An immunofluorescent staining method and its kit for rapidly evaluating testicular spermatogenic function
A kit and reagent technology, applied in the field of reproductive medicine, can solve the problems of strong subjectivity and time-consuming, and achieve the effects of convenient operation, less time-consuming, and low detection cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] Embodiment 1 detection kit
[0038] Reagent A: erythrocyte lysate;
[0039] Reagent B: 4% paraformaldehyde fixative;
[0040] Reagent C: PBS containing 5% fetal bovine serum (BSA) and 0.5% Triton X-100
[0041] Reagent D1: FITC-labeled rabbit anti-human GFRA1 antibody; PE-labeled mouse anti-human c-KIT antibody;
[0042] Reagent D2: FITC-labeled rabbit anti-human SCP3 antibody; PE-labeled mouse anti-human PNA antibody;
[0043] Reagent D3: 488 donkey anti-rabbit fluorescent secondary antibody; 555 donkey anti-mouse fluorescent secondary antibody;
[0044] Reagent E: fluorescent mounting medium;
[0045] Reagent F: PBS solution.
Embodiment 2
[0046] Embodiment 2 detection steps
[0047] Reagent preparation stage: Dilute reagents D1, D2, and D3 with reagent C at a certain ratio (recommended 1:500, which can be adjusted according to the staining situation) to make working solutions.
[0048] Stages of seminiferous tubule slide preparation:
[0049] (1) Obtain human seminiferous tubules (the length of which is 3-5cm can be sufficient for detection), put them into the upper filter of the improved EP tube, and rinse in reagent F (PBS solution) for 3 minutes;
