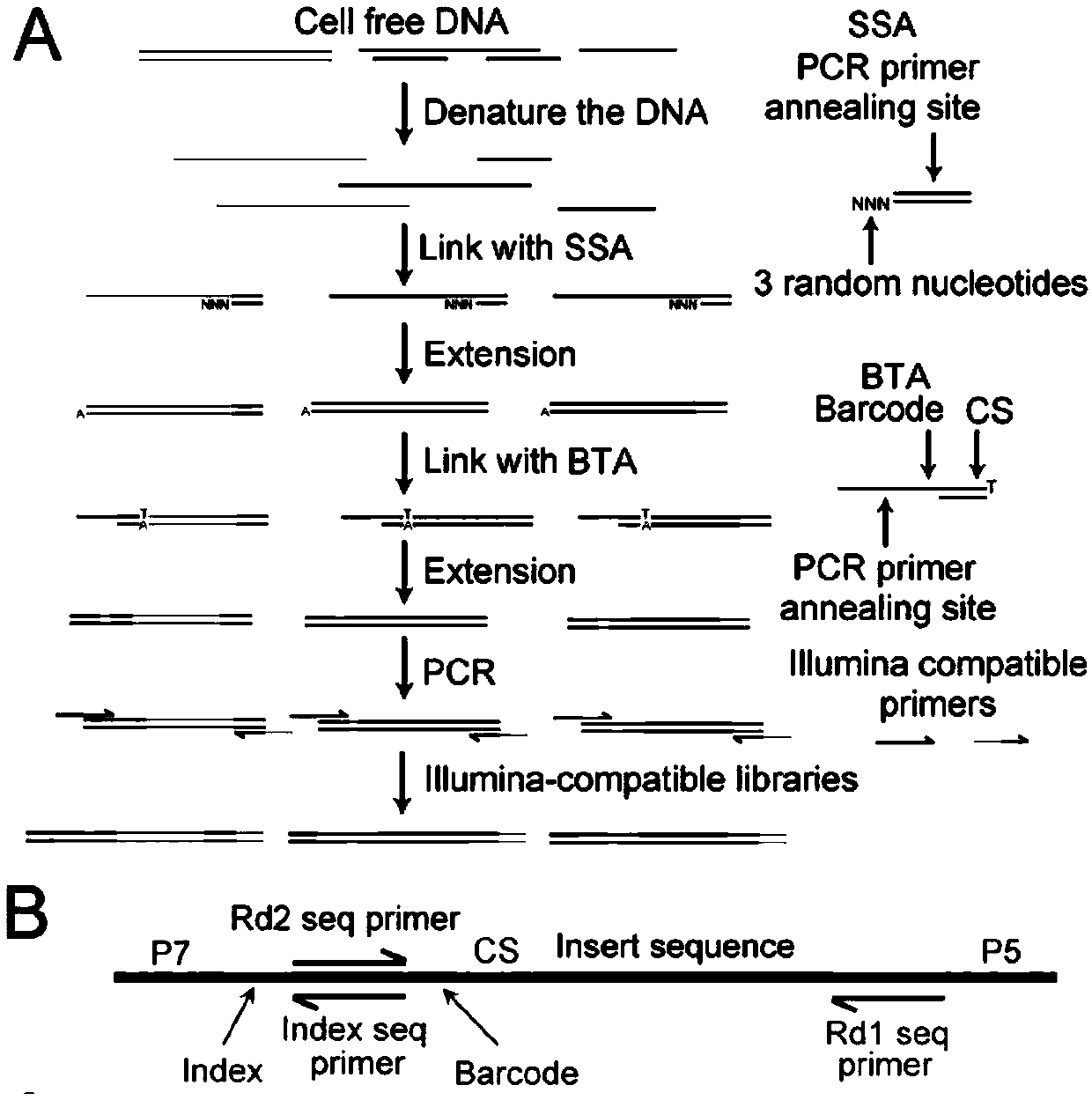
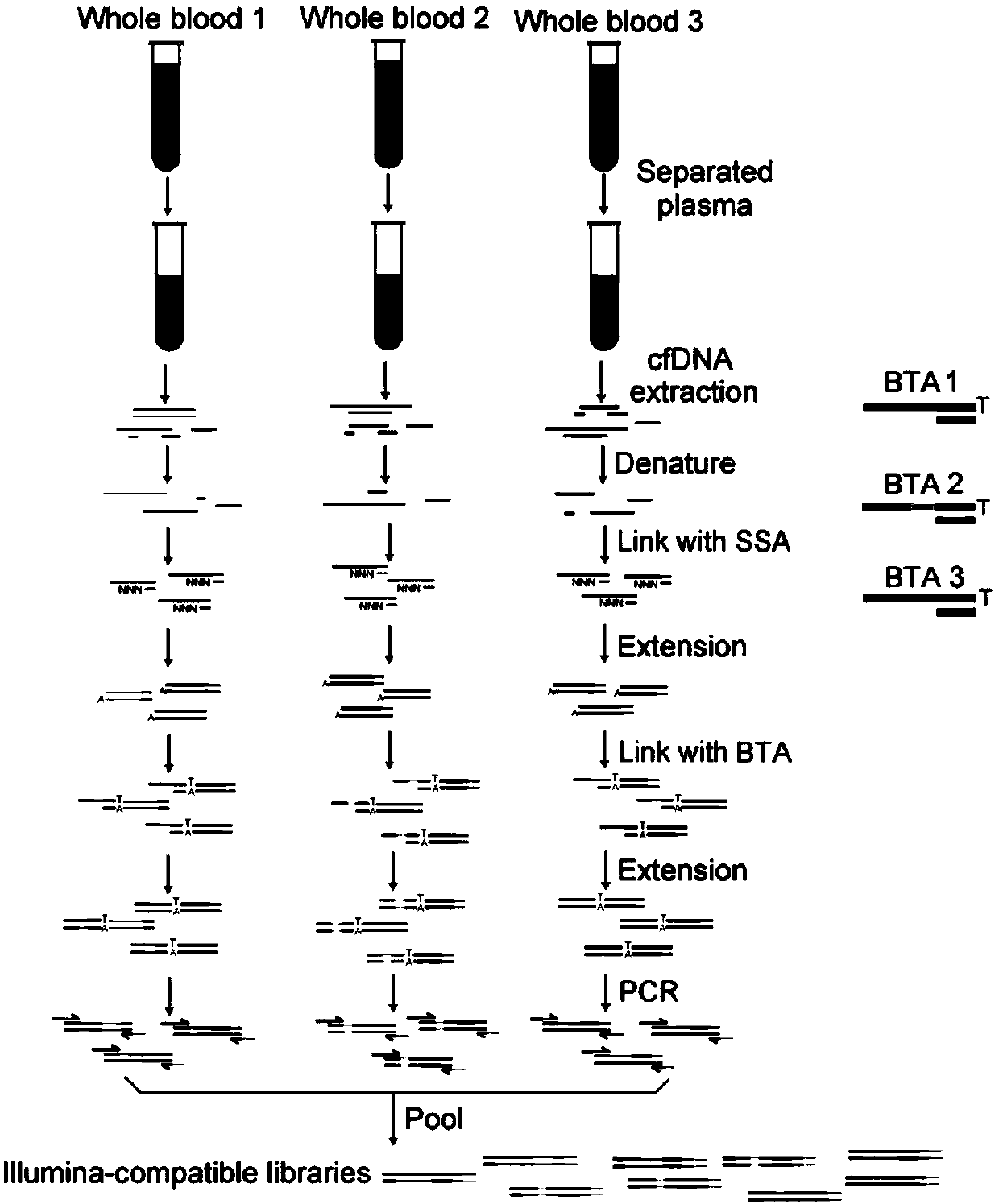
Method for carrying out high-flux sequencing on physiological status of individual to which cfDNA (Circulating cell-free DNA) belongs based on blood free DNA, and application thereof
A technology for individual physiology and sequencing analysis, applied in the field of biomedicine, can solve problems such as false positives, complex bioinformatics predictions, and ctDNA abundance failure, and achieve the effects of avoiding human errors, simplifying processing procedures, and avoiding the introduction of errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Example 1 Esophageal cancer detection based on cfDNA NGS
[0041] Experimental materials and methods
[0042] Sample collection: A total of 19 whole blood samples were collected with the help of Jinling Hospital Affiliated to Nanjing University School of Medicine (Nanjing, China). Among them, four were collected from normal subjects, eleven were collected from preoperative esophageal cancer patients, and five were collected from postoperative esophageal cancer patients (Table 1).
[0043] Table 1. cfDNA source information
[0044]
[0045]
[0046] Cell-free DNA extraction: Whole blood samples were centrifuged at 1,600g for 15 minutes at 4°C, and the supernatant was transferred to a new centrifuge tube. The tube containing the supernatant was centrifuged at 16,000g for 10 minutes at 4°C, and the supernatant was the plasma. All plasma was stored at -80°C for later use. Using the Plasma Circulating DNA kit (TIANGEN, DP339), 200 μL plasma was used as the starting...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap