Method for controlling finite time of discrete networked multi-agent system having communication delay
A multi-agent system and finite time technology, applied in the field of control, can solve problems that affect finite time control performance and cannot actively compensate network communication time lag, etc., to achieve the effect of active network communication time lag and compensation of network communication time lag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
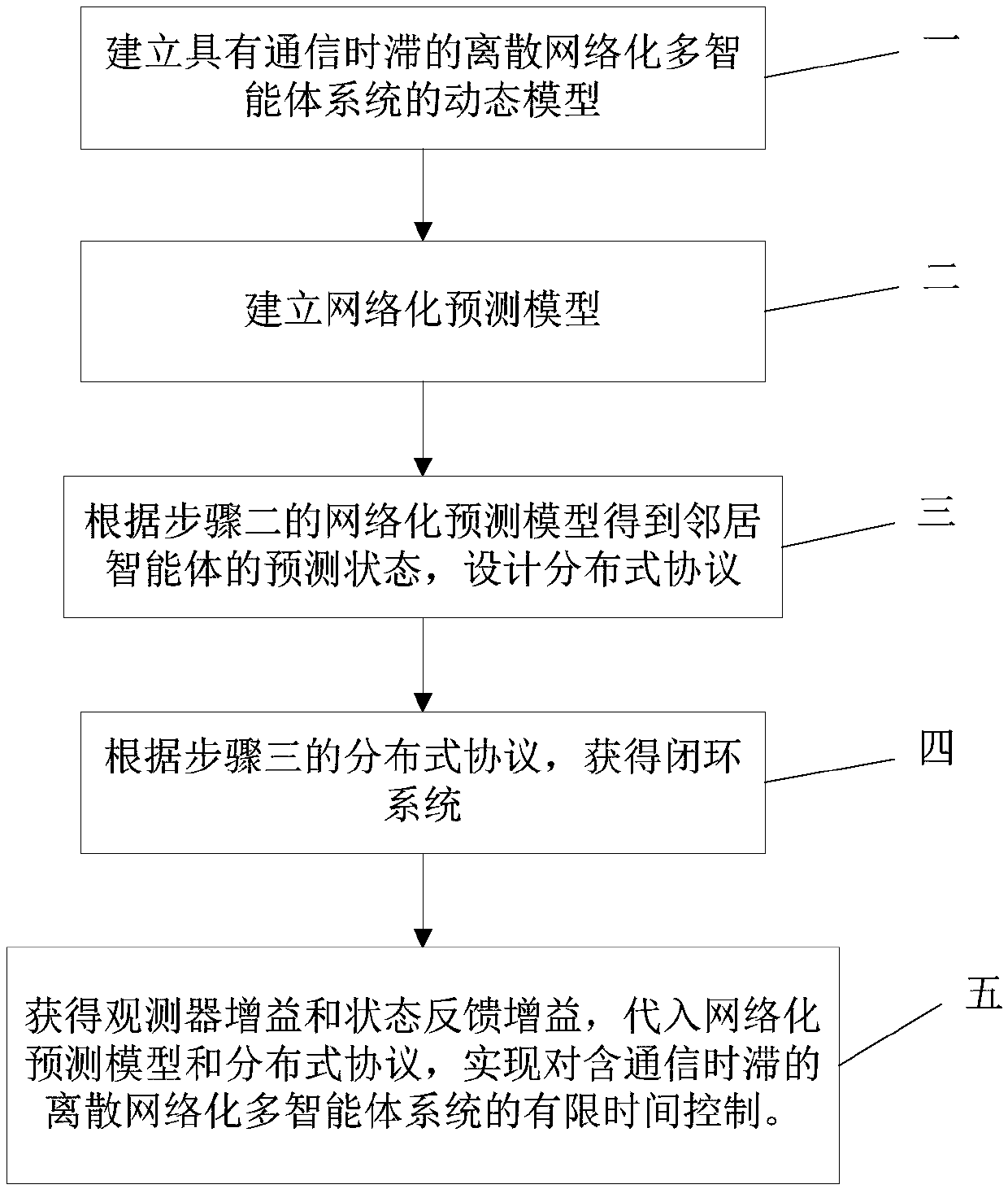
[0048] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination figure 1 To describe this embodiment,
[0049] A finite-time control method for a discrete networked multi-agent system with communication time delay, comprising the following steps:
[0050] Step 1. Establishing a dynamic model of a discrete networked multi-agent system with communication time delay;
[0051] A dynamic model of a discrete networked multi-agent system with constant communication time delay and N agents is established, where the state space of agent i is described as:
[0052]
[0053] where x i (k) is the state variable of agent i at time k, k=0,1,2,...; x i (k+1) is the state variable of agent i at time k+1, x i (0) is the state of agent i at the initial moment, x i0 is the initial value of the state of the agent i at the initial moment, i=1,2,...,N; u i (k) is the control input of agent i at time k, y i (k) is the measurement output of agent i at time k; A is the system matrix, B is the input matri...
Embodiment
[0082] Adopt the method described in specific embodiment one to carry out simulation:
[0083] System parameters:
[0084]
[0085] Furthermore, given N=4, M=10, γ=1.001, c 1 = 1,c 2 The initial value of is 20;
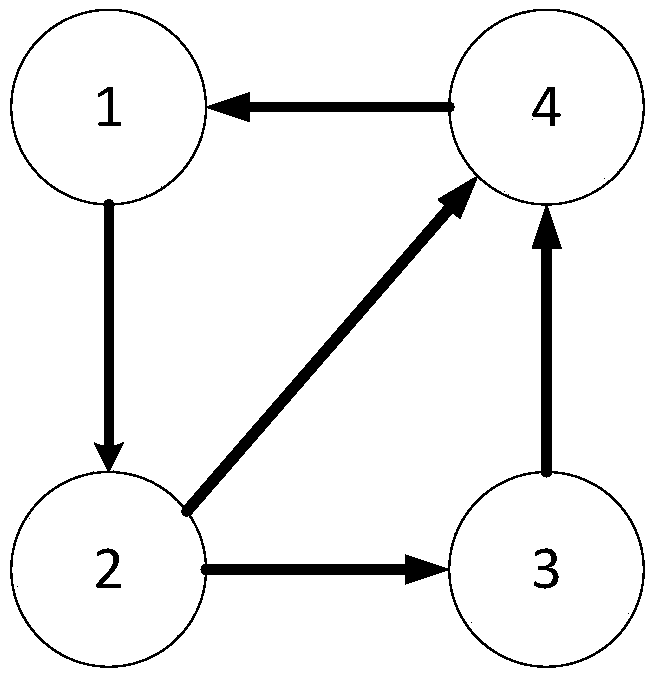
[0086] communication topology such as figure 2 shown;
[0087] Next, use the method of the present invention to carry out finite time control on the discrete networked multi-agent system, and control the parameter c 2 optimize:
[0088] Case 1: The communication network has no communication time lag, that is, τ=0;
[0089] State estimation gain matrix L and state feedback gain matrix K are solved:
[0090] For formula (5), formula (6), formula (7), formula (8) and
[0091]
[0092] Solve to obtain the state feedback gain matrix K and state estimation gain matrix L as follows
[0093]
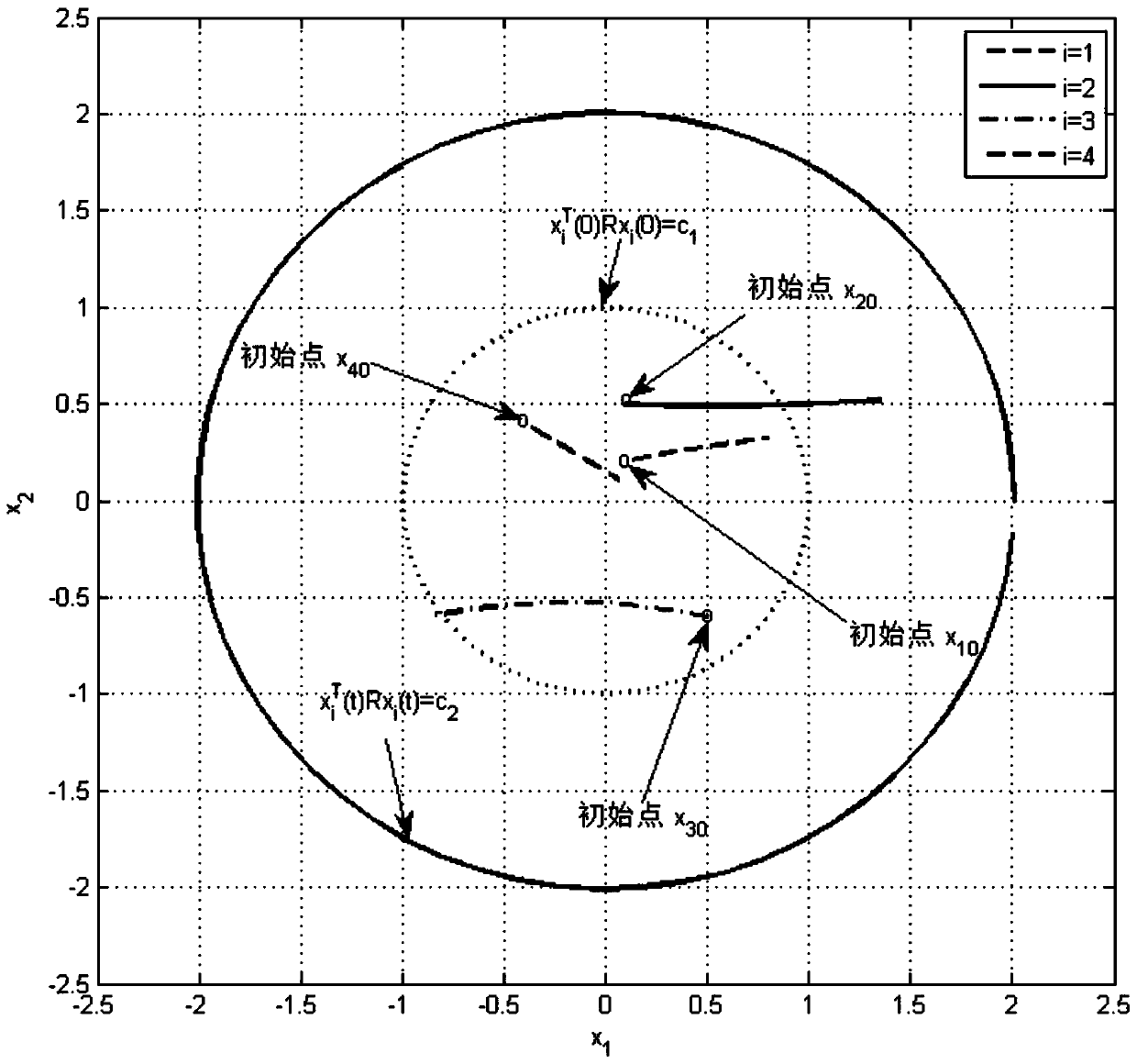
[0094] Finite-time control effects on discrete networked multi-agent systems with no communication delays:
[0095]Formula (5), formula (6), formula (7), formula (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com