A Rate Compatible Coding Method Based on Feedback Block Markov Superposition Coding
A technology of packet Markov and superposition coding, which is applied in the direction of coding, coding components, code conversion, etc., can solve the problem that the non-recursive packet Markov superposition coding method is not suitable for decoding energy consumption time-varying communication systems, and packet Markov Superimposed encoding and decoding delay and decoding complexity increase, encoder and decoder do not have a unified structure, etc., to achieve the effect of low hardware implementation complexity, approachable channel capacity, and low hardware implementation complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024] The present invention will be described in further detail below in conjunction with the examples and accompanying drawings, but the implementation of the present invention is not therefore limited to the following examples.
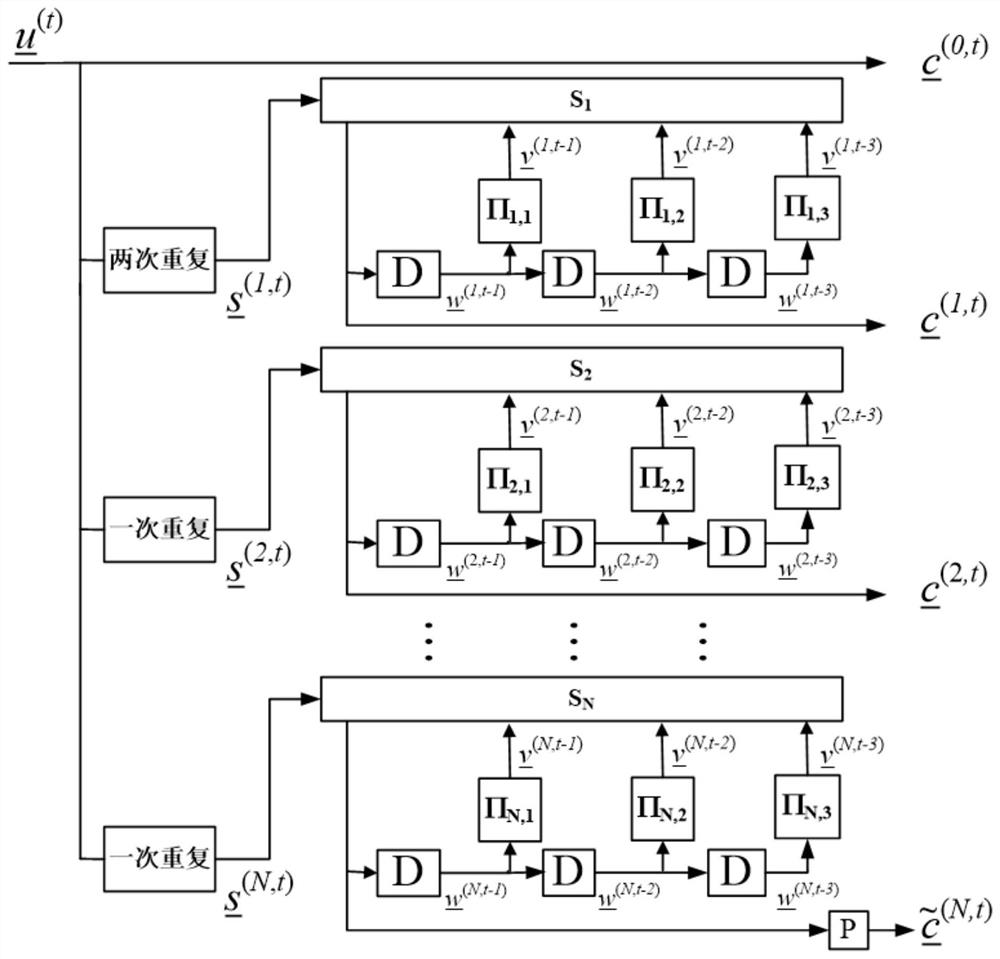
[0025] In the rate-compatible coding method based on feedback packet Markov superposition coding in this embodiment, set m=3, and set the first basic code C 1 [n 1 ,k] is n 1 The repetition code of =3k, all the other basic codes C are set i [n i ,k] is n i =2k repetition codes, where 1
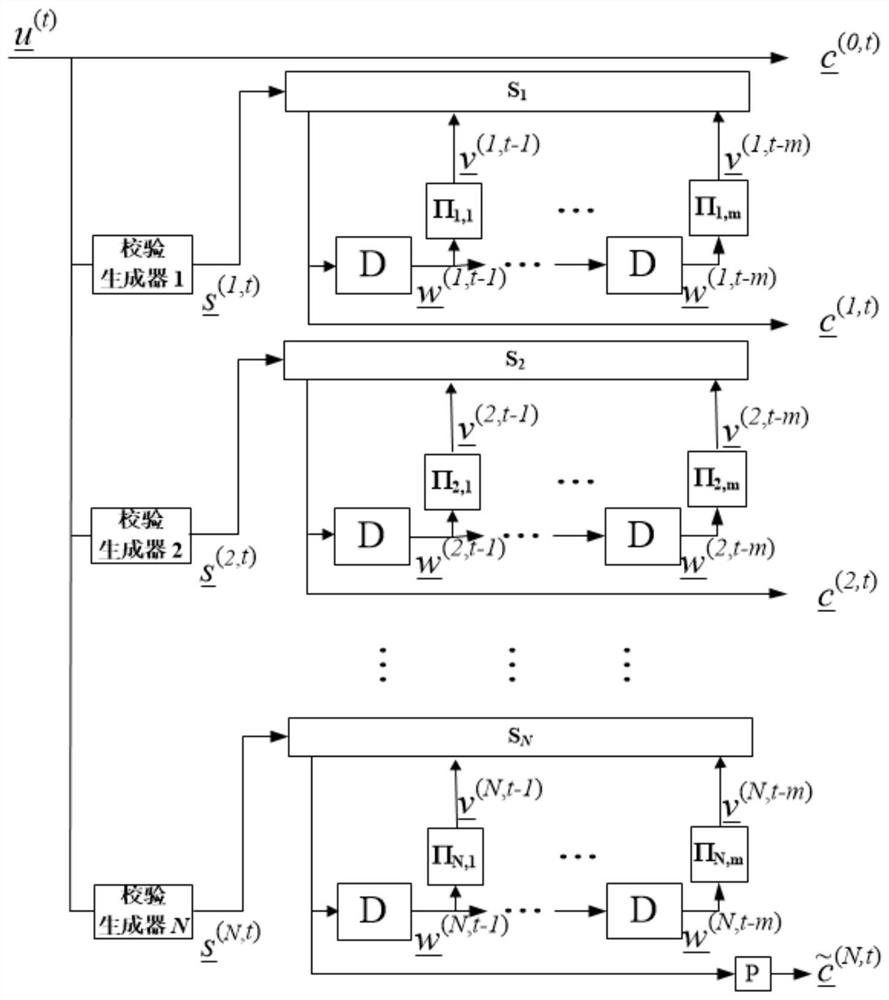
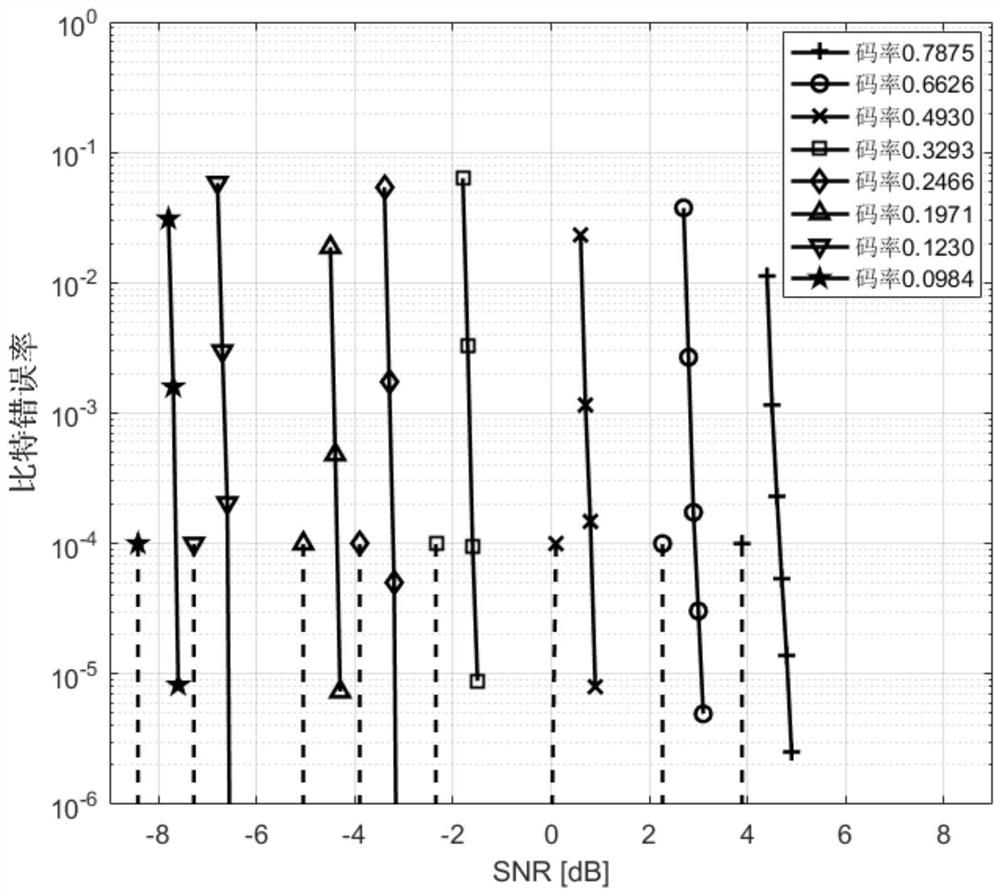
[0026] refer to figure 1 , the coding diagram corresponding to this embodiment is as follows figure 2 . Set T=d=9. refer to figure 2 , a binary information sequence whose length is K=kL...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com