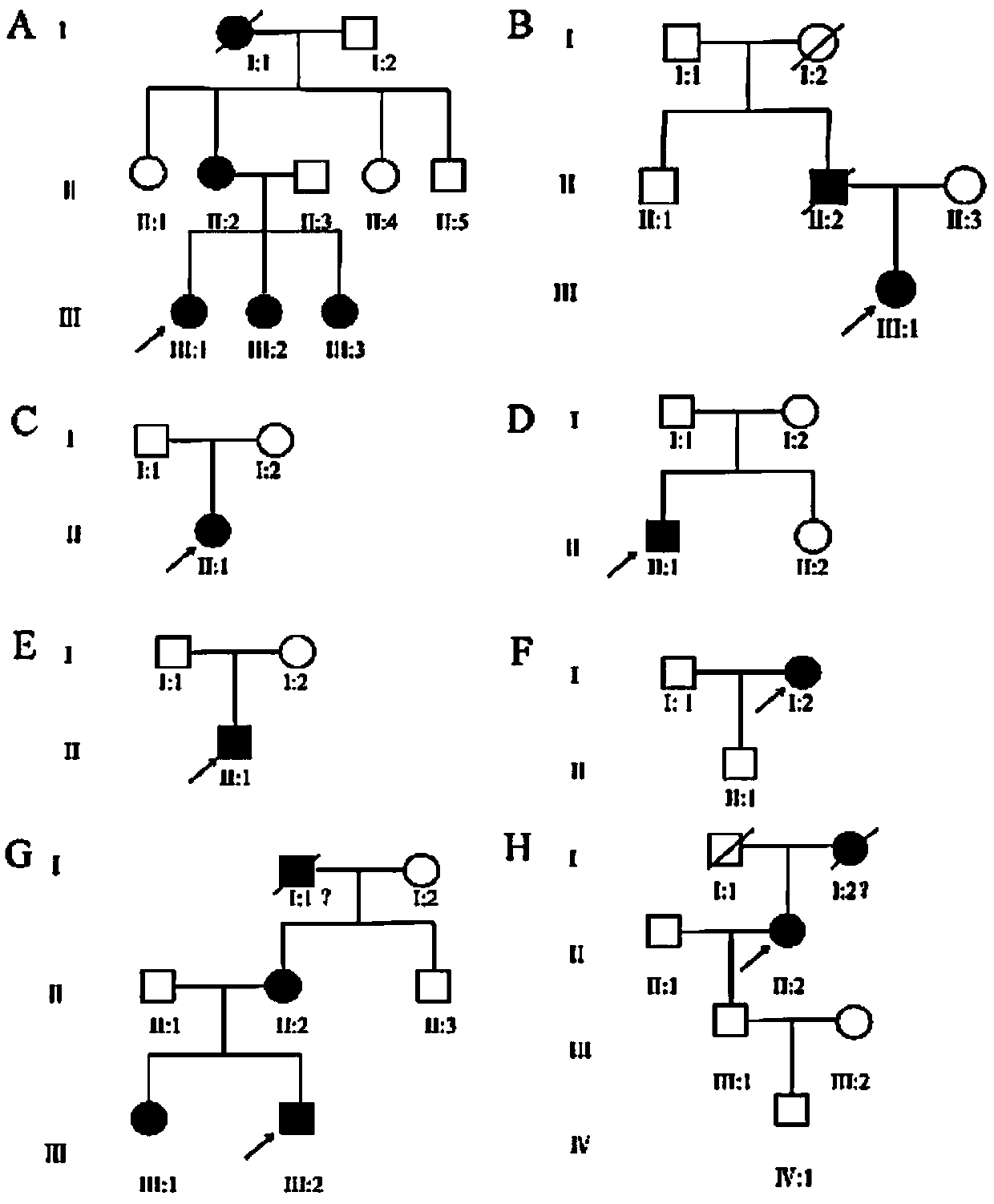
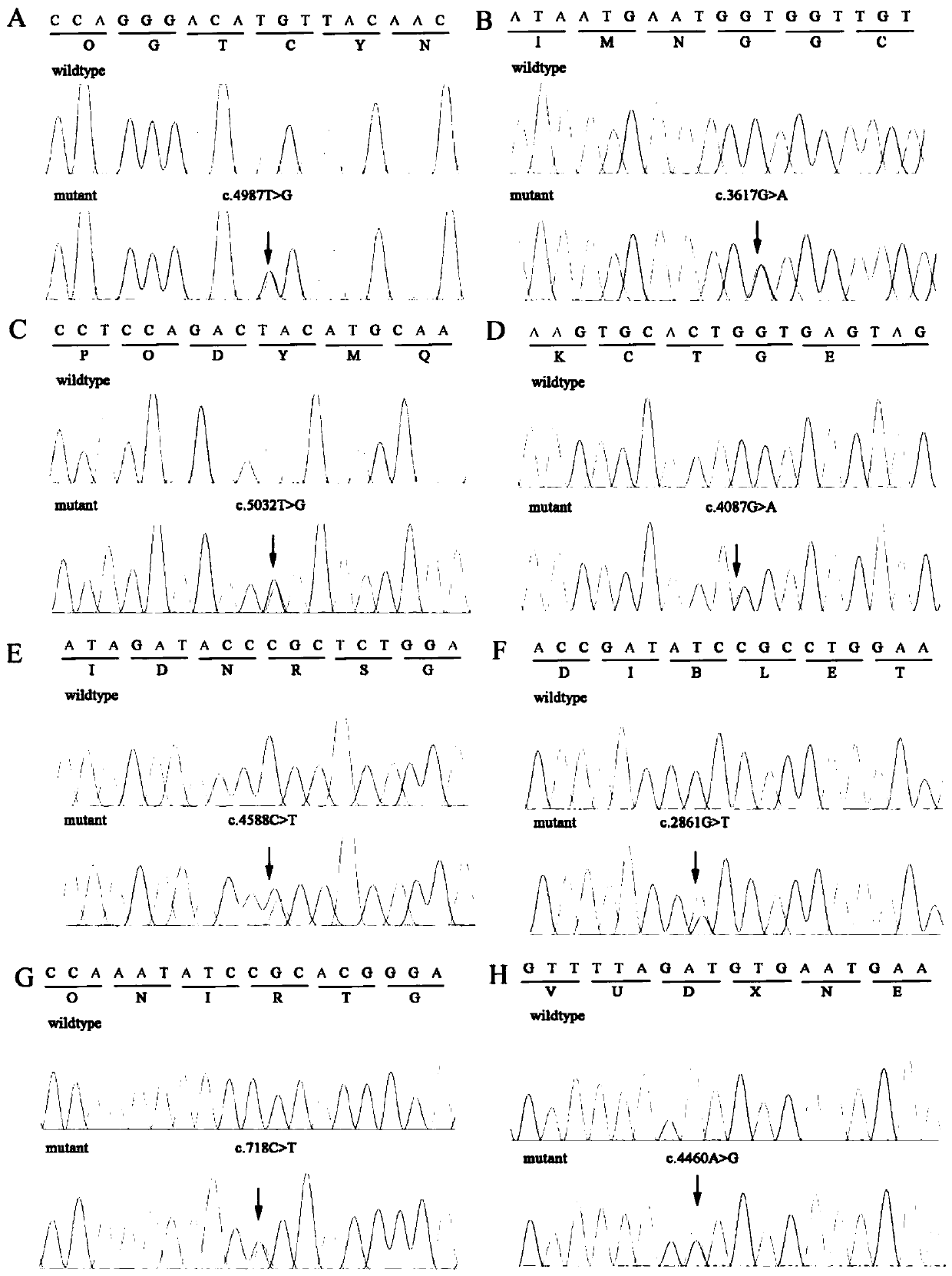
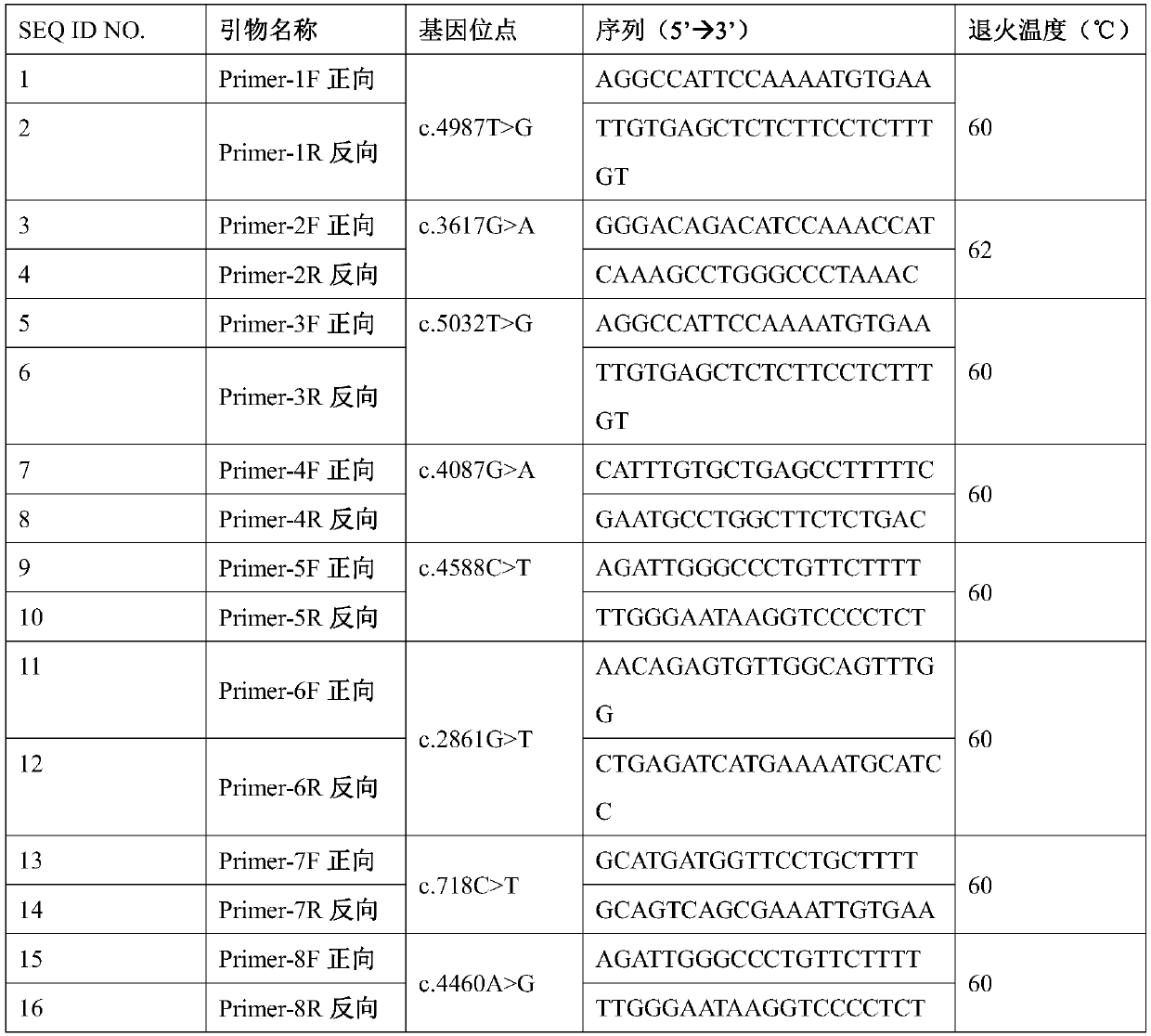
Multi-site screening kit for Marfan syndrome
A kit and reagent technology, applied in the field of SNP, can solve problems such as false negatives, and achieve reliable specificity and broad prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] Embodiment Kit of the present invention and method of use
[0032] All components, content and method of use in the kit of the present invention are as follows:
[0033] 1. PCR amplification reagent (50 people):
[0034] The PCR amplification reagent is used to amplify a DNA sequence where the SNP site is located, and its composition is shown in Table 1.
[0035] Table 1 PCR amplification reagents
[0036] components
concentration
volume
PCR mix
2×
1.2ml
Primer pair
10μM
100μl
pure water
2ml
[0037] The PCR mixture in Table 1 includes Taq enzymes, dNTPs, magnesium ions and other components required for conventional PCR; the primer pair information is shown in Table 2.
[0038] Table 2 Primers used for FBN1 gene amplification
[0039]
[0040] 2. FBN1 gene variation typing detection reagent (50 people):
[0041] The reagent includes the components shown in Table 3.
[0042] Table 3 FBN1 gene vari...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com