A cross-linking treatment method for improving the stability of biological valve elastin
An elastin and cross-linking treatment technology, which is applied in the field of biomedical materials and medical devices, can solve problems such as no good methods, and achieve the effects of prolonging service life, increasing elastin content and anti-calcification performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
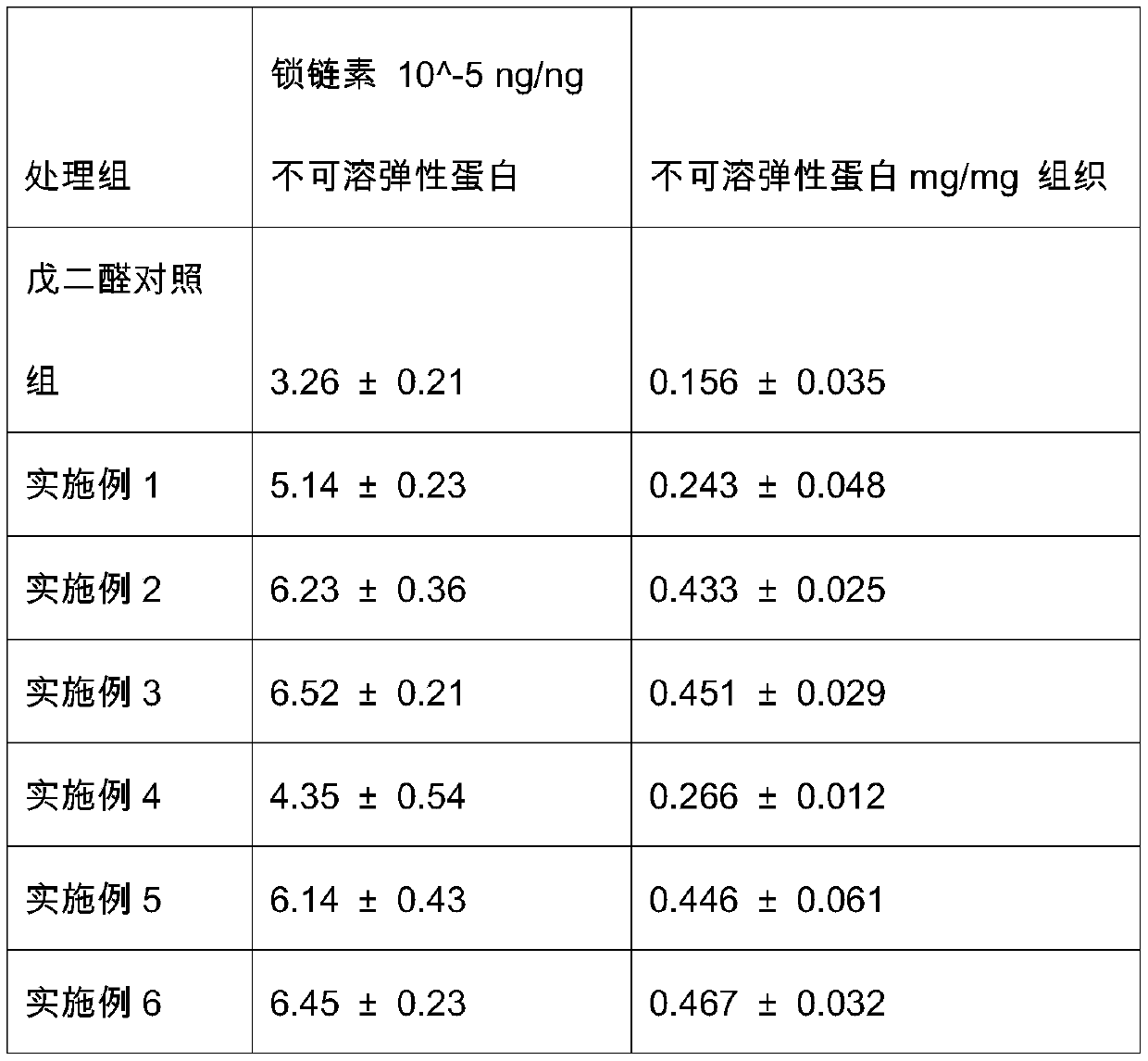
[0024] This example provides a cross-linking treatment method for improving the stability of biological valve elastin. In all embodiments, fresh pig pericardium comes from a local slaughterhouse.
