Method for calculating relative permeability of two-phase fluid in spontaneous imbibition process of tight reservoir
A technology of relative permeability and spontaneous imbibition, which is applied to the calculation of relative permeability of two-phase fluids of spontaneous imbibition in tight reservoirs, and can solve the problems of inaccurate measurement, difficult dynamic characterization of two-phase fluids, and inapplicability
Inactive Publication Date: 2019-06-25
SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
View PDF7 Cites 6 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
In the process of spontaneous imbibition, the force of the two-phase seepage process is mainly capillary pressure and gravity, and there is no external displacement pressure, so it cannot be accurately measured. This makes the conventional relative permeability test and calculation metho
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
 Login to View More
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
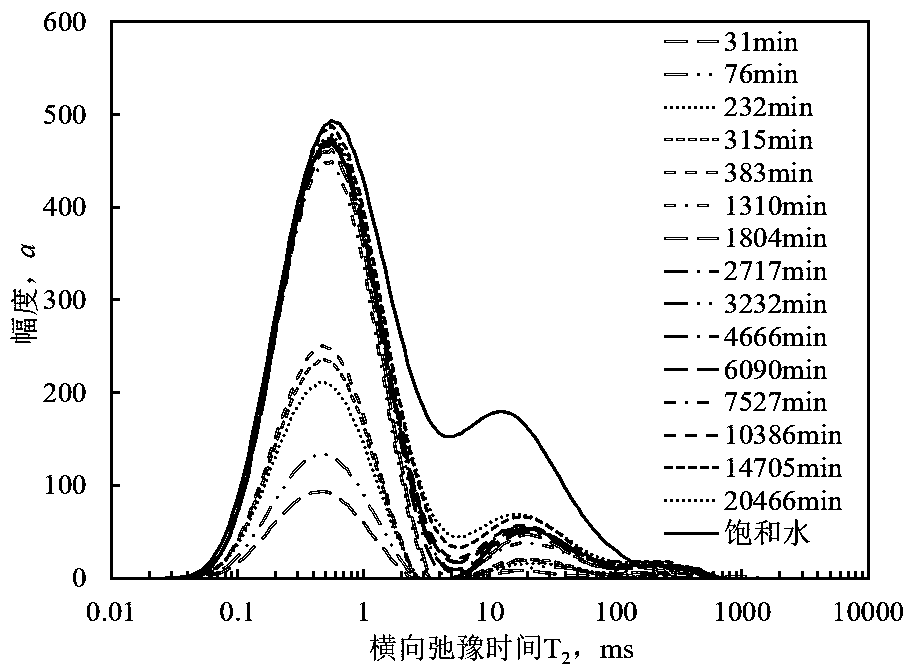
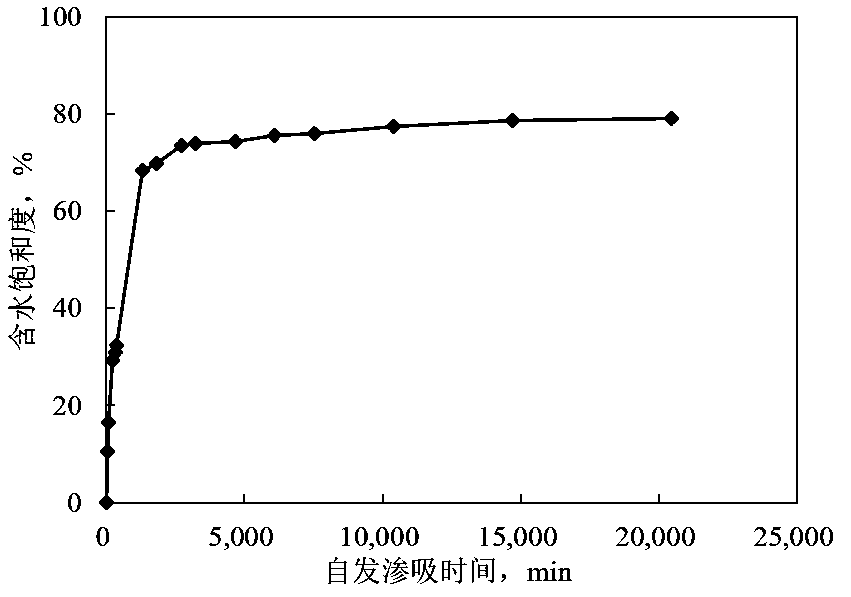
The invention relates to a method for calculating the relative permeability of a two-phase fluid in a spontaneous imbibition process of a tight reservoir. The method is an effective means for evaluating the seepage dynamics of a spontaneous imbibition two-phase fluid in a tight reservoir. The method successively comprises steps of: (1) preparing a core for a spontaneous imbibition NMR experiment;(2) obtaining a sample saturated simulated formation water condition NMR T2 spectrum; (3) performing a sample NMR spontaneous imbibition experiment to obtain different spontaneous imbibition time T2 spectrums; (4) calculating the water saturation of different spontaneous imbibition time samples and a T2 spectrum logarithmic mean value; and (5) calculating the relative permeability of two-phase fluid in spontaneous imbibition process. The method, in combination with the saturated water state and the spontaneous imbibition process NMR T2 spectrum, accurately calculates the relative permeabilityof the two-phase fluid in the spontaneous imbibition process of the tight reservoir, and lays a foundation for the dynamic evaluation of the tight reservoir development.
Description
technical field [0001] The invention relates to a method for calculating the relative permeability of spontaneous imbibition two-phase fluid of reservoir, especially for the calculation of relative permeability of spontaneous imbibition two-phase fluid of tight reservoir. Mainly combined with the spontaneous imbibition nuclear magnetic resonance experiment of tight reservoir cores, it can quantitatively calculate the relative permeability of gas-water (or oil-water) two-phase seepage in the process of spontaneous imbibition of tight oil to tight reservoirs. It is an accurate and effective tight reservoir A dynamic evaluation method for spontaneous imbibition in the development process. Background technique [0002] With the sharp increase in global energy demand and the depletion of conventional oil and gas resources, the exploration and development of unconventional resources represented by tight oil and gas has been paid more and more attention. Different from conventiona...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): G01N15/08G01N24/08
CPCY02A90/30
Inventor 陈猛戴家才刘向君况晏秦民君裴阳王中涛苟顺超
Owner SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com