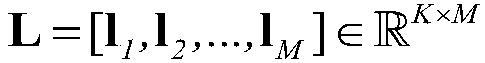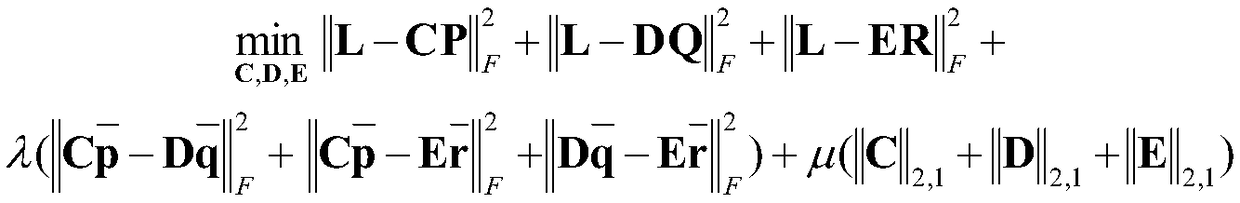A microexpression recognition method based on sparse projection learning
A technology of sparse projection and recognition method, which is applied in the field of pattern recognition, can solve problems such as the fusion of spatial and temporal features without objective consideration, and achieve the effect of simple implementation, low computational complexity, and good recognition accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
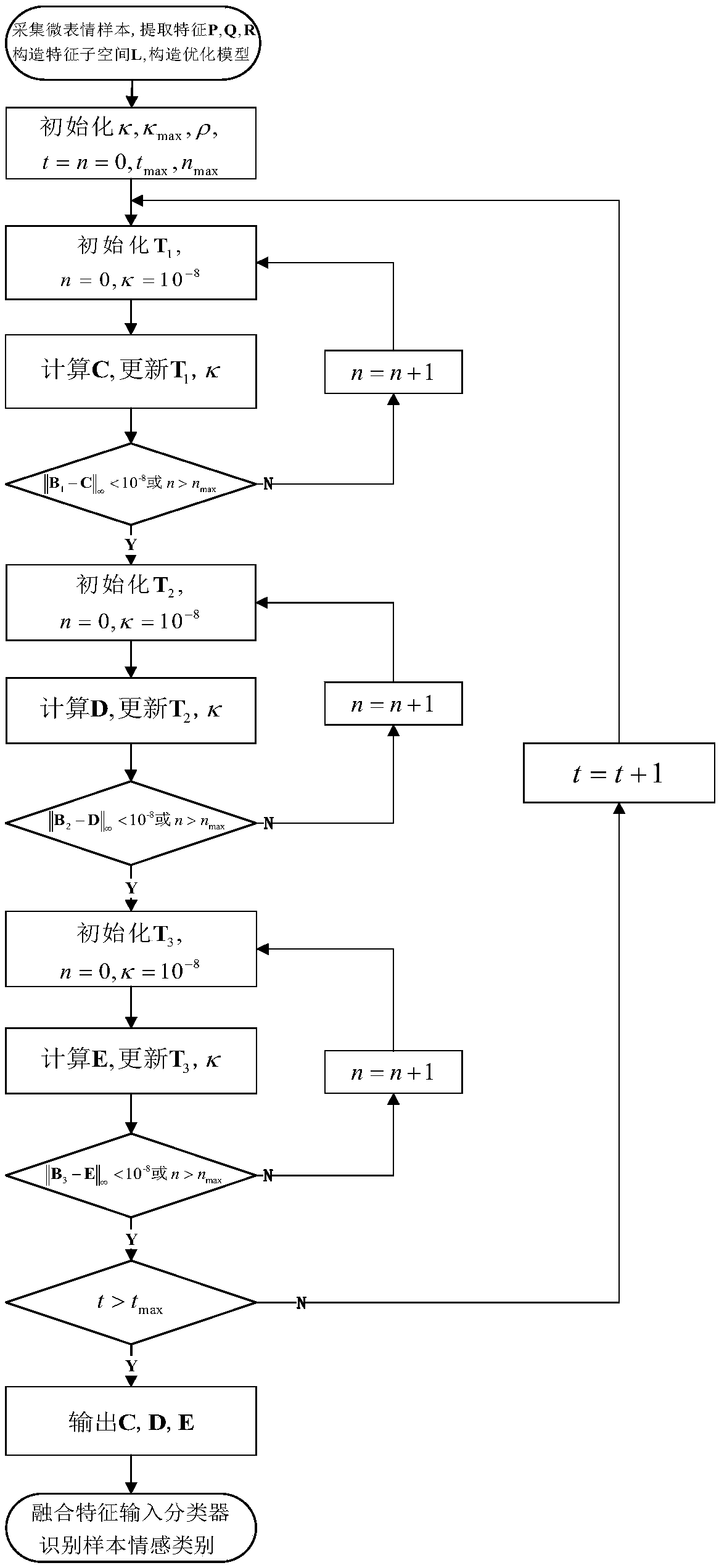
[0022] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
[0023] (1) Collect M micro-expression samples, and extract LBP (Local Binary Patterns) features from the image frame sequence in each sample on three orthogonal planes (XY plane, XT plane and YT plane), denoted as where d is the dimension of LBP features. If there are K types of emotions, the emotion label matrix can be defined:
[0024]
[0025] in Represents the sentiment category label vector of the i-th sample. If the emotion of the i-th sample belongs to the k-th category, then l i is a K-dimensional vector whose k-th element is 1 and the rest are 0. Construct an optimization model:
[0026]
[0027] in C, D, E are feature optimization variables, ||·|| F is the Frobenius norm of the matrix, ||·|| 2,1 represents the sum of the binorms of all columns of the matrix, λ, μ are the parameters to control the sparsity of the m...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com