A Method of Correcting Atmospheric Refraction for Optical Imaging Satellites Using Stellar Observation Data
A technology for imaging satellites and correcting optics, which is applied in the field of remote sensing image processing and can solve the problems of not reflecting the short-term fluctuation of atmospheric refractive index, not discussing it, and not taking into account atmospheric refraction.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0039] The specific embodiments of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0040] The technical solution of the present invention is: a method for correcting the atmospheric refraction of optical imaging satellites using star observation data, specifically comprising the following steps:
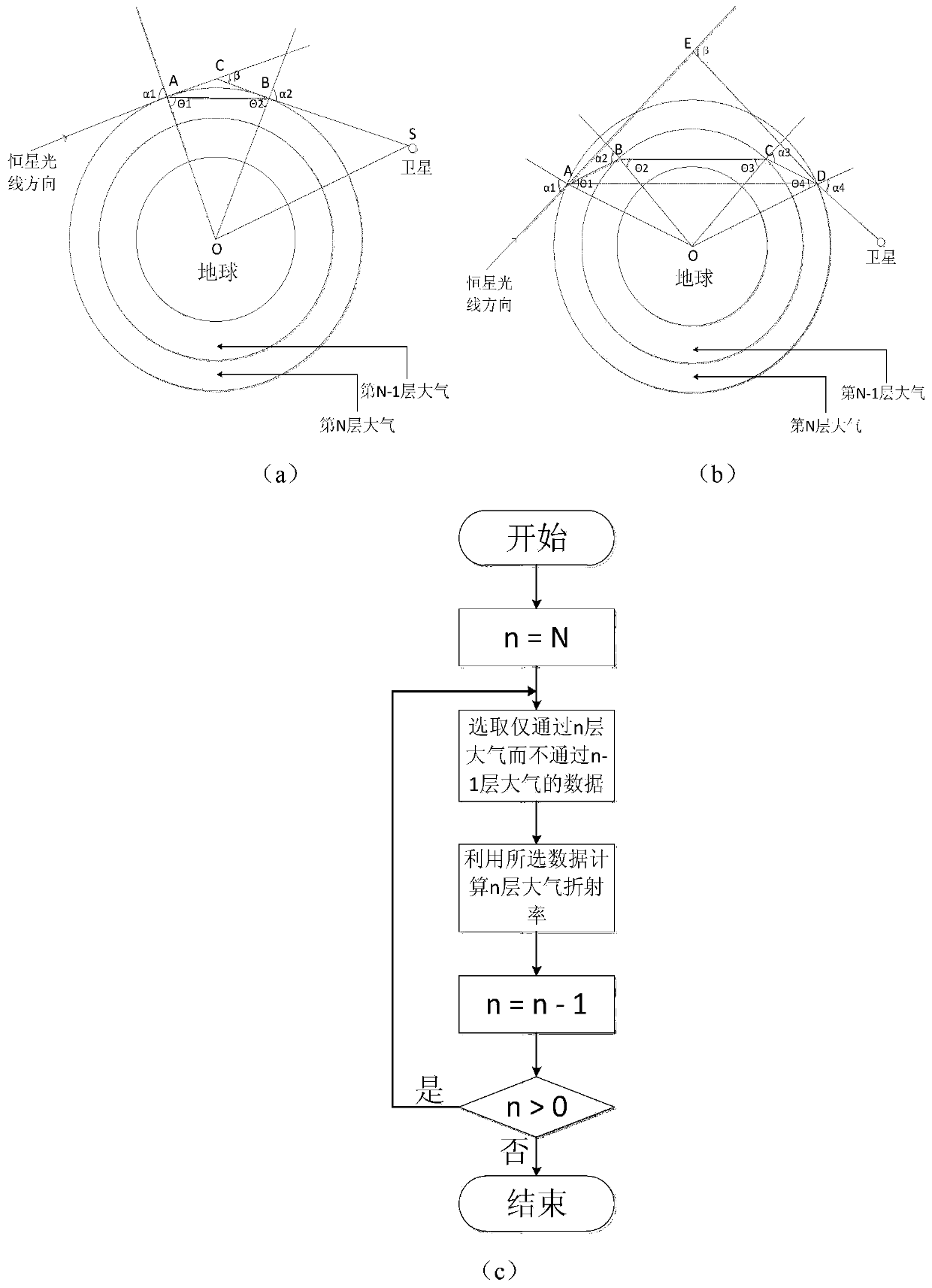
