Path planning method for robot leaded by global planner
A technology of global planning and path planning, applied in the field of robotics, can solve the problems of complex evaluation factors, many paths, and consumption of computing resources of the local path evaluator, and achieve the effect of overcoming transparent obstacles that cannot be avoided
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0022] Now in conjunction with embodiment, accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described:
[0023] The navigation algorithm includes the following steps: SLAM, 3D robot construction, robot positioning, building a local grid map, setting the end point, planning a global path, planning a local path, updating the global and local grid maps, and updating the state of the robot.
[0024] The SLAM step 1 is to use the lidar sensor to map the indoor environment. This step will generate a two-dimensional virtual map for the initial positioning of the robot, obstacle positioning and path planning.
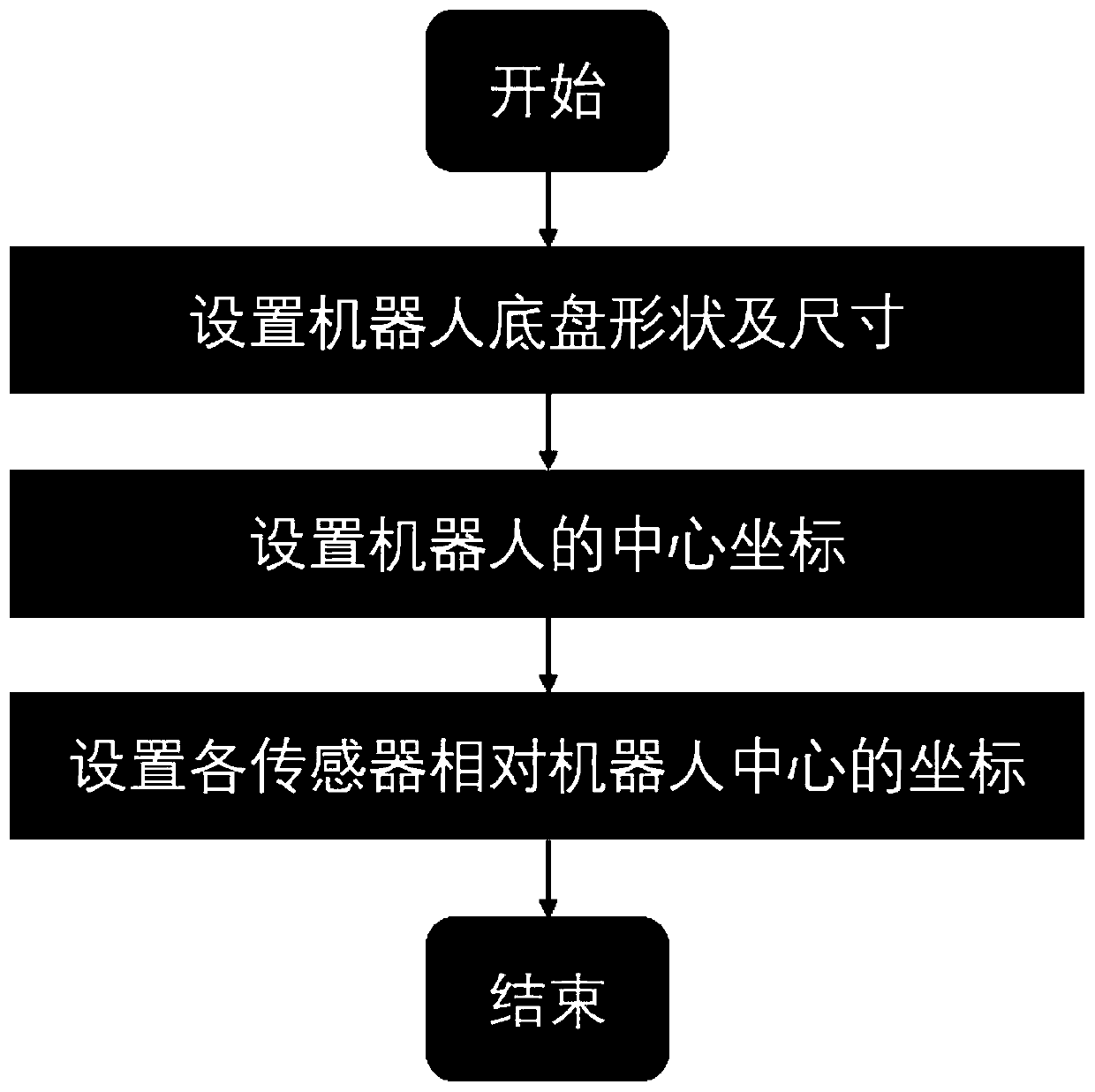
[0025] The step 2 of the three-dimensional robot construction includes the following steps: setting the shape of the robot, setting the size of the robot, and setting the coordinates of the center point of the robot. This step virtualizes the physical robot, and the virtualized robot is the execution unit of the navigation movement. The robot will be displayed on the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com