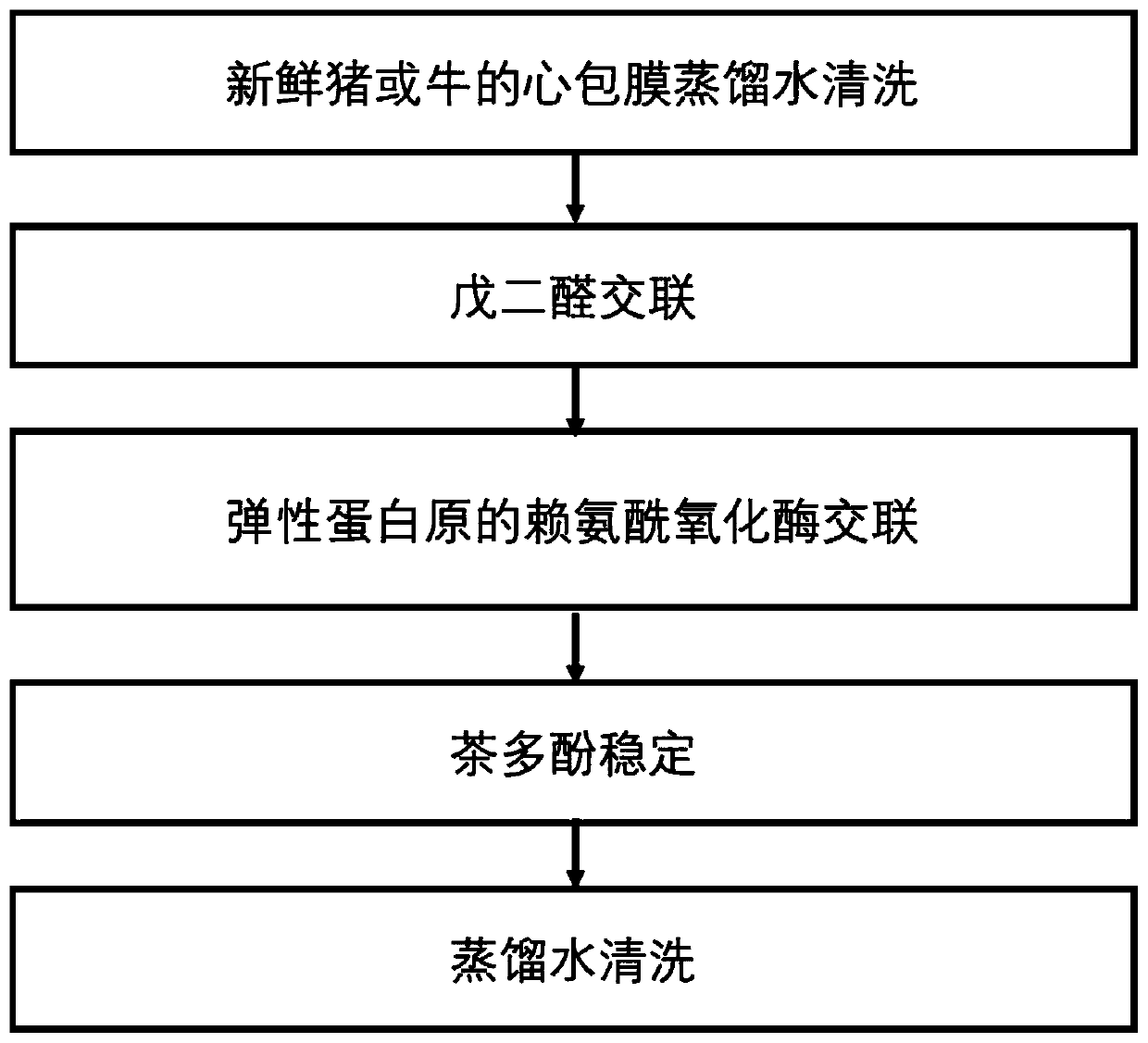
[0025] Such as figure 1 As shown, the freshly collected porcine pericardium was washed in distilled water for 2 hours at 4 degrees Celsius and 100 RPM under shaking conditions, and then soaked in 0.625% glutaraldehyde for 24 hours, and then the pericardium was soaked in tropoelastin and lysyl oxidation. In the enzyme aqueous solution for 24 hours, the mass feed ratio is 0.01mg proelastin: 1mg pericardium and 1ug lysyl oxidase: 1mg pericardium. Finally, the pericardium was soaked in 1% epigallocatechin gallate aqueous solution for 24 hours.
