Fault restarting method for parallel multi-terminal direct-current transmission line
A DC transmission line, multi-terminal DC technology, applied in the direction of emergency protection circuit devices, electrical components, power transmission AC network, etc., to achieve the effect of rapid extinguishment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
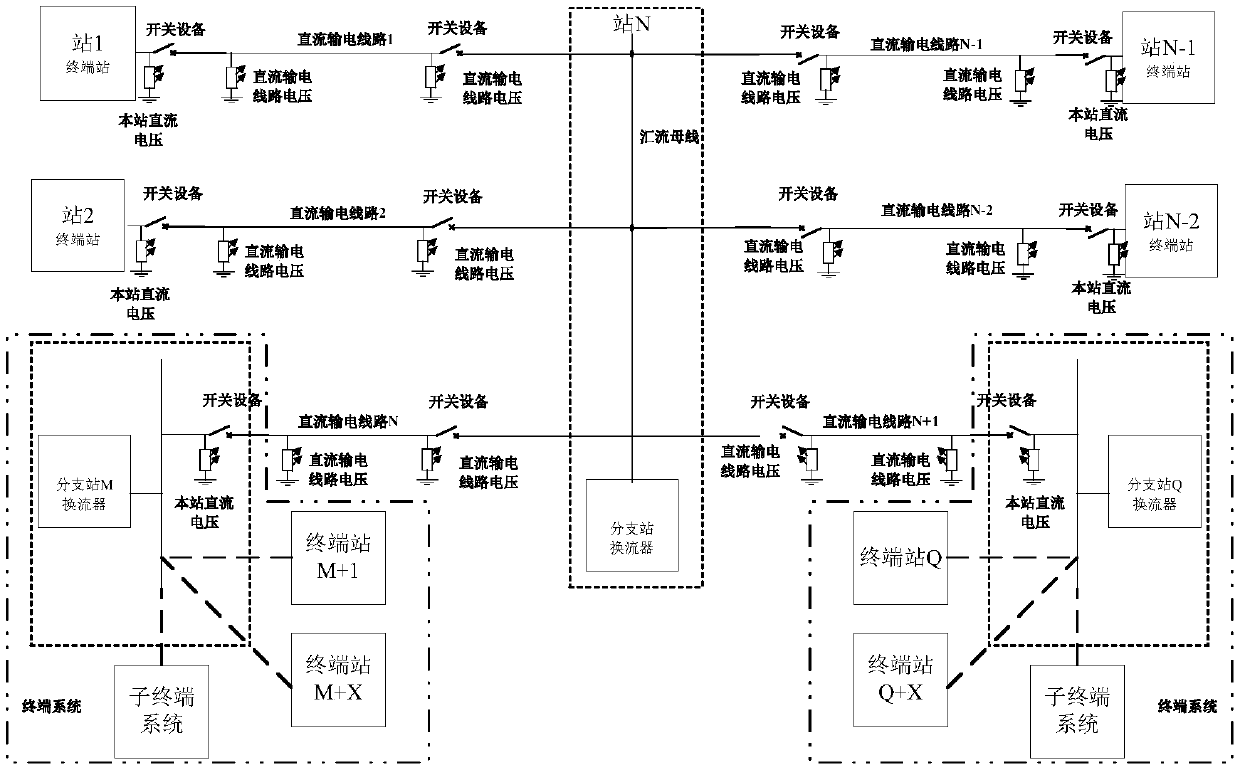
[0054] Figure 4 It is a flowchart of a fault restart method for parallel multi-terminal direct current transmission lines, which includes the following steps:
[0055] Step 1, select the branch station connected to the faulty DC transmission line as the leading station for restarting the faulty DC transmission line;
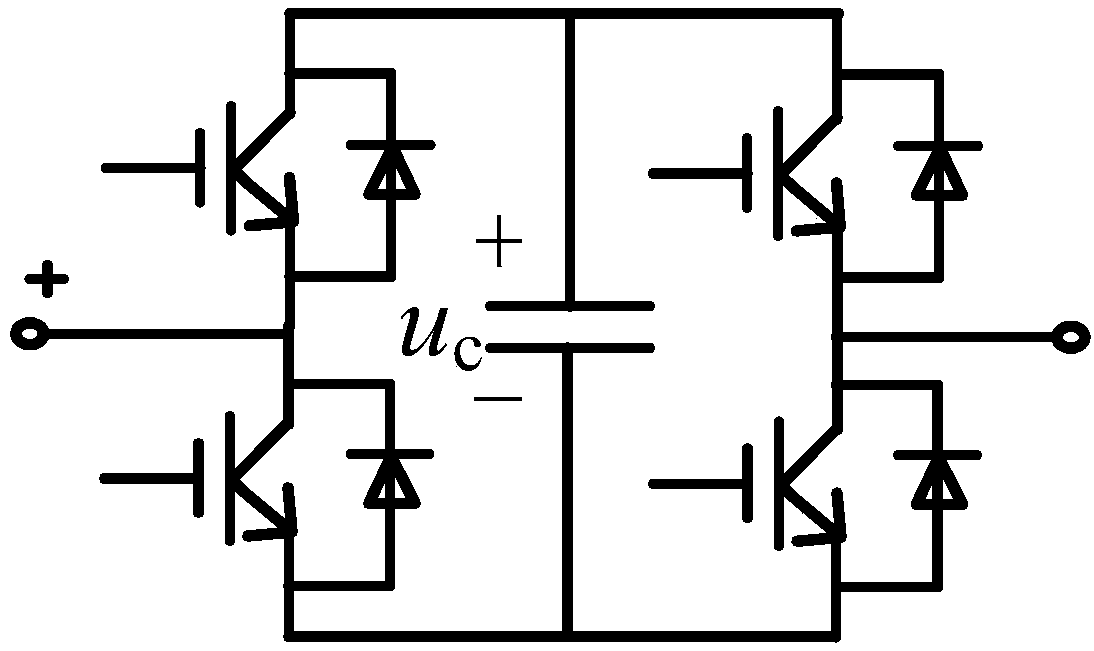
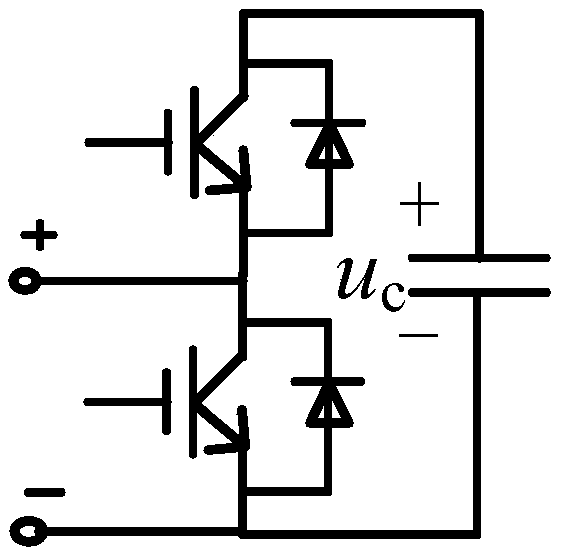
[0056] Step 2: Immediately after the DC transmission line fault occurs, all converter stations with LCC converters adjust the ignition angle to be greater than 150 degrees and less than 180 degrees, and all converter stations with VSC converters control the DC voltage of the station to zero or immediate temporary closure;
[0057] Step 3, all terminal stations with VSC converters connected to the main station isolate the DC transmission lines from themselves through switchgear;
[0058] Step 4, the branch stations of all terminal systems connected to the main station isolate the DC transmission lines from their own systems through switchgear;
[0059] Step 5,...
Embodiment 2
[0073] Related fault points and switchgear such as Figure 5 shown.
[0074] Assuming that instantaneous fault F1 occurs on DC transmission line 1, DC transmission line 1 connects station 1 of the terminal station and main station N, and station 1 is a converter station with a VSC converter. After the protection action of the DC transmission line, the converter station with the LCC converter in the entire parallel multi-terminal DC transmission system immediately adjusts the ignition angle to be greater than 150 degrees and less than 180 degrees, and the converter station with the VSC converter controls the direct current of the station. Voltage to zero (or immediately and temporarily blocked); all terminal stations with VSC converters connected to the leading station pull the switchgear between the station and the DC transmission line to isolate the DC transmission line from itself (for example, station 1 pulls Open the switchgear K11); the branch stations of all terminal sy...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Related fault points and switchgear such as Figure 5 shown.
[0077] Assuming that permanent fault F1 occurs on DC transmission line 1, DC transmission line 1 connects station 1 of the terminal station and main station N, and station 1 is a converter station with a VSC converter. After the protection action of the DC transmission line, the converter station with the LCC converter in the entire parallel multi-terminal DC transmission system immediately adjusts the ignition angle to be greater than 150 degrees and less than 180 degrees, and the converter station with the VSC converter controls the direct current of the station. Voltage to zero (or immediate temporary blocking) so that the fault current at the fault point of the DC transmission line is quickly extinguished; all terminal stations with VSC converters connected to the main station open the switchgear between the station and the DC transmission line to The DC transmission line is isolated from itself (for ex...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com