A block chain-based distributed generation marketization transaction architecture and a design method thereof
A distributed power generation, blockchain technology, applied in the direction of buying/selling/lease transactions, computing, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of distributed power generation instability, lack of trust and centralization, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
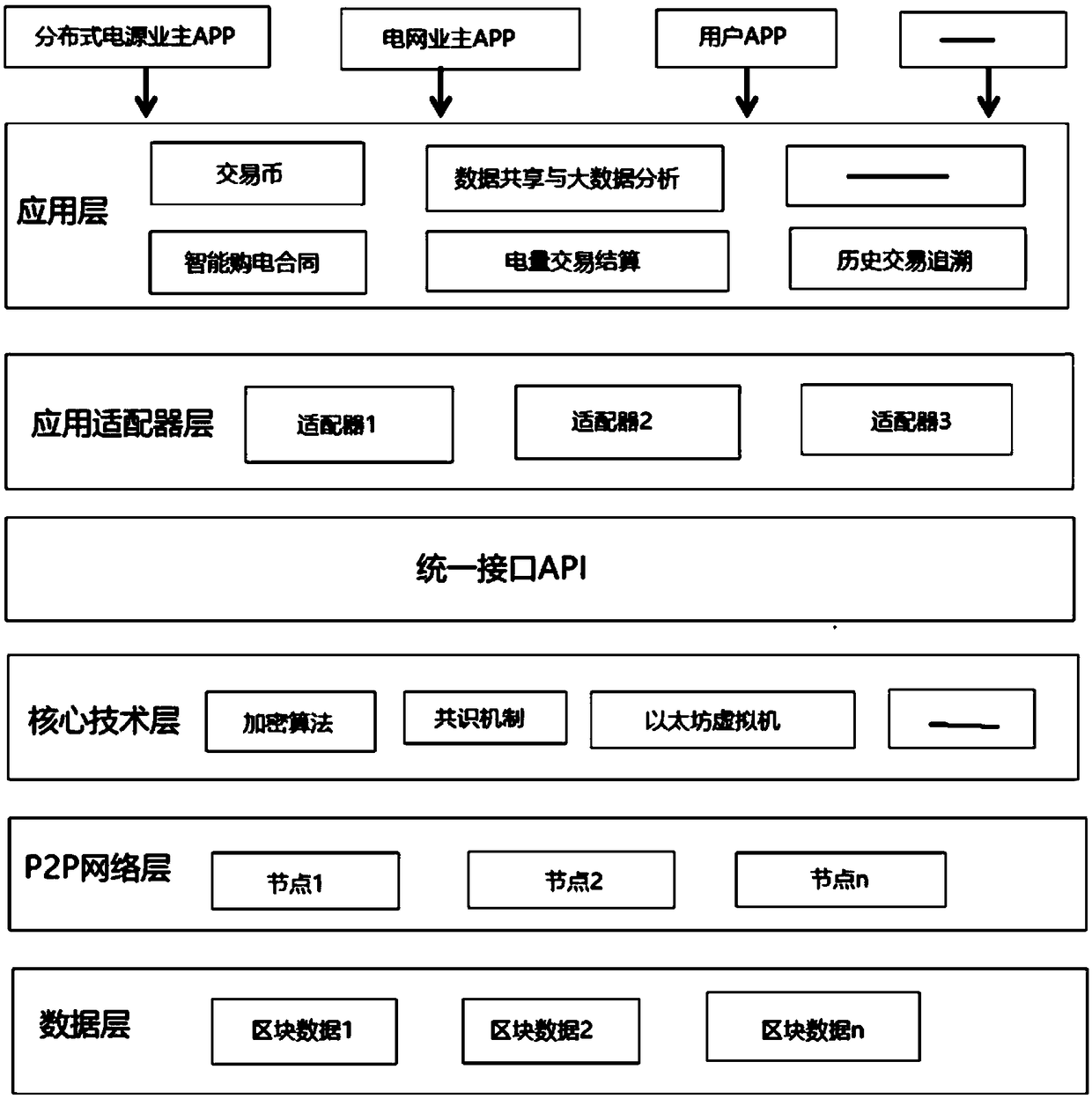
[0044] Such as figure 1 As shown, a blockchain-based distributed power generation market-oriented transaction architecture includes a blockchain data layer, a P2P network layer, a core technology layer, a unified interface layer, an application adapter layer, an application layer, and a user APP layer. The layers from bottom to top are:
[0045] The blockchain data layer is a database, which is used to save the full backup of historical transaction data, so that all historical transactions can be traced;
[0046] The P2P network layer is used to provide P2P network protocols for exchange by all transaction nodes. All subjects, including distributed power generation owners, power grid enterprises, and users, are abstracted into individual transaction nodes; all transaction nodes in the P2P network are exchanged through the P2P network protocol , there is no central node, it has the characteristics of attack resistance and high fault tolerance, and the failure of a certain node...