[0050] (2) Take out the filter screen and discard the waste liquid in the lower layer, add 1ml of reagent B, and incubate at room temperature for 10 minutes;
[0051] (3) (Optional step, used when the obtained testicular tissue contains blood clots and a lot of blood) Take out the filter screen and discard the waste liquid in the lower layer, add 1ml of reagent A, and place on a shaker at room temperature for 10 minutes;
[0052] (4) Take out the filter screen a...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Embodiment 3 detection method
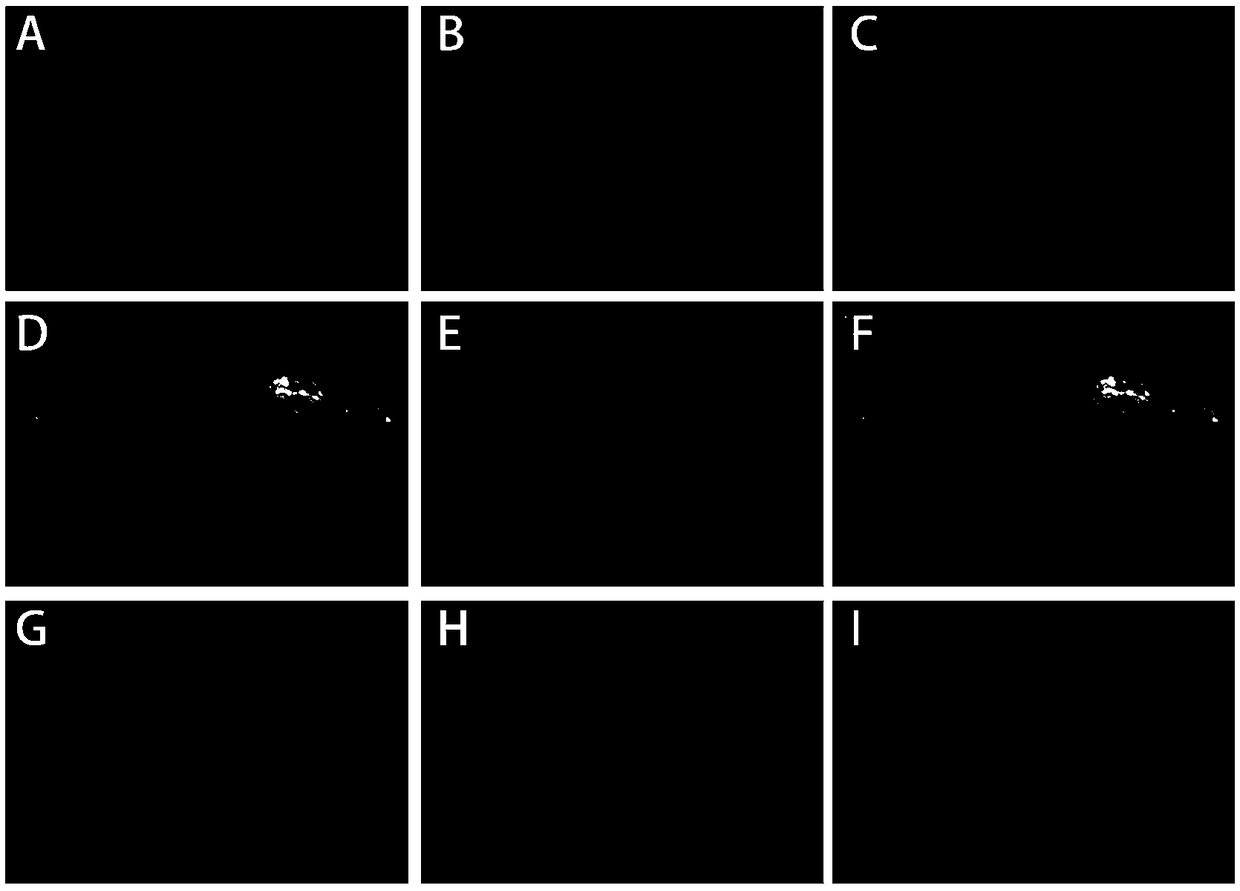
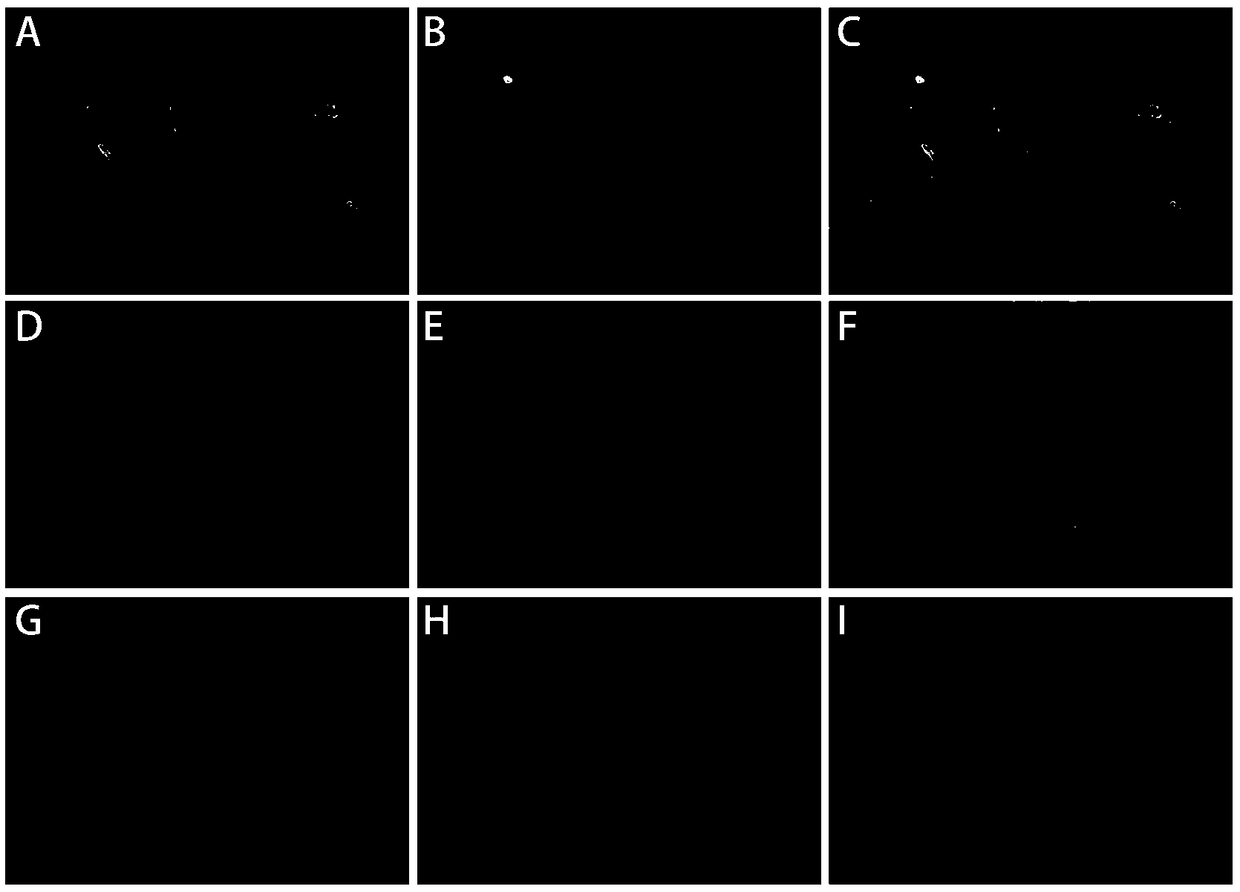
[0059] Use fluorescently labeled IgG antibodies to specifically bind to the currently recognized marker proteins of spermatogonial stem cells, differentiated spermatogonia, spermatocytes, and sperm (or sperm cells), and determine testicular spermatogenesis by observing the staining results The number and distribution of various spermatogenic cells in the tube can be used to determine the spermatogenic function of the patient's testis. In the seminiferous tubules incubated with reagent D1: the undifferentiated spermatogonia surface marker GFRA1 excited green fluorescence under the fluorescence microscope, and the differentiated spermatogonial cell surface marker c-KIT excited green fluorescence under the fluorescence microscope; the reagent D2 incubated In the seminiferous tubule: the pre-meiotic marker SCP3 of spermatocytes excites green fluorescence under the fluorescence microscope, and the sperm (sperm cell) acrosome marker PNA excites...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com