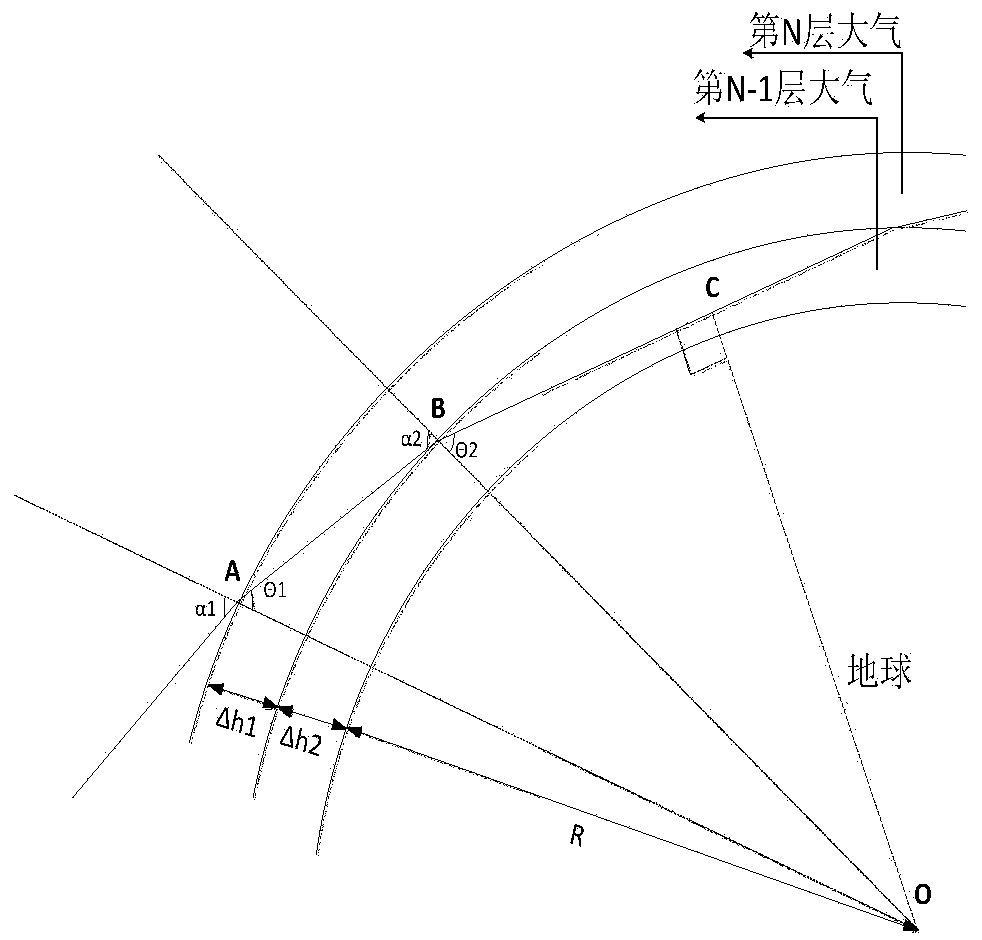
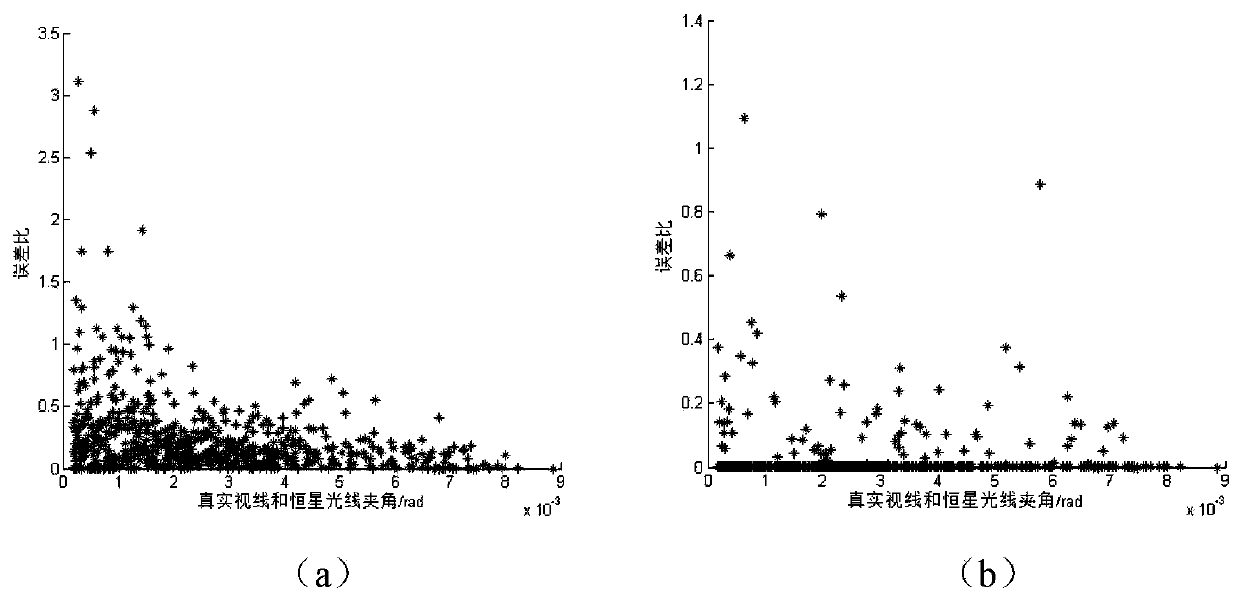
[0041]S1 establishes the atmospheric stratification model according to the observed light wave band. In this example, the atmospheric stratification modeling is carried out based on the infrared light with a wavelength of 4.5 μm used in satellite observations, and the atmospheric refractive index in this band varies greatly in the troposphere. The stratosphere changes slowly, and the atmosphere is stratified at 0-20km intervals at 0.2km intervals in the troposphere, and stratified at 0.5km intervals at 20-50km for the stratosphere region.
[0042] S2 Under the assumption of a spherical atmosphere and a spherical Earth model, a st...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com