Embodiment 2
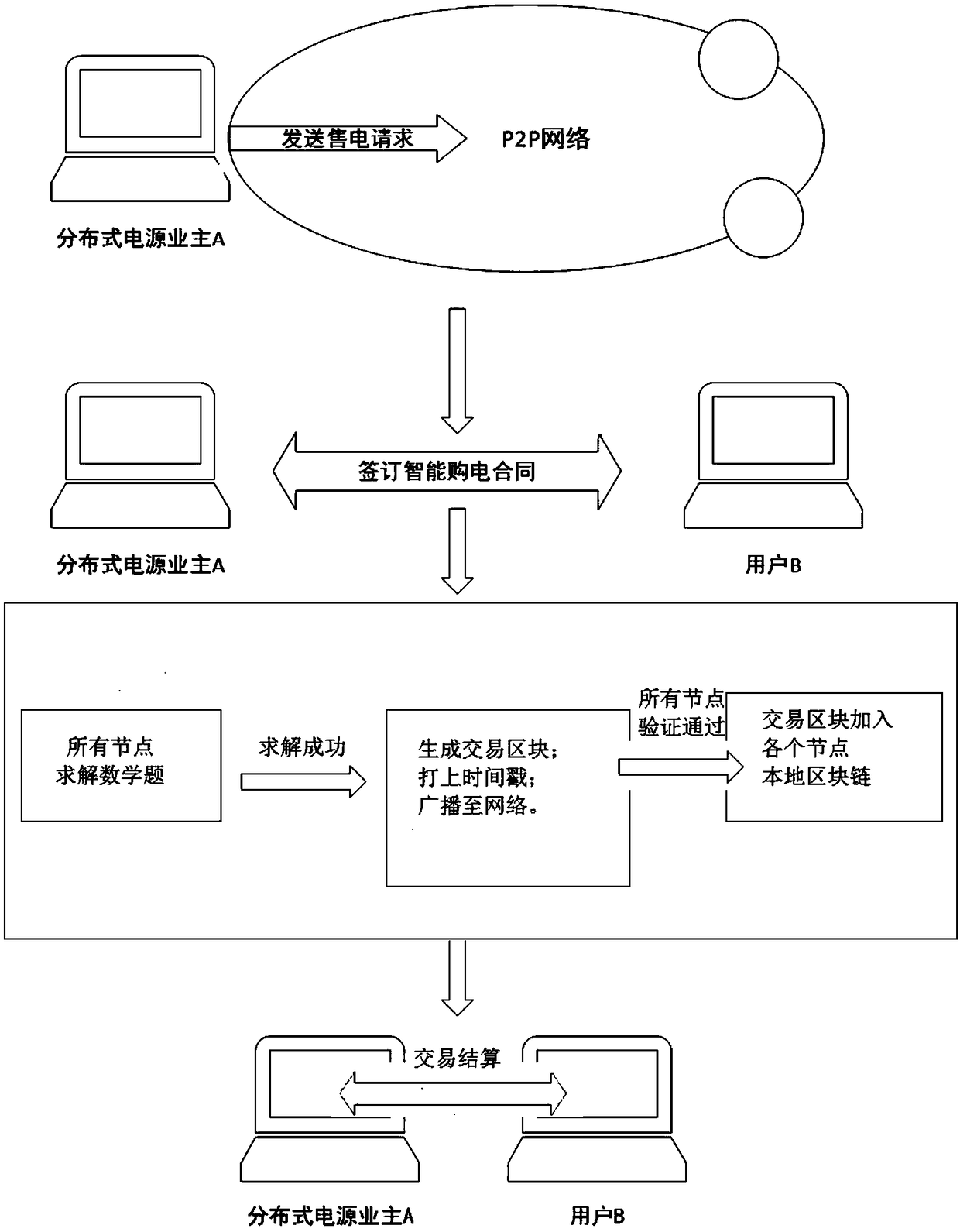
[0055] Such as figure 2 As shown, a blockchain-based distributed generation market-oriented transaction architecture design method includes the following steps:
[0056] (1) Distributed power generation owner A publishes electricity sales information on the P2P network through the operation terminal. The electricity sales information includes electricity sales and intended electricity sales prices, and all nodes will receive this information;
[0057] (2) User B with purchase intention sends purchase information to distributed power generation owner A through the P2P network. The purchase information includes purchase quantity and intended purchase price;
[0058] (3) Distributed power generation owner A selects one or several users B according to the quotation information of each user B, and signs a power purchase contract written in code form through the P2P network, specifically: call the smart contract template written in code form in advance, When A and B sign the smart...
