Multiparty fair PDF contract signing method based on block chain
A blockchain and contract technology, applied in the field of information security, can solve problems such as easy bottlenecks and high TTP requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
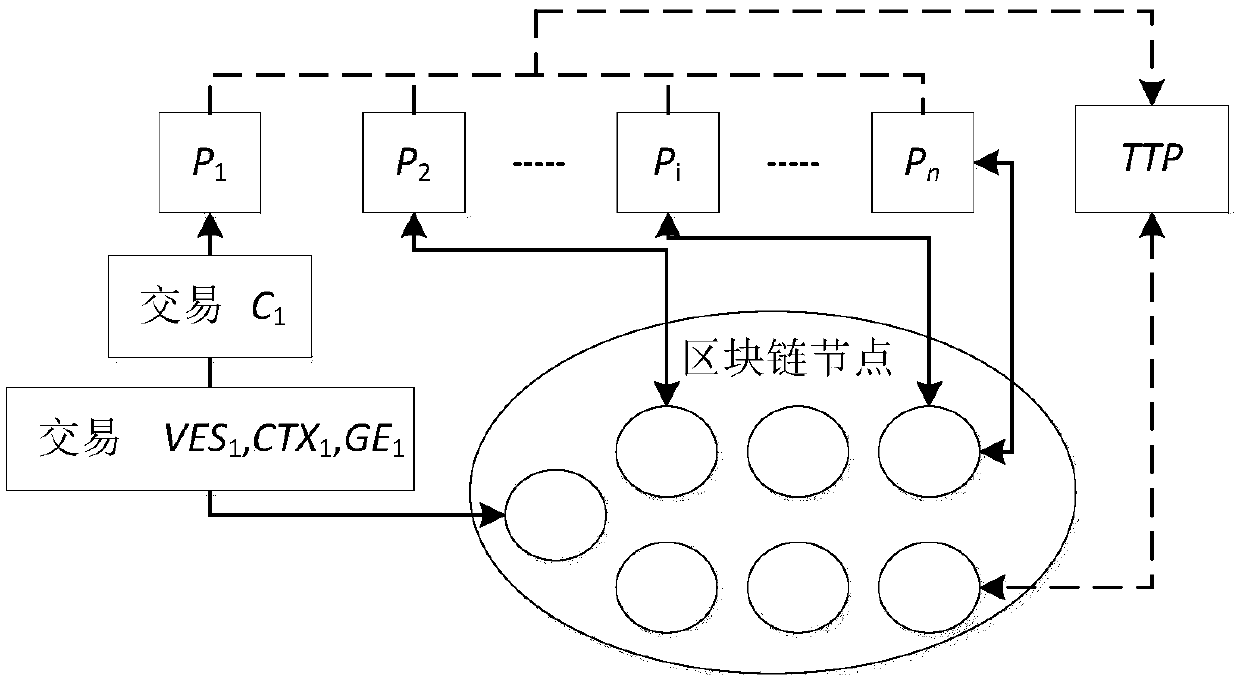
[0054] Set multiple contract signatories P 1 ,...,P n , a trusted third-party TTP and Ethereum blockchain node. Each contract signing party has a public and private key of the Ethereum digital signature. Ethereum adopts the ECDSA digital signature scheme, and the elliptic curve is SECP-256k1. The digital signature scheme (BC.Gen, BC.Sign, BC.Verify) of each contract signer represents the corresponding key generation algorithm, signature algorithm and signature verification algorithm in ECDSA. The blockchain public key and private key of each contract signer are obtained using the ECDSA key generation algorithm. For example, P 1 private key of Expressed as:
[0055] S:8b9519e7f1dd9fa5d47ebf205bfd7dd800c404a0b7aa1991dae344118f7713aa;
[0056] public key The corresponding expression is:
[0057] X:2da31c6cd1cd7dd0f43299bf01676731b1ab40217b659c13ac2a5726a3f9ab1
[0058] Y:390a7665a6dc1505af34261bc9309fc56d0417984c10c7102f37355d02119cb9;
[0059] Each contract signing ...
Embodiment 2
[0105] Embodiment 2 is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that Embodiment 2 runs on smart contract platforms such as QTUM and Fabric.
Embodiment 3
[0107] Embodiment 3 is basically the same as Embodiment 1, except that Embodiment 3 uses specific schemes such as DSA digital signature, DSA-VES verifiable signature, and SHA-3-256 hash scheme.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com