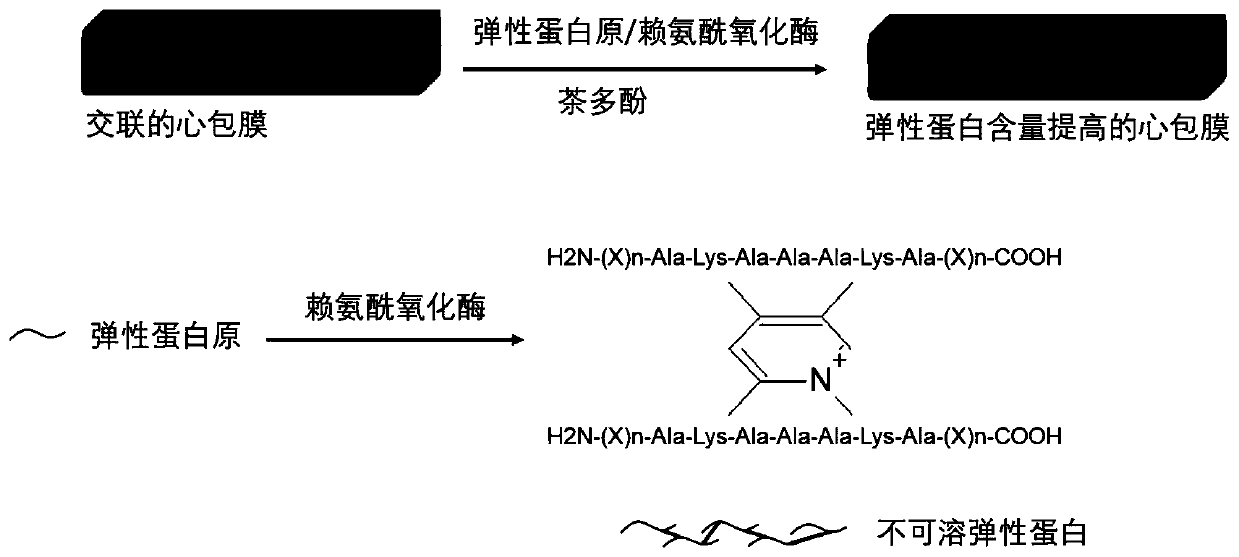
[0026] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the principle of using tropoelastin and lysyl oxidase cross-linking and tea polyphenol combined treatment to improve the content and stability of pericardium elastin.
[0027] Du...
Embodiment 2
[0029] This example provides a cross-linking treatment method for improving the stability of biological valve elastin. In all embodiments, fresh pig pericardium comes from a local slaughterhouse.
[0030] Such as figure 1 As shown, the freshly collected porcine pericardium was washed in distilled water for 2 hours at 4 degrees Celsius and 100 RPM under shaking conditions, and then soaked in 0.625% glutaraldehyde for 24 hours, and then the pericardium was soaked in tropoelastin and lysyl oxidation. In the enzyme aqueous solution for 24 hours, the mass feed ratio is 0.05mg proelastin: 1mg pericardium and 1ug lysyl oxidase: 1mg pericardium. Finally, the pericardium was soaked in 1% epigallocatechin gallate aqueous solution for 24 hours.
[0031] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the principle of using tropoelastin and lysyl oxidase cross-linking and tea polyphenol combined treatment to improve the content and stability of pericardium elastin.
Embodiment 3
[0033] This example provides a cross-linking treatment method for improving the stability of biological valve elastin. In all embodiments, fresh pig pericardium comes from a local slaughterhouse.
[0034] Such as figure 1 As shown, the freshly collected porcine pericardium was washed in distilled water for 2 hours at 4 degrees Celsius and 100 RPM under shaking conditions, and then soaked in 0.625% glutaraldehyde for 24 hours, and then the pericardium was soaked in tropoelastin and lysyl oxidation. In the enzyme aqueous solution for 24 hours, the mass feed ratio is 0.25mg proelastin: 1mg pericardium and 1ug lysyl oxidase: 1mg pericardium. Finally, the pericardium was soaked in 1% epigallocatechin gallate aqueous solution for 24 hours.
[0035] Such as figure 2 As shown, it is a schematic diagram of the principle of using tropoelastin and lysyl oxidase cross-linking and tea polyphenol combined treatment to improve the content and stability of pericardium elastin.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com