Embodiment 3
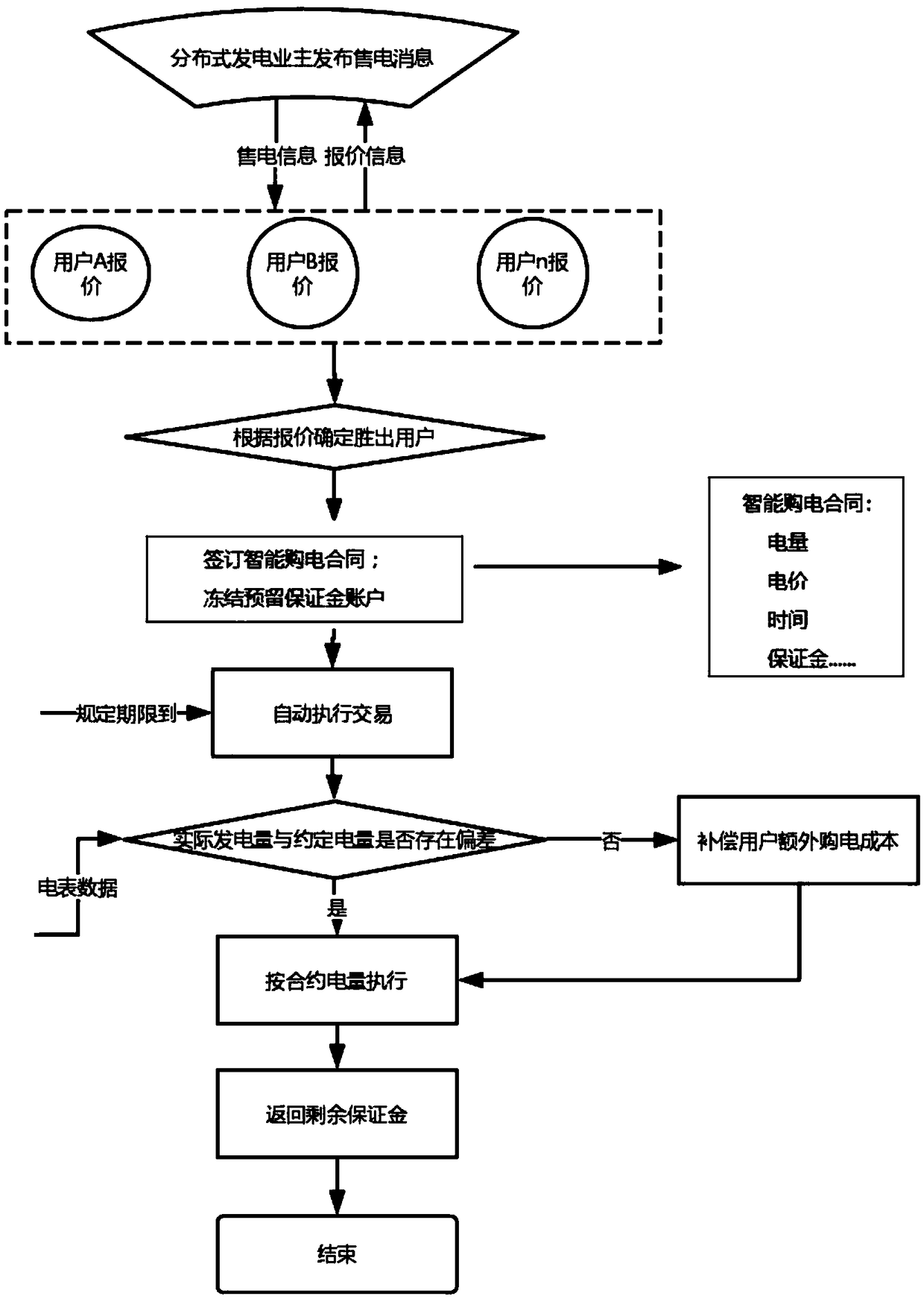
[0064] Compared with Embodiment 2, this embodiment also includes the actual transaction power measurement authentication steps:
[0065] 4.1 After distributed power generation owner A and user B conduct power transactions, the network reads the actual transaction power data of distributed power generation owner A and user B's smart meters. The reading method can be through the data preset on the system It can also be read through the transmission interface, or it can be read offline, or transmitted and obtained through the network, or the data of the smart meter can be imported into the network in a way that can be realized in the prior art;
[0066] The blockchain-based distributed generation transaction architecture described in 4.2 assigns a unique ID to the transaction and stamps it with a time stamp;
[0067] 4.3 The transaction record is added to the legal blockchain described in step (6) and cannot be tampered with. Users can trace any historical power transaction to pr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com