A path-based knowledge graph embedding method
A knowledge graph and path technology, applied in the field of knowledge graph, can solve the problems of indistinguishable embedding, irrespective of the direction and type of relationship, lack of information, etc., to improve performance, improve quality, and reduce training time.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
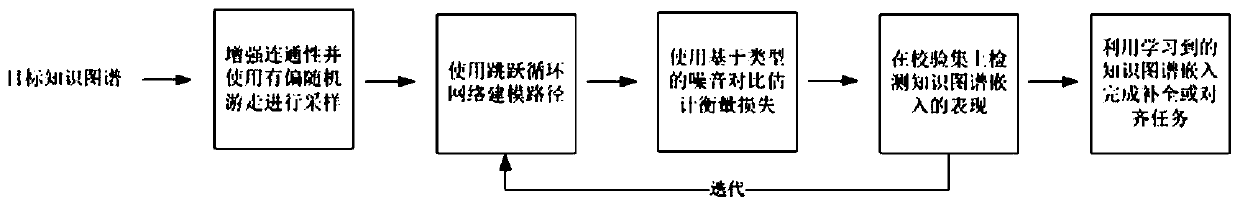
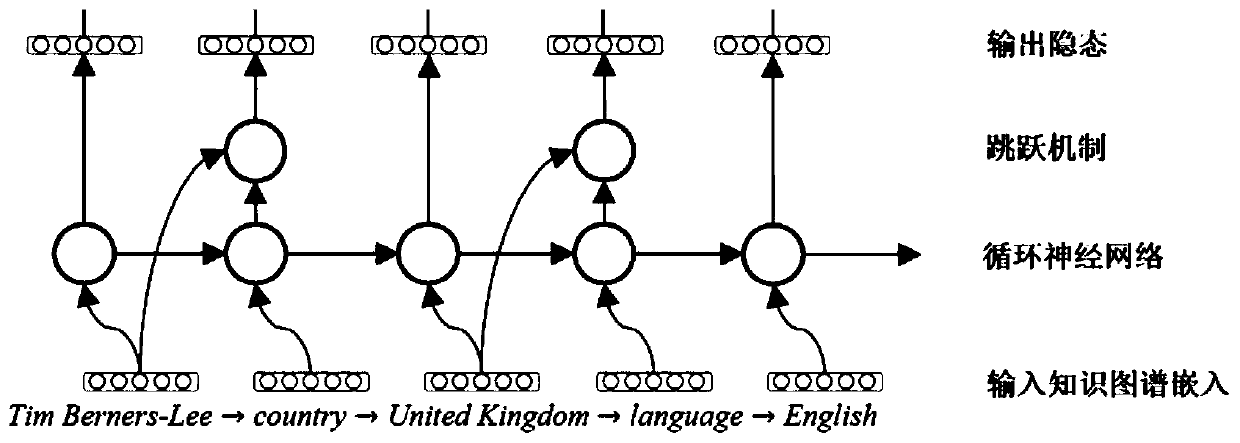
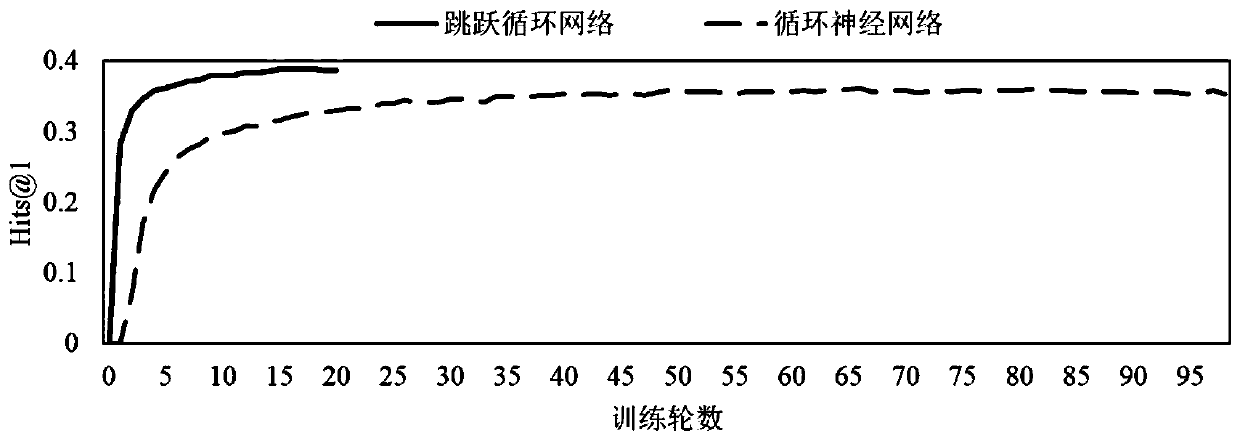
[0018] The overall process of the present invention is as figure 1 As shown, it includes 5 parts: use biased random walk to sample paths from the target knowledge map, use skip cycle network to model the dependencies between elements in the path, and use type-based noise comparison estimation method to measure the loss of the network, according to The results on the validation set are iteratively trained, and the trained knowledge graph embedding is used for entity alignment and knowledge graph completion tasks.
[0019] The specific implementation is described as follows:
[0020] 1. Use biased random walks to sample the target knowledge map path
[0021]For a given target knowledge graph (single or joint knowledge graph), its connectivity is first enhanced to improve sampling efficiency. The details are as follows: First, for each triplet (h,r,t), create a reverse triplet (t,r-,h), where r- is completely different from r. Secondly, for the entity alignment task, the tripl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com