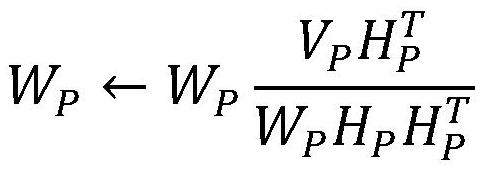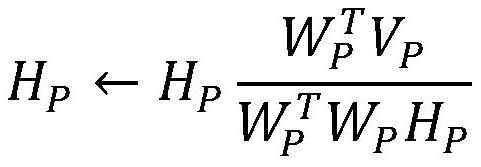A Face Recognition Method Based on Improved Incremental Non-negative Matrix Factorization
A technology of non-negative matrix decomposition and face recognition, which is applied in the field of computer face recognition, can solve problems such as slow convergence speed, high inter-class confusion in subspace, failure to effectively use training samples, etc., to achieve fast convergence speed, training short time effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
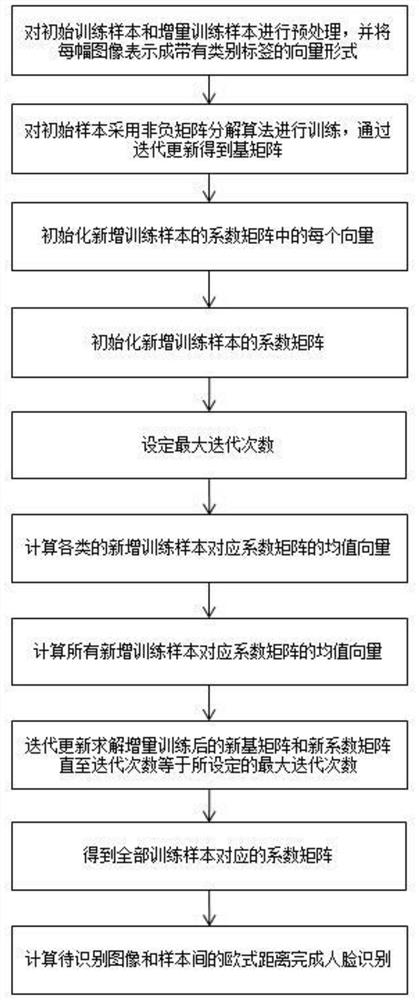
[0045] Embodiment: a kind of face recognition method based on improved incremental non-negative matrix factorization of the present embodiment, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
[0046] A. Preprocess the initial training samples and incremental training samples, and represent each image as a vector form with category labels. The initial training sample matrix is V P , the new training sample matrix is V Q , all training samples are V R ={V P ,V Q}, V P The corresponding coefficient matrix is H P ,V Q The corresponding coefficient matrix is H Q ,V R The corresponding coefficient matrix is H R , the total number of class labels of all samples is C class;
[0047] B. For the initial sample V P The non-negative matrix factorization algorithm is used for training, and the base matrix W is obtained through the iterative update of the following formula P :
[0048]
[0049]
[0050] base matrix W P As the base matrix W in incrementa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com