Three-dimensional laser scanning method for surface deformation of similar materials in underground engineering simulation test
An underground engineering and three-dimensional laser technology, applied in the direction of using optical devices, instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems that observation errors cannot meet the test requirements, cannot capture small information changes, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., and achieve error levels. The effect of less human intervention and ensuring the accuracy of observation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
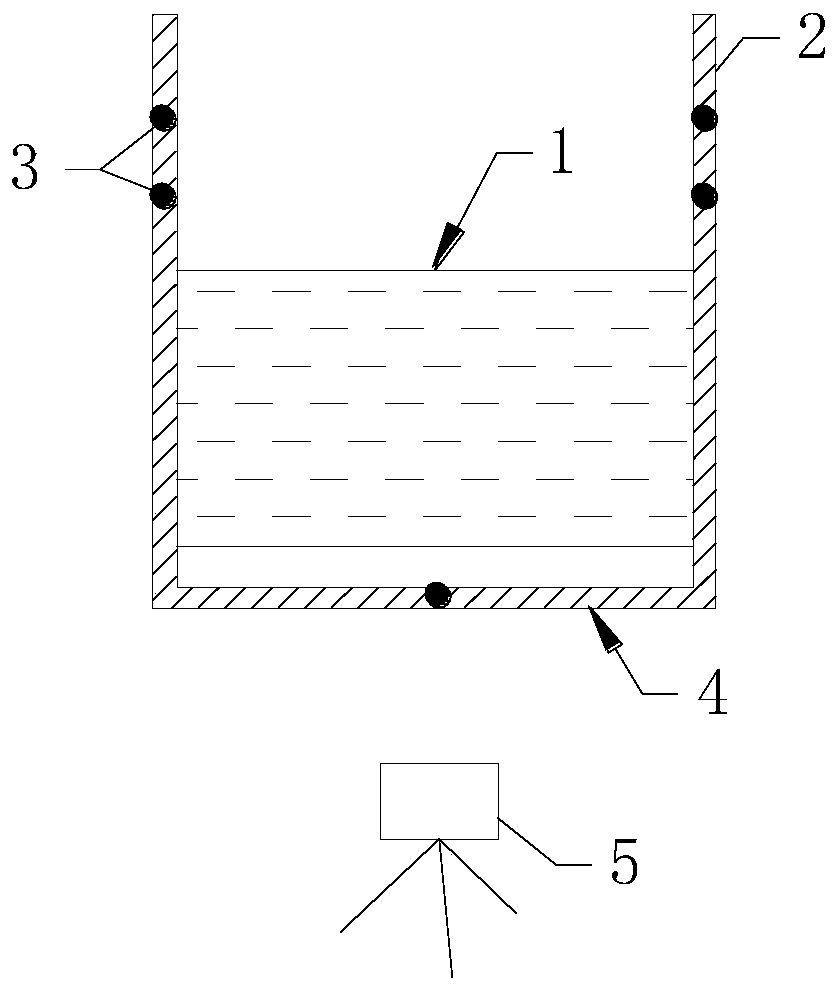
[0045] A three-dimensional laser scanning method for surface deformation of similar materials in underground engineering simulation tests, using the five-point mark control point method, these five points are used as point cloud matching references, after determining the scanning parameters, use three-dimensional laser scanning for underground engineering before and after excavation to obtain similar The surface point cloud deformation data of the material simulation test, after the data is processed and modeled, is visualized to generate a visualized cloud map. Specific steps are as follows:
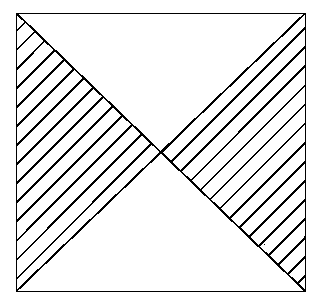
[0046] (1) Prepare as figure 2 The square target paper of 10cm*10cm shown; figure 1 As shown, there are channel steel uprights on both sides of the test bench, and the five-point mark control point method is to paste two target papers on the left and right channel steel uprights 2 on both sides of the test bench 1 as reference points 3, and on the same side of the uprights The distan...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com