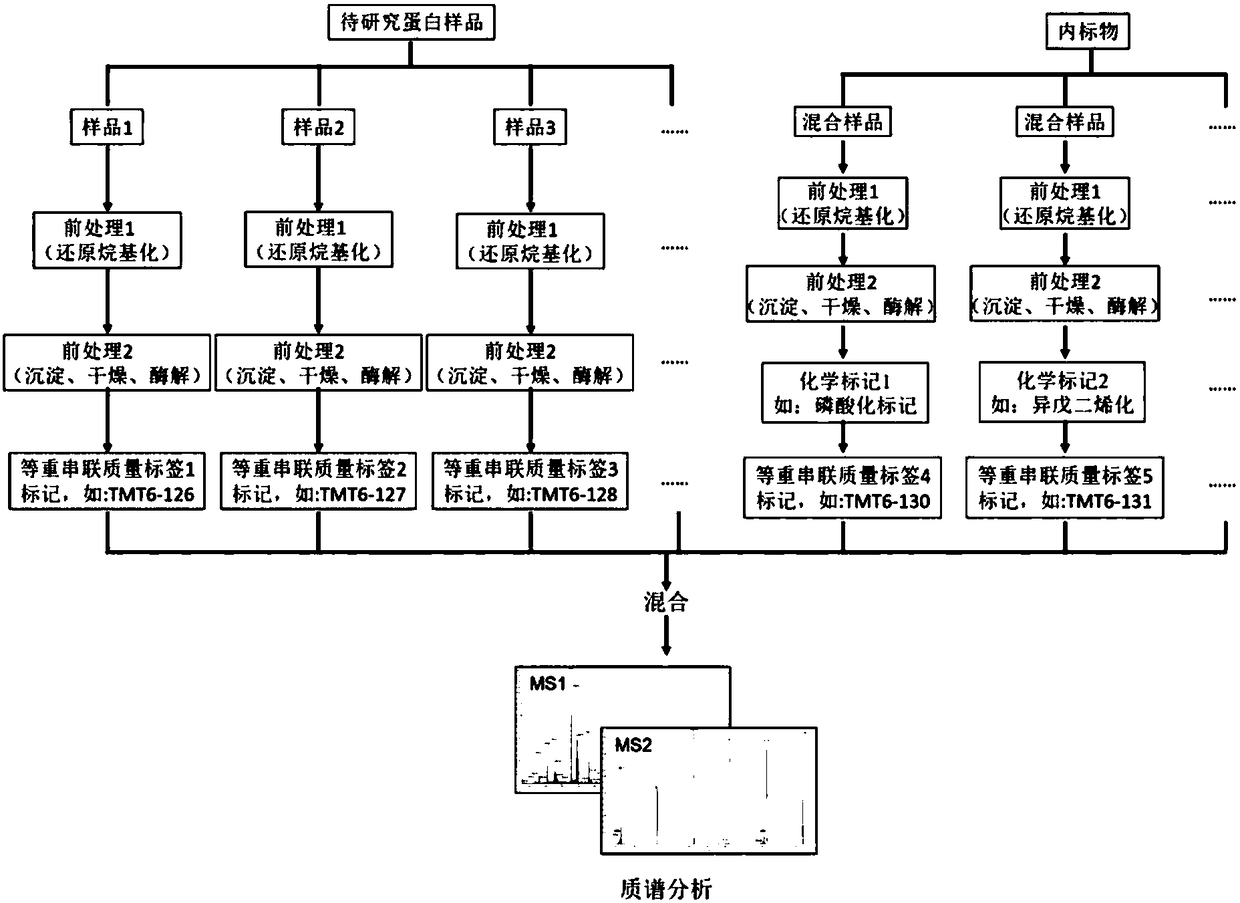
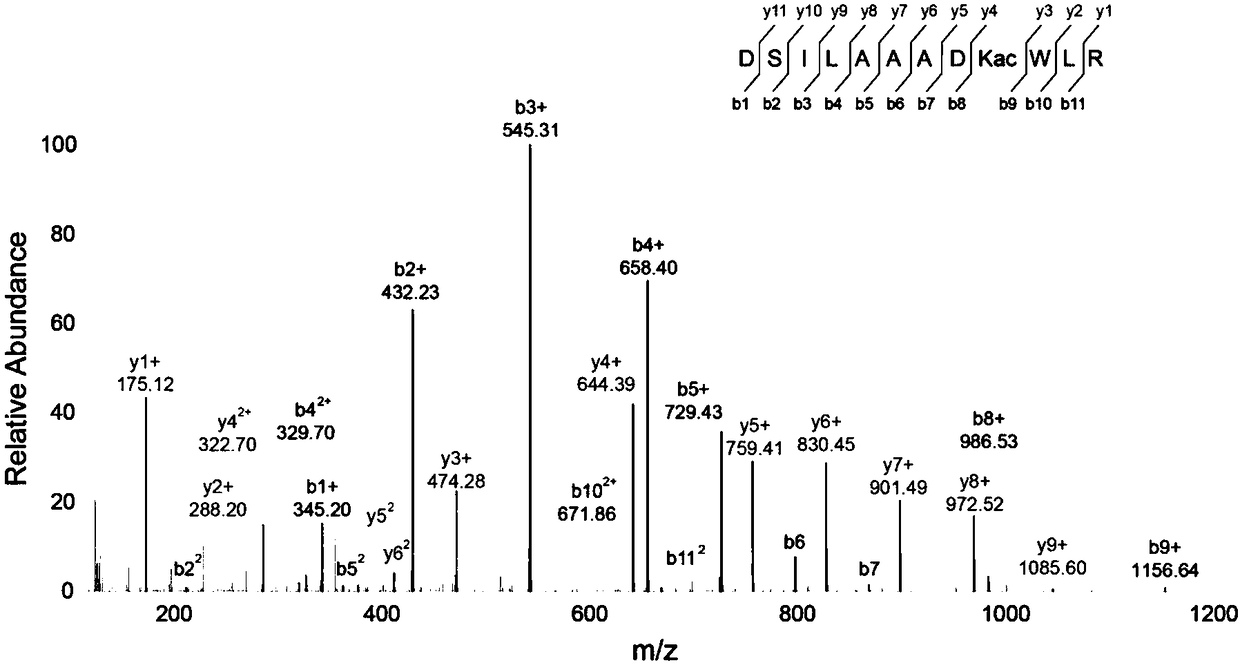
Detection and quantification method for post-translational modification proteomics
A post-translational modification and proteomics technology, which is applied in the detection and quantification of post-translational modification proteomics, can solve the problems of low detection throughput, difficulty, qualitative and quantitative detection throughput, etc., to shorten the experimental process, Effects of reducing experiment costs and increasing chances of MS/MS analysis
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0075] Example 1 Comparative acetylation proteomics and comparative 2-hydroxyisobutyrylation proteomics in the liver of high-fat diet mice
[0076] (1) Feeding mice. The mice were divided into two groups with equal numbers, one group was fed with normal diet, and the other group was fed with high-fat diet, both were fed for 16 weeks.
[0077] (2) Mouse liver tissue collection. Get the experimental mouse, anesthetize the mouse with a dose of 0.04mL / 10g (the anesthetic is 10% chloral hydrate), and wash it with 1×PBS solution (sodium chloride 8.0g / L, potassium chloride 0.2g / L, seven Disodium hydrogen phosphate hydrate 2.72g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.245g / L) perfused the mouse liver through the hepatic portal vein to obtain liver tissue, quick-frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at -80°C until use.
[0078] (3) Protein extraction from mouse liver tissue.
[0079] Take 100mg mouse liver tissue sample, add 1mL PBS lysate (containing 1% NP-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate,...
Embodiment 2
[0109] Example 2 Comparative dimethylation proteomics in the liver of mice fed a high-fat diet
[0110] (1) Feeding mice. (with embodiment 1)
[0111] (2) Mouse liver tissue collection. (with embodiment 1)
[0112](3) Protein extraction from mouse liver tissue. (with embodiment 1)
[0113] (4) Experimental grouping.
[0114] Single chemical labeling group (protein samples to be studied): four groups in total, the first group is 50 μg normal diet mouse (No. 1) liver tissue protein extract, the second group is 50 μg high-fat diet mouse (No. 11) liver tissue For protein extracts, the third group was 50 μg protein extract from liver tissue of mice with normal diet (No. 2), and the fourth group was 50 μg protein extract from liver tissue of mice with high-fat diet (No. 12).
[0115] Double chemical labeling group (internal standard): a total of 1:1:1:1 mixture of normal diet mice and high-fat diet mice liver tissue protein extract 50ug;
[0116] (4) Reductive alkylation of p...
Embodiment 3
[0129] Example 3 Quantitative Phosphoromics Analysis of Colorectal Cancer Samples
[0130] (1) Acquisition of clinical samples of colorectal cancer: All clinical samples of colorectal cancer were obtained from colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgical resection in the Department of Oncology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University;
[0131] (2) Protein extraction: take 3 pairs of colorectal cancer tissues (tumor tissue and paracancerous tissue) each to take 100mg, add 1ml RIPA lysate (1% NP-40, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, 150mM sodium chloride, 50mM Tris (pH=7.5), 25mM nicotinamide, 10mM sodium butyrate, 1× protease inhibitor (cocktail), 1× phosphatase inhibitor solution A, 1× phosphatase inhibitor solution B), tissue homogenizer, broken tissue , ultrasonic cracking, high-speed centrifugation (20000g, 30min, 4°C), the supernatant was taken, and the protein concentration was determined by the BrandFord method.
[0132] (3) Experimental grouping.
[0133] Single chemical ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com