Adaptive non-integer time delay estimation method for use in low signal-to-noise ratio impulse noise environment
A technology for impulse noise and time delay estimation, applied in transmission monitoring, electrical components, transmission systems, etc., can solve problems such as large influence of fractional positioning, non-sharp correlation peaks, and difficulty in finding peak positions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] In order to make the present invention more comprehensible, preferred embodiments are described in detail below with accompanying drawings.
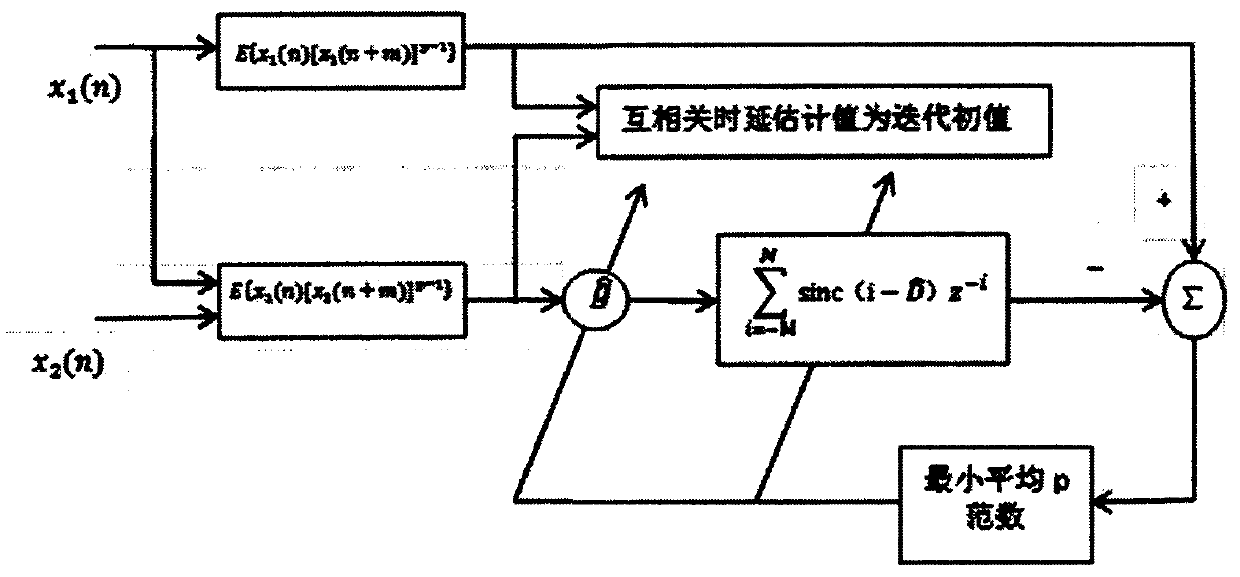
[0019] combine figure 1 , the present invention provides a method for estimating adaptive non-integer time delay in a low signal-to-noise ratio impulse noise environment comprising the following steps:
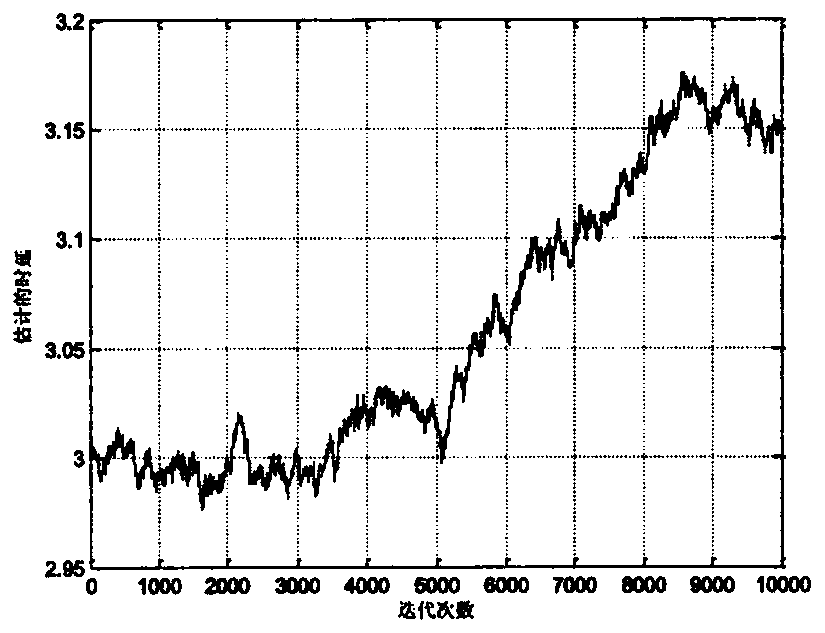
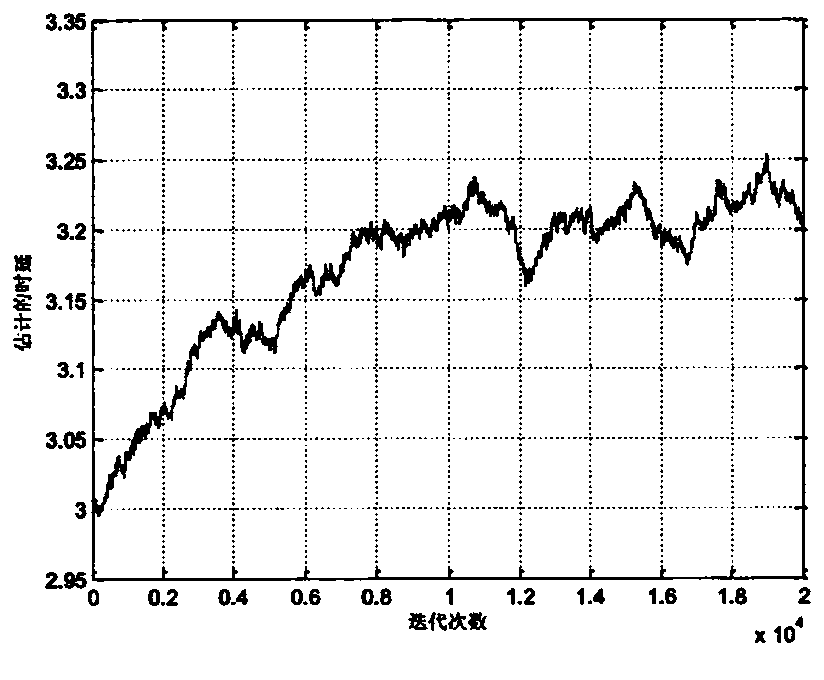
[0020] Step 1. For two received signals x 1 (n) and x 2 (n) Find mutual covariation sequence R c12 , for the received signal x 1 (n) Find the self-covariant sequence R c11 , followed by the intercovariant sequence R c12 , self-covariant sequence R c11 As the equivalent time series as the input signal of the LMPFTDE algorithm, the correlation method time delay is used to estimate the mutual covariation sequence R c12 , self-covariant sequence R c11 Carry out the integer bit estimation of the time delay estimated value first, and use the obtained estimated value as the initial value of the time delay value iteration of the L...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com