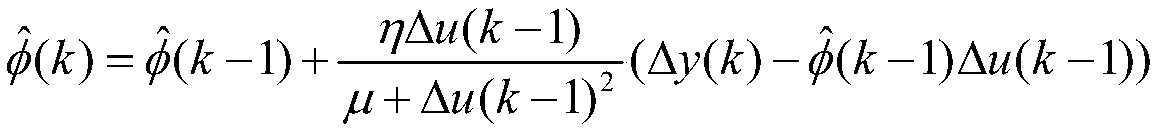Improved model-free adaptive course control algorithm based on input-output data fusion for naval vessel
A model-free self-adaptive, data fusion technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, non-electric variable control, control/regulation system, etc. The effect of robustness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0019] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
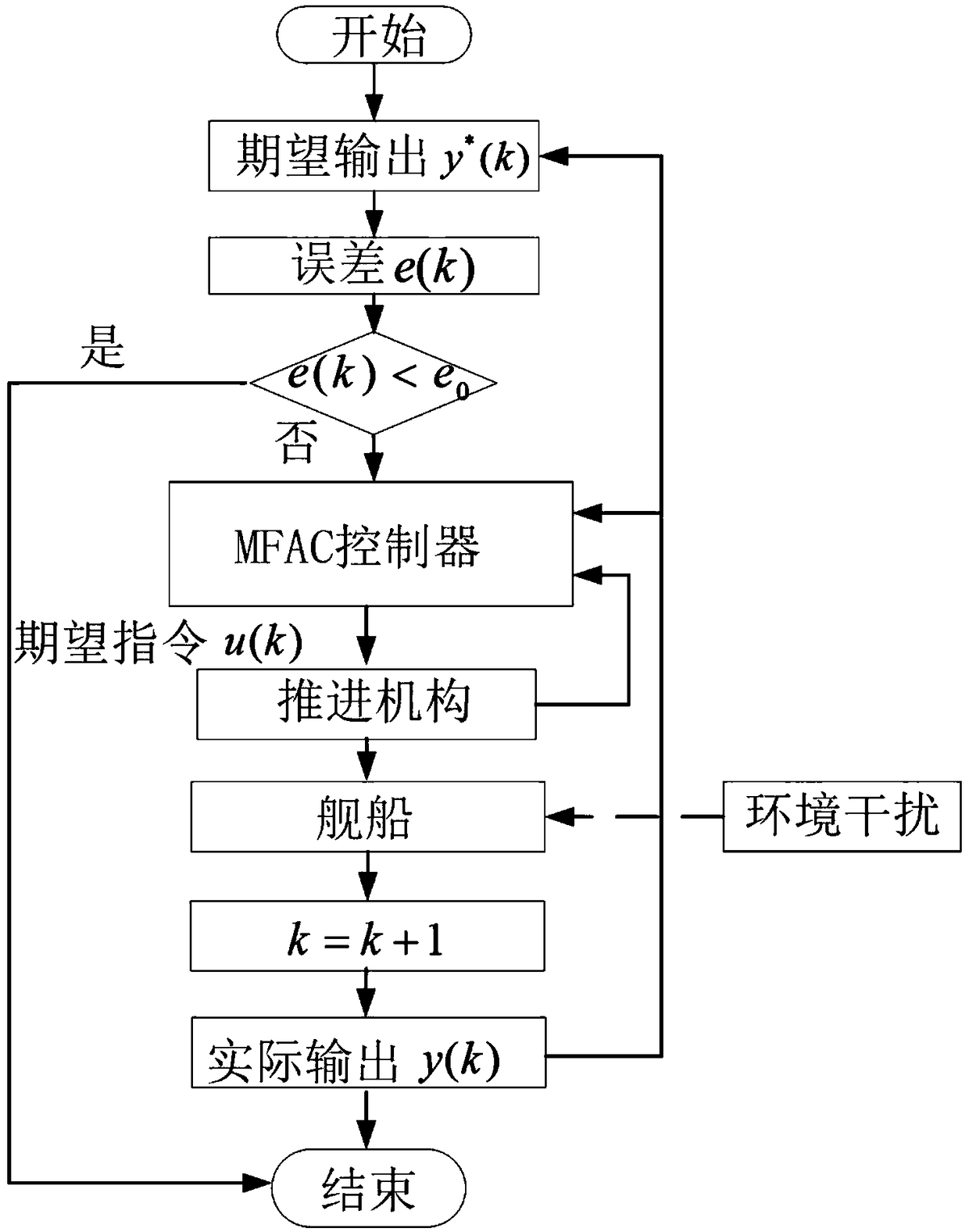
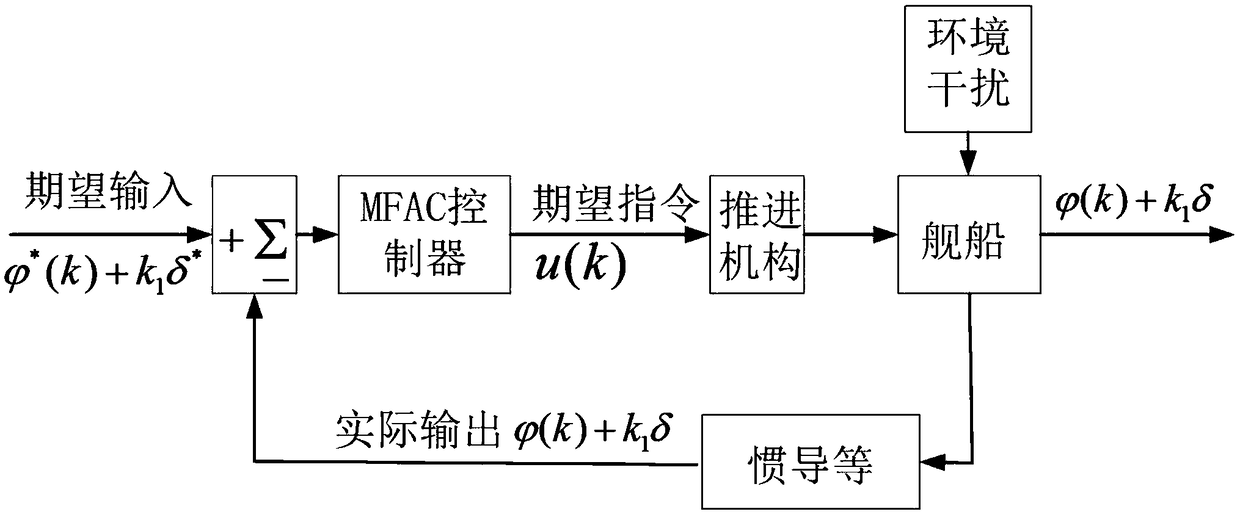
[0020] The invention discloses an improved model-free self-adaptive course control algorithm for fusion of input and output data for ships. The ship heading control system does not satisfy the "quasilinear" assumption of the model free adaptive control (MFAC) algorithm, which causes the MFAC algorithm to be unsuitable for ship heading control. The input and output of the controlled system of the ship of the present invention The data fusion improved model-free adaptive heading control algorithm solves the above problems and expands the scope of application of MFAC theory. The main steps:
[0021] (1) with the rudder angle as a part of the system output, the output y (k) of the original system is the heading angle ψ, which is redefined as the form of y (k)=f (δ, ψ), and the present invention uses the linear superposition form as For example, define the system